Abstract
Purpose
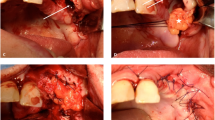
The aim of this retrospective study was to describe the efficacy of management of bisphosphonate-related maxillary osteonecrosis, which had resulted in an oroantral fistula formation, by performing sequestrectomy, platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and buccal fat pad (BFP) flap.
Patient and Methods
A total of 7 patients diagnosed with stage III maxillary medication-related osteonecrosis according to guidelines of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. All patients complained of persistent pain, swelling and purulent drainage with sinusitis. In order to keep the infection under control, the patients first received an antibiotic combination for 2 weeks. Then, sequestrectomy and bone debridement were performed under general anesthesia. After that, an antrectomy was performed via endoscopic sinus surgery in some cases. And the fistula was closed with BFP after or before the PRF application to the region depending on the size of the fistula.
Results
The fistula was successfully closed. After a mean follow-up of 16 months, no symptoms were seen in the patients.
Conclusions
The patients were successfully managed with a combined treatment consisted of sequestrectomy, PRF and BFP. We suggest that large defects arose from medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw can be managed with such a combined approach in order to lessen the recurrence risk.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Agbaloo T, Mebrotra B, O’Ryan F (2014) American Association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72(10):1938–1956
Bamias A, Kastritis E, Bamia C, Moulopoulos LA, Melakopoulos I, Bozas G, Koutsoukou V, Gika D, Anagnostopoulos A, Papadimitriou C, Terpos E, Dimopoulos M (2005) Osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer after treatment with bisphosphonates: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Oncol 23(34):8580–8587
Ruggiero SL, Mehrotra B, Rosenberg TJ, Engroff SL (2004) Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates: a review of 63 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62(5):527–534
Mast G, Otto S, Mucke T, Schreyer C, Bissinger O, Kolk A, Wolff KD, Ehrenfeld M, Stürzenbaum SR, Pautke C (2012) Incidence of maxillary sinusitis and oro-antral fistulae in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40(7):568–571
Maurer P, Sandulescu T, Kriwalsky MS, Rashad A, Hollstein S, Stricker I, Hölzle F, Kunkel M (2011) Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the maxilla and sinusitis maxillaris. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40(3):285–291
Dolanmaz D, Tuz H, Bayraktar S, Metin M, Erdem E, Baykul T (2004) Use of pedicled buccal fat pad in the closure of oroantral communication: analysis of 75 cases. Quintessence 35(3):241–246
Egyedi P (1977) Utilization of the buccal fat pad for closure of oro-antral and/or oro-nasal communications. J Maxillofac Surg 5(4):241–244
Poeschl PW, Baumann A, Russmueller G, Poeschl E, Klug C, Ewers R (2009) Closure of oroantral communications with Bichat’s buccal fat pad. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67(7):1460–1466
Gallego L, Junquera L, Pelaz A, Hernando J, Megias J (2012) The use of pedicled buccal fat pad combined with sequestrectomy in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the maxilla. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 17(2):e236–e241
Rotaru H, Kim MK, Kim SG, Park YW (2015) Pedicled buccal fat pad flap as a reliable surgical strategy for the treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 73(3):437–442
Roy S, Driggs J, Elgharably H, Biswas S, Findley M, Khanna S, Gnyawali U, Bergdall VK, Sen CK (2011) Platelet-rich fibrin matrix improves wound angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell proliferation. Wound Repair Regen 19:753–766
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJJ, Mouhyi J, Gogly B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate part II: platelet related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:e45–e50
He L, Lin Y, Hu X, Zhang Y, Wu H (2009) A comparative study of platelet rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:707–713
Gülşen U, Şentürk MF, Mehdiyev I (2016) Flap-free treatment of an oroantral communication with platelet-rich fibrin. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54:702–703
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Gogyl B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:37–44
Marx RE (2003) Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(9):1115–1117
Wang J, Goodger NM, Pogrel MA (2003) Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with cancer chemotherapy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(9):1104–1107
Migliorati CA (2003) Bisphosphanates and oral cavity avascular bone necrosis. J Clin Oncol 21(22):4253–4254
Allen MR, Burr DB (2009) The pathogenesis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: so many hypotheses, so few data. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67(5 suppl):61–70
Otto S, Hafner S, Mast G, Tischer T, Volkmer E, Schieker M, Stürzenbaum SR, Tresckow EV, Kolk A, Ehrenfeld M, Pautke C (2010) Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: is pH the missing part in the pathogenesis puzzle? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68(5):1158–1161
Sato M, Grasser W, Endo N, Akins R, Simmons H, Thompson DD, Golub E, Rodan GA (1991) Bisphosphonate action. Alendronate localization in rat bone and effects on osteoclast ultrastructure. J Clin Invest 88(6):2095–2105
Bell GW, Joshi BB, Macleod RI (2011) Maxillary sinus disease: diagnosis and treatment. Br Dent J 210(3):113–118
Costa F, Emanuelli E, Robiony M, Zerman N, Polini F, Politi M (2007) Endoscopic surgical treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis of dental origin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65(2):223–228
Gupta V, Bains BK, Singh GP, Mathur A, Bains R (2011) Regenerative potential of platelet rich fibrin in dentistry: literature review. Asian J Oral Health Allied Sci 1:22–28
Gassling V, Douglas T, Warnke PH, Açil Y, Wiltfang J, Becker ST (2010) Platelet-rich fibrin membranes as scaffolds for periosteal tissue engineering. Clin Oral Implants Res 21:543–549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esen, A., Akkulah, S. Management of Large Oroantral Fistulas Caused by Medication-Related Osteonecrosis with the Combined Sequestrectomy, Buccal Fat Pad Flap and Platelet-Rich Fibrin. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 76–82 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01278-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01278-x