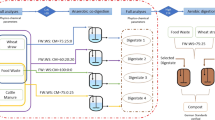
Abstract
The use of poultry manure (PM) in anaerobic digestion applications at high PM proportions is very limited due to its high nitrogen content since high levels of ammonia in the feedstock can lead to unstable and sub-optimal anaerobic digestion operation. This study investigated three methods to improve methane potential from PM at high PM proportions: (1) co-digestion of PM with a mixed substrate (MS) of a cheese factory and coffee-ground wastes at PM:MS ratios of 100:0, 75:25, 50:50, 25:75, and 0:100; (2) two-stage anaerobic digestion of PM and MS at PM:MS ratios of 100:0, 75:25, and 50:50, and (3) a novel post-hydrolysis ammonia stripping at pH 10 and 55 °C. The results indicated that co-digestion increased the methane potential in the samples due to reduced ammonia levels. A two-stage anaerobic digestion system further improved the methane potential by 21 and 41% in the cases of PM:MS at 100:0 and 75:25, while no improvement was observed in the case of PM:MS at 50:50. Post-hydrolysis ammonia stripping under the tested conditions achieved 79.2, 69, and 78.6% ammonia removal in PM:MS of 100:0, 75:25, and 50:50 and improved methane potential by 200, 150, and 64% when compared with the untreated samples.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tauseef, S.M., Premalatha, M., Abbasi, T., Abbasi, S.A.: Methane capture from livestock manure. J. Environ. Manage. 117, 187–207 (2013)
Michalk, D.L., Kemp, D.R., Badgery, W.B., Wu, J., Zhang, Y., Thomassin, P.J.: Sustainability and future food security—a global perspective for livestock production. L. Degrad. Dev. 30, 561–573 (2019)
Ara, E., Sartaj, M., Kennedy, K.: Effect of microwave pre-treatment of thickened waste activated sludge on biogas production from co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste, thickened waste activated sludge and municipal sludge. Waste Manag. Res. 32, 1200–1209 (2014)
Adghim, M., Abdallah, M., Saad, S., Shanableh, A., Sartaj, M.: Assessment of the biochemical methane potential of mono- and co-digested dairy farm wastes. Waste Manag. Res. 38, 88–99 (2019)
Nielsen, A.M., Christensen, K.V., Møller, H.B.: Inline NH3 removal from biogas digesters. Biomass Bioenerg. 50, 10–18 (2013)
Yan, L., Ye, J., Zhang, P., Xu, D., Wu, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, H., Fang, W., Wang, B., Zeng, G.: Hydrogen sulfide formation control and microbial competition in batch anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse wastewater sludge: effect of initial sludge pH. Bioresour. Technol. 259, 67–74 (2018)
Akindele, A.A., Sartaj, M.: The toxicity effects of ammonia on anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 71, 757–766 (2018)
Serna-Maza, A., Heaven, S., Banks, C.J.: Ammonia removal in food waste anaerobic digestion using a side-stream stripping process. Bioresour. Technol. 152, 307–315 (2014)
Wang, X., Yang, G., Feng, Y., Ren, G., Han, X.: Optimizing feeding composition and carbon-nitrogen ratios for improved methane yield during anaerobic co-digestion of dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 120, 78–83 (2012)
Bousek, J., Scroccaro, D., Sima, J., Weissenbacher, N., Fuchs, W.: Influence of the gas composition on the efficiency of ammonia stripping of biogas digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 203, 259–266 (2016)
Nair, A., Sartaj, M., Kennedy, K., Coelho, N.M.G.: Enhancing biogas production from anaerobic biodegradation of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste through leachate blending and recirculation. Waste Manag. Res. 32, 939–946 (2014)
Capson-Tojo, G., Moscoviz, R., Astals, S., Robles, A., Steyer, J.-P.: Unraveling the literature chaos around free ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 117, 109487 (2020)
Nie, H., Jacobi, H.F., Strach, K., Xu, C., Zhou, H., Liebetrau, J.: Mono-fermentation of chicken manure: ammonia inhibition and recirculation of the digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 238–246 (2015)
Borowski, S., Kucner, M., Czyżowska, A., Berłowska, J.: Co-digestion of poultry manure and residues from enzymatic saccharification and dewatering of sugar beet pulp. Renew. Energy. 99, 492–500 (2016)
Ara, E., Sartaj, M., Kennedy, K.: Enhanced biogas production by anaerobic co-digestion from a trinary mix substrate over a binary mix substrate. Waste Manag. Res. 33, 578–587 (2015)
Magbanua, B.S., Adams, T.T., Johnston, P.: Anaerobic codigestion of hog and poultry waste. Bioresour. Technol. 76, 165–168 (2001)
Wang, X., Lu, X., Li, F., Yang, G.: Effects of temperature and carbon-nitrogen (C/N) ratio on the performance of anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure, chicken manure and rice straw: focusing on ammonia inhibition. PLoS ONE 9, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097265
Babaee, A., Shayegan, J., Roshani, A.: Anaerobic slurry co-digestion of poultry manure and straw: effect of organic loading and temperature. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 11, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336x-11-15
Valenti, F., Zhong, Y., Sun, M., Porto, S.M.C., Toscano, A., Dale, B.E., Sibilla, F., Liao, W.: Anaerobic co-digestion of multiple agricultural residues to enhance biogas production in southern Italy. Waste Manag. 78, 151–157 (2018)
Rodriguez-Verde, I., Regueiro, L., Lema, J.M., Carballa, M.: Blending based optimisation and pretreatment strategies to enhance anaerobic digestion of poultry manure. Waste Manag. 71, 521–531 (2018)
Lu, J., Gavala, H.N., Skiadas, I.V., Mladenovska, Z., Ahring, B.K.: Improving anaerobic sewage sludge digestion by implementation of a hyper-thermophilic prehydrolysis step. J. Environ. Manage. 88, 881–889 (2008)
Yin, D.M., Qiao, W., Negri, C., Adani, F., Fan, R., Dong, R.J.: Enhancing hyper-thermophilic hydrolysis pre-treatment of chicken manure for biogas production by in-situ gas phase ammonia stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 287, 121470 (2019)
Malave, A.C.L., Bernardi, M., Fino, D., Ruggeri, B.: Multistep anaerobic digestion (MAD) as a tool to increase energy production via H2 + CH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 40, 5050–5061 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.02.068
Tsigkou, K., Tsafrakidou, P., Kopsahelis, A., Zagklis, D., Zafiri, C., Kornaros, M.: Used disposable nappies and expired food products valorisation through one- & two-stage anaerobic co-digestion. Renew. Energy. 147, 610–619 (2020)
Baldi, F., Pecorini, I., Iannelli, R.: Comparison of single-stage and two-stage anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and activated sludge for hydrogen and methane production. Renew. Energy. 143, 1755–1765 (2019)
Baldi, M., Collivignarelli, M.C., Abbà, A., Benigna, I.: The valorization of ammonia in manure digestate by means of alternative stripping reactors. Sustain. 10, 1–14 (2018)
Abouelenien, F., Fujiwara, W., Namba, Y., Kosseva, M., Nishio, N., Nakashimada, Y.: Improved methane fermentation of chicken manure via ammonia removal by biogas recycle. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 6368–6373 (2010)
Bonmatı, A., Flotats, X.: Air stripping of ammonia from pig slurry: characterisation and feasibility as a pre- or post-treatment to mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 23, 261–272 (2003)
Zhang, W., Heaven, S., Banks, C.J.: Continuous operation of thermophilic food waste digestion with side-stream ammonia stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 244, 611–620 (2017)
Pedizzi, C., Lema, J.M., Carballa, M.: A combination of ammonia stripping and low temperature thermal pre-treatment improves anaerobic post-digestion of the supernatant from organic fraction of municipal solid waste treatment. Waste Manag. 78, 271–278 (2018)
APHA: 2540 Solids. In: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington, DC (2005)
Evans, M.J., Rosenthal, J.S.: Probability and Statistics the Science of Uncertainty. University of Toronto, Toronto (2013)
Kafle, G.K., Chen, L.: Comparison on batch anaerobic digestion of five different livestock manures and prediction of biochemical methane potential (BMP) using different statistical models. Waste Manag. 48, 492–502 (2016)
Khoufi, S., Louhichi, A., Sayadi, S.: Optimization of anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater and liquid poultry manure in batch condition and semi-continuous jet-loop reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 182, 67–74 (2015)
Fotidis, I.A., Wang, H., Fiedel, N.R., Luo, G., Karakashev, D.B., Angelidaki, I.: Bioaugmentation as a solution to increase methane production from an ammonia-rich substrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 7669–7676 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/es5017075
De la Rubia, M.Á., Walker, M., Heaven, S., Banks, C.J., Borja, R.: Preliminary trials of in situ ammonia stripping from source segregated domestic food waste digestate using biogas: effect of temperature and flow rate. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 9486–9492 (2010)
Abouelenien, F., Namba, Y., Nishio, N., Nakashimada, Y.: Dry co-digestion of poultry manure with agriculture wastes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 178, 932–946 (2016)
Fuchs, W., Wang, X., Gabauer, W., Ortner, M., Li, Z.: Tackling ammonia inhibition for efficient biogas production from chicken manure: Status and technical trends in Europe and China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 97, 186–199 (2018)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) for providing funding for the project (NSERC Engage Grant 536400-18). The authors would like to thank Mr. George Wright from Castor River Farm for facilitating the collection of the poultry manure samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adghim, M., Sartaj, M. & Abdehagh, N. Enhancing Mono- and Co-digestion of Poultry Manure by a Novel Post-hydrolysis Ammonia Stripping Approach in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion Process. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 6045–6056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01439-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01439-5