Abstract
Introduction
Contemporary published data present confounding results on use of PRF in soft- and hard-tissue healing in the oral cavity, and many authors have suggested for further studies to reach the definitive conclusion.
Aim
Our main objective therefore was to evaluate soft-tissue healing and osseous regeneration (by using VIXWIN PRO software) in extraction sites of mandibular third molars with substantial sample size to understand the effect of PRF in bony defects.
Methodology
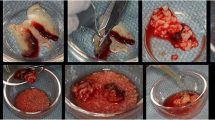
Sixty patients had their bilaterally impacted third molars (120 sites) extracted in the split mouth study, following which platelet-rich fibrin was placed in one of the sockets. Patients were followed up clinically and radiographically, and pain score, presence of infection, exudation of graft and VIXWIN PRO software were used to evaluate healing of soft tissue and bone.
Result and Conclusion
Our study advocates the use of PRF for enhanced soft- and hard-tissue healing. Though the osseous regeneration could be differentiated in both the groups at second month interval only, pain scores were better with PRF at most instances. Subsequent phase to the research should include histopathological investigations for ancillary support.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate, Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E37–E44
Eppley B, Pietrzak W, Blanton M (2006) Platelet-rich plasma: a review of biology and applications in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:147e–15
Gassling V, Douglas T, Warnke PH, Açil Y, Wiltfang J, Becker ST (2010) Platelet-rich fibrin membranes as scaffolds for periosteal tissue engineering. Clin Oral Implant Res 21:543–549
Sammartino G, Tia M, Marenzi G, Espedito Di Lauro A, D’Agostino E, Claudio PP (2005) Use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in periodontal defect treatment after extraction of impacted mandibular third molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63(6):766–770
Sunitha Raja V, Munirathnam NE (2008) Platelet-rich fibrin: evolution of a second-generation platelet concentrate. Indian J Dent Res 19:42–46
Kumar Y, Mohanty S, Verma M, Reet Kaur R, Bhatia P, Kumar V, Chaudhary Z (2015) Platelet-rich fibrin: the benefits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2015.10.015
Gürbüzer B, Pikdöken L, Tunalı M, Urhan M, Küçükodaci Z, Ercan F (2010) Scintigraphic evaluation of osteoblastic activity in extraction sockets treated with platelet-rich fibrin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:980–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.09.092
Jansen RC, Reinink K, Van der Heijden GWAM (1993) Analysis of grey level histograms by using statistical methods for mixture of distributions. Pattern Recogn Lett 14:585–590
Tanomaru FM, Laitano SC, Gonçalves M, Tanomaru JMG (2006) Evaluation of the radiopacity of root-end filling materials by digitization of radiographic images. Braz J of Oral Sciences 5(14):1021–1024
Carvalho FB, Goncalves M, Tanomaru JMG, Filho MT (2009) Evaluation of periapical changes following endodontic therapy: digital subtraction technique compared with computerized morphometric analysis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38:438–444
De Hingh IH, Nienhuijs SW, Overdevest EP, Scheele K, Everts PA (2009) Mesh fixation with autologous platelet-rich fibrin sealant in inguinal hernia repair. Eur Surg Res 43(3):306–309
Hoaglin DR, Lines GK (2013) Prevention of localized osteitis in mandibular third-molar sites using platelet-rich fibrin. Int J Dent 2013, Article ID 875380
Gassling V, Açil Y, Springer I, Hubert N, Wiltfang J (2010) Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in human cell cultures: response to letter of Dr. David Dohan Ehrenfest. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 110:421–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.05.060
David DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan A, Mouhyi J et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate. Part 1: Technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E45–E50
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:E56–E60
Diss A, Dohan M, Mouhyi J, Mahler P (2008) Osteotome sinus floor elevation using Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin as grafting material: a 1-year prospective pilot study with microthreaded implants. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 105:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.08.021
Aghaloo TL, Moy PK, Freymiller EG (2002) Investigation of platelet-rich plasma in rabbit cranial defects: a pilot study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Standards
Study was conducted in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki guidelines.
Informed Consent
Informed Consent was taken from the patient for the procedure which was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Sharma, P., Sharma, S.D. et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin as an Aid to Soft- and Hard-Tissue Healing. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 496–501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01317-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01317-7