Abstract
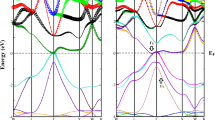
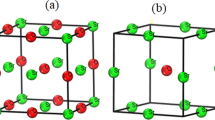
In order to explore the neotype functional properties contained in transition metal elements-doped L12-type TiAl3 materials, we used the first-principles calculation method based on density functional theory (DFT) to study systematically the electronic, optical, and thermodynamic properties of c-TiAl3 with M doping (M = V, Nb, Ta). The calculation results of formation enthalpies \(\Delta H_{f}\) and the density of states showed that these seven phases are thermodynamically stable, and the order of thermodynamic stability is Ti8Al23M > c-TiAl3 > Ti7Al24M. The research of electronic properties showed that these seven phases are all metallic, and the order of conductivity is Ti8Al23M > Ti7Al24M > c-TiAl3. The research results of optical properties showed that these seven phases are also metallic. After M atoms are doped with c-TiAl3, the dielectric properties and conductivity of the doping system are improved, and the order of the dielectric properties and conductivity is consistent with the result of electronic properties. Therefore, their application potential in optoelectronic materials is extremely high. Finally, we use the quasi-harmonic Debye model to study the thermodynamic properties of these seven phases in the pressure range of 0–40 GPa and the temperature range of 0–1200 K, including heat capacity (CV, CP), thermal expansion coefficient (α), and Debye temperature (θD).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Grytsiv, P Rogl, H Schmidt, G Giester, P Hundegger, G Wiesinger and V Pomjakushin Intermetallics. 12 563 (2004)
J Tan and K Zhu J. Computational Physics. 34 365 (2017)
J C Pang, X P Cui, A B Li, G H Fan, L Geng, Z Z Zheng and Q W Wang Materials Sci. & Engineering A Structural Materials Properties Microstructure & Processing. 579 57 (2013)
M T Whittaker, W Harrison, P J Hurley and S Williams Materials Sci. & Engineering A. 527 4365 (2010)
M Castillo-Rodríguez, M L Nó, J A Jiménez, O A Ruano and J S Juan Acta Mater. 527 4365 (2016)
Y Chen, F Kong, J Han, Z Chen and T Jing Intermetallics. 13 263 (2005)
J Li and M Zhang J. Alloy. Compo. 556 214 (2013)
C Colinet and A Pasturel Intermetallics. 10 751 (2002)
G X Jin, L J Qiao, K W Gao, T Kimura and W Y Chu Acta Metallrugica Sinica. 40 179 (2004)
H Y Wang, Q K Hu, W P Yang and X S Li Acta Physica Sinica. 7 256 (2016)
S Q Tang, S J Qu, A H Feng and S Li Rarer. Metals. 41 81 (2017)
J C Viala, N Peillon and L Clochefert Sci. Engine. A 203 222 (1995)
M Kogachi and A Kameyama Intermetallics. 3 327 (1995)
Y G Li and M H Loretto Act. Metall. Et Materialia. 42 2009 (1994)
Y F Li, H Xu and Q L Xia Sci. and Engine. Powd. Metallurgy. 15 102 (2010)
G L Zhu, S Da, Y B Dai, J Wang and B D Sun Acta Physica Sinica. 58 210 (2009)
H Hai, X Wu, W Rui and Z Jia J. Alloy. Compo. 666 185 (2016)
W Kohn and L Sham Phys. Rev. 140 1133 (1965)
M D Segall, P J D Lindan, M J Probert, C J Pickard, P J Hasnip and S J Clark J. Physics Condensed Matter. 14 2717 (2002)
J P Perdew, K Burke and Y Wang Phys. Rev. B, Cond. Matter. 54 16533 (1997)
J P Perdew and W Yue Physical Review. B, Cond. Matter. 45 13244 (1992)
P John Rev. Lett. 77 3865 (1997)
S N Sun, N Kioussis and M Ciftan Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter. 54 3074 (1996)
J D Pack and H J Monkhorst Phys. Rev. B, Cond. Matter. 16 1748 (1977)
D., J., and Chadi Phys. Rev. B Cond. Matter. 13 5188 (1977)
C Zhong J. Atomic and Mole. Phys. 35 666 (2018)
A A Maradudin, E W Montroll and G H Weiss ResearchGate. 5 0556 (1971)
M A Blanco and E Francisco Phys. Commun. 158 57 (2004)
M Flórez, J Recio, E Francisco and M Blanco Rev. B Cond. Matter. 66 144112 (2002)
H Rached, D Rached, S Benalia and A H Reshak Chem. Phys. 143 93 (2013)
S J Clark, M D Segallii, C J Pickardii and P J Hasnipiii Kris- Cryst. Mater. 220 567 (2005)
F Birch Phys. Rev. 71 809 (1947)
G Ghosh, S Vaynman, M Asta and M E Fine Intermetallics. 15 44 (2007)
S Zhou, B Peng, Y Cao and Y Xu B Cond. Matter. 571 118 (2019)
G F Zhan, B Yang and Y He J. Shangrao Normal Univer. 38 41 (2018)
C Lai and Y Hu Chem. Chem. Phys. 22 9009 (2020)
J Chen, X Zhang, C Ying, H Ma and H Guo Ceram. Int. 46 4595 (2020)
Z P Chen Ningxia University (2018)
H W Shou, R Y Xie, M J Peng and Y H Duan B Cond. Matter. 560 41 (2019)
M Peng, H Shou and Y Cao Phys. B: Cond. Matter. 561 29 (2019)
D Qu, L Bao, Z Kong and Y Duan Vacuum 179 109488 (2020)
R Khenata, M Sahnoun, H Baltache, M Rerat, A H Rashek, N Illes and B Bouhafs Solid State Commun. 136 120 (2005)
D Liu, Y Duan and W Bao Ceramics Int. 44 11438 (2018)
J Zhang, Y Duan and C Li Ceramics Int. 43 13948 (2017)
F W Xie, Y Ping and L Pei Commun. 285 2660 (2012)
Y Wu, X Wang, Y Wang and Y Duan Mater. 114 110963 (2021)
B Peng Kunming University of Sci. and Technol. (2020)
L Bao, Z Kong and D Qu J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 142 109465 (2020)
Z Huang, J Feng and W Pan Solid State Commun. 151 1559 (2011)
Y Liu, W C Hu, D J Li, X Q Zeng and C S Xu B Cond. Matter. 432 33 (2014)
A Rb, B Zz, C Aak, D Sa, E Mi, A Mi, F Buh and G Mk J. Solid State Chem. 302 122388 (2021)
H Hua, Z Wen, Y Zhao, F Li and P Han Intermetallics. 44 110 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, item number (51761021, 51761020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cao, Y. & Zhou, S. First-principles prediction of electronic, optical, and thermodynamic properties of c-TiAl3 with M doping (M = V, Nb, Ta). Indian J Phys 97, 2943–2960 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02656-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02656-5