Abstract
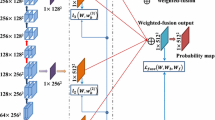
Retinal vessels are important biomarkers for many ophthalmological and cardiovascular diseases. Hence, it is of great significance to develop automatic models for computer-aided diagnosis. Existing methods, such as U-Net follows the encoder-decoder pipeline, where detailed information is lost in the encoder in order to achieve a large field of view. Although spatial detailed information could be recovered partly in the decoder, while there is noise in the high-resolution feature maps of the encoder. And, we argue this encoder-decoder architecture is inefficient for vessel segmentation. In this paper, we present the detail-preserving network (DPN), which avoids the encoder-decoder pipeline. To preserve detailed information and learn structural information simultaneously, we designed the detail-preserving block (DP-Block). Further, we stacked eight DP-Blocks together to form the DPN. More importantly, there are no down-sampling operations among these blocks. Therefore, the DPN could maintain a high/full resolution during processing, avoiding the loss of detailed information. To illustrate the effectiveness of DPN, we conducted experiments over three public datasets. Experimental results show, compared to state-of-the-art methods, DPN shows competitive/better performance in terms of segmentation accuracy, segmentation speed, and model size. Specifically, (1) Our method achieves comparable segmentation performance on the DRIVE, CHASE_DB1, and HRF datasets. (2) The segmentation speed of DPN is over 20-160\(\times\) faster than other methods on the DRIVE dataset. (3) The number of parameters of DPN is around 120k, far less than all comparison methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzopardi G, Petkov N (2013) Automatic detection of vascular bifurcations in segmented retinal images using trainable cosfire filters. Pattern Recognit Lett 34(8):922–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2012.11.002
Azzopardi G, Strisciuglio N, Vento M, Petkov N (2015) Trainable cosfire filters for vessel delineation with application to retinal images. Med Image Anal 19(1):46–57
Budai A, Bock R, Maier A, Hornegger J, Michelson G (2013) Robust vessel segmentation in fundus images. Int J Biomed Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/154860
Cao L, Li H, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Xu L (2020) Hierarchical method for cataract grading based on retinal images using improved haar wavelet. Inf Fusion 53:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.06.022
Christodoulidis A, Hurtut T, Tahar HB, Cheriet F (2016) A multi-scale tensor voting approach for small retinal vessel segmentation in high resolution fundus images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 52:28–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2016.06.001
Fraz MM, Remagnino P, Hoppe A, Uyyanonvara B, Rudnicka AR, Owen CG, Barman SA (2012) Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images—a survey. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 108(1):407–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2012.03.009
Fu H, Xu Y, Lin S, Wong DWK, Liu J (2016) Deepvessel: retinal vessel segmentation via deep learning and conditional random field. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 132–139, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_16
Garg S, Sivaswamy J, Chandra S (2007) Unsupervised curvature-based retinal vessel segmentation. In: IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro, IEEE, pp 344–347, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2007.356859
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and statistic (AISTATS), PMLR, Proceedings of machine learning research, vol 9, pp 249–256
Guo S, Wang K, Kang H, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Li T (2019) Bts-dsn: deeply supervised neural network with short connections for retinal vessel segmentation. Int J Med Inform 126:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.03.015
Irshad S, Akram MU (2014) Classification of retinal vessels into arteries and veins for detection of hypertensive retinopathy. In: Cairo international biomedical engineering conference (CIBEC), IEEE, pp 133–136
Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick R, Guadarrama S, Darrell T (2014) Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 675–678. https://doi.org/10.1145/2647868.2654889
Jin Q, Meng Z, Pham TD, Chen Q, Wei L, Su R (2019) Dunet: a deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. Knowl Based Syst 178:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.04.025
Kingma DP, Ba JL (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International conference on learning representations, pp 1–13
Lee CY, Xie S, Gallagher P, Zhang Z, Tu Z (2015) Deeply-supervised nets. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, proceedings of machine learning research, vol 38, pp 562–570. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v38/lee15a.html
Li Q, You J, Zhang L, Bhattacharya P (2006) A multiscale approach to retinal vessel segmentation using gabor filters and scale multiplication. IEEE Int Conf Syst Man Cybern 4:3521–3527. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSMC.2006.384665
Liskowski P, Krawiec K (2016) Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(11):2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2546227
Maninis KK, Pont-Tuset J, Arbeláez P, Van Gool L (2016) Deep retinal image understanding. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 140–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_17
Mookiah MRK, Hogg S, MacGillivray TJ, Prathiba V, Pradeepa R, Mohan V, Anjana RM, Doney AS, Palmer CN, Trucco E (2020) A review of machine learning methods for retinal blood vessel segmentation and artery/vein classification. Med Image Anal 68:101905
Oliveira A, Pereira S, Silva CA (2018) Retinal vessel segmentation based on fully convolutional neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 112:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.06.034
Orlando JI, Prokofyeva E, Blaschko MB (2016) A discriminatively trained fully connected conditional random field model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(1):16–27
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, New York, pp 234–241,. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Saleh MD, Eswaran C, Mueen A (2011) An automated blood vessel segmentation algorithm using histogram equalization and automatic threshold selection. J Digit Imaging 24(4):564–572
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunović H (2018) Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 67:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.07.004
Scott IU, Alexandrakis G, Cordahi GJ, Murray TG (1999) Diffuse and circumscribed choroidal hemangiomas in a patient with sturge-weber syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 117(3):406–407
Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T (2017) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):640–651. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683
Srinidhi CL, Aparna P, Rajan J (2017) Recent advancements in retinal vessel segmentation. J Med Syst 41(4):70
Srinidhi CL, Aparna P, Rajan J (2018) A visual attention guided unsupervised feature learning for robust vessel delineation in retinal images. Biomed Signal Process Control 44:110–126
Staal J, Abràmoff MD, Niemeijer M, Viergever MA, Van Ginneken B (2004) Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23(4):501–509. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2004.825627
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Villalobos-Castaldi FM, Felipe-Riverón EM, Sánchez-Fernández LP (2010) A fast, efficient and automated method to extract vessels from fundus images. J Vis 13(3):263–270
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Wang Y, Ji G, Lin P, Trucco E (2013) Retinal vessel segmentation using multiwavelet kernels and multiscale hierarchical decomposition. Pattern Recognit 46(8):2117–2133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2012.12.014
Wang B, Qiu S, He H (2019a) Dual encoding u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Berlin, pp 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_10
Wang W, Wang W, Hu Z (2019b) Retinal vessel segmentation approach based on corrected morphological transformation and fractal dimension. IET Image Process 13(13):2538–2547
Wang X, Jiang X, Ren J (2019c) Blood vessel segmentation from fundus image by a cascade classification framework. Pattern Recognit 88:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.11.030
Wang J, Sun K, Cheng T, Jiang B, Deng C, Zhao Y, Liu D, Mu Y, Tan M, Wang X et al (2020) Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2983686
Wong TY, Coresh J, Klein R, Muntner P, Couper DJ, Sharrett AR, Klein BE, Heiss G, Hubbard LD, Duncan BB (2004) Retinal microvascular abnormalities and renal dysfunction: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(9):2469–2476. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000136133.28194.E4
Wong TY, Sun J, Kawasaki R, Ruamviboonsuk P, Gupta N, Lansingh VC, Maia M, Mathenge W, Moreker S, Muqit MM et al (2018) Guidelines on diabetic eye care: the international council of ophthalmology recommendations for screening, follow-up, referral, and treatment based on resource settings. Ophthalmol 125(10):1608–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.04.007
Wu Y, Xia Y, Song Y, Zhang Y, Cai W (2018) Multiscale network followed network model for retinal vessel segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 119–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_14
Wu Y, Xia Y, Song Y, Zhang D, Liu D, Zhang C, Cai W (2019) Vessel-net: retinal vessel segmentation under multi-path supervision. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Berlin, pp 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_30
Xie S, Tu Z (2017) Holistically-nested edge detection. Int J Comput Vis 125(1–3):3–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-017-1004-z
Xu R, Ye X, Jiang G, Liu T, Li L, Tanaka S (2020) Retinal vessel segmentation via a semantics and multi-scale aggregation network. IEEE international conference on acoustics. Speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 1085–1089
Yan Z, Yang X, Cheng KT (2018a) Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(9):1912–1923
Yan Z, Yang X, Cheng KT (2018b) A three-stage deep learning model for accurate retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(4):1427–1436. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2872813
Yin Y, Adel M, Bourennane S (2012) Retinal vessel segmentation using a probabilistic tracking method. Pattern Recognit 45(4):1235–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2011.09.019
Yu H, Barriga S, Agurto C, Zamora G, Bauman W, Soliz P (2012) Fast vessel segmentation in retinal images using multi-scale enhancement and second-order local entropy. Medical imaging 2012: computer-aided diagnosis. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, pp 386–397
Zhao Y, Zheng Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Luo L, Yang S, Na T, Wang Y, Liu J (2017) Automatic 2-d/3-d vessel enhancement in multiple modality images using a weighted symmetry filter. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(2):438–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work is supported by PhD research startup foundation of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (No.1960320048).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of data and material
All data generated and used during this study will available at https://github.com/guomugong/DPN.
Code availability
The source code will be available at https://github.com/guomugong/DPN.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is supported by PhD research startup foundation of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (No.1960320048).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S. DPN: detail-preserving network with high resolution representation for efficient segmentation of retinal vessels. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 5689–5702 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03422-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03422-3