Abstract
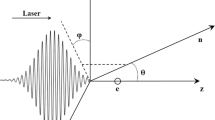
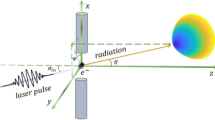
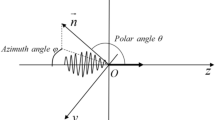
Based on the knowledge of electrodynamics and the nonlinear Thomson scattering framework, a single-electron motion and radiation model is established and numerical simulation is carried out to study the effect of the initial phase on the electron motion and radiation characteristics under a tightly focused linearly polarized laser pulse. It is demonstrated that when the initial phase of the tightly focused laser pulse varies within 0–π and 2π–π, respectively, the electron motion spectrum and radiation power distribution break the symmetric distribution mode. On this basis, the motion state and radiation distribution of single electron change with the initial phase are described in detail. Further analysis shows that the extreme point where the peak value and peak power angle of the upper and lower parts of the stimulated electron radiated power distribution vary with the initial phase both appears at \(\Delta \phi = {15}0^\circ\) when the initial phase changes from 0 to π, and appears around \(\Delta \phi = {3}0^\circ\) when it changes from 2π to π. The change curves of both show a special antisymmetry phase phenomenon under tight focus. This discovery offers a theoretical and numerical foundation for the investigation of high-energy electron radiation from multiple perspectives and aids in the precise measurement of ultra-intense laser characteristics in practical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
I Pastor, F R Álvarez-Estrada and L Roso J. Phys. Commun. 4 065010 (2020)
Z Jun et al Acta Phys. Sin. 54 1018 (2005)
B Chen, Z Zhang and P Jixiong JOSA A 26 862 (2009)
B Shen, W Yu, G Zeng and Z Xu Opt. Commun. 136 239 (1997)
F P Lan Plasmas 13 0131061 (2006)
Y I Salamin FHM Faisal Phys. Rev. A. 5 44383 (1996)
H Hora Z. Phys. 226 156 (1969)
S Corde, K T Phuoc, G Lambert, R Fitour, V Malka, A Rousse, A Beck and E Lefebvre Rev. Mod. Phys. 85 1–48 (2013)
Z Sheng and J Zhang Phys. Plasmas 12 123103 (2005)
M Tanimoto, S Kato, E Miura et al Phys. Rev. E 68 026401 (2003)
T Popmintchev, C M Chen, D Popmintchev, P Arpin, S Brown, S Ališauskas and C H Kapteyn Science 336 1287 (2012)
M Boca and V Florescu Phys. Rev. A 80 053403 (2009)
D Seipt and B Kämpfer Phys. Rev. A 83 022101 (2011)
F He, W Yu, P Lu, H Xu, L Qian, B Shen and X Yuan Phys. Rev. E 68 046407 (2003)
W Huai Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2185 (2003)
Z Chen, J Pu and D Zhao Phys. Lett. A 375 2958 (2011)
K P Singh, D N Gupta and H K Malik Phys. Scr. 77 045401 (2008)
K P Singh, D N Gupta and V Sajal Laser Part. Beams 27 635 (2009)
S Kumar, D N Gupta, H K Malik and D Singh Plasmas 27 043105 (2020)
D N Gupta, H Suk and M S Hur Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 211101 (2007)
K Li, L Li, Q Shu, Y Tian, Y Shi and Z Zhang Optik 183 813 (2019)
P Yu, H Lin, Z Gu, K Li and Y Tian Laser Phys. 30 045301 (2020)
Y I Salamin and C H Keitel Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 095005 (2002)
Y I Salamin and G R Mocken Rev. ST Accel. Beams 5 101301 (2002)
Y I Salamin J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 39 1353 (2006)
Y I Salamin, G R Mocken and C H Keitel Phys. Rev. E 67 016501 (2003)
Y I Salamin J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 38 4095 (2005)
Y Liu and Q Gong J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 43 205601 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China under Grant No. 10947170/A05 and No. 11104291, Natural science fund for colleges and universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant No. 10KJB140006, Natural Sciences Foundation of Shanghai under Grant No. 11ZR1441300 and Foundation of NJUPT under Grant No. NY212080 and sponsored by Jiangsu Qing Lan Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, J., Yu, P. & Tian, Y. Influence of initial phase on electron motion and spatial emission characteristics from electron driven by tightly focused linearly polarized laser pulse. Indian J Phys 97, 4039–4047 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02742-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02742-8