Abstract
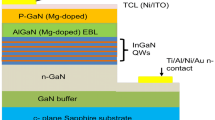
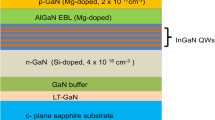
In the present study, optical and electrical properties of e-beam deposited Ni/Au/ITO (1.5/1/50 nm) contacts on p-GaN are investigated and compared with conventional thin Ni/Au (5/5 nm) semitransparent p-contacts. The contacts were annealed at 560 °C for 5 min in N2 + O2 ambient in a rapid thermal annealing system. The current–voltage (I–V) characteristics of both metal schemes showed linear behavior. The specific contact resistances and sheet resistances extracted from measured resistance versus contact pads spacing of Ni/Au and Ni/Au/ITO contacts were recorded ~ 2.71 × 10−3 Ω-cm2, 4.94 × 10−4 Ω-cm2, 2.021 × 105 Ω/□ and 2.1898 × 105 Ω/□, respectively. The normalized transmittance of Ni/Au/ITO film was recorded 81.6% at 463 nm, which was 8.5% higher than the conventional Ni/Au film (73.1%). Scanning electron microscopy images of contacts showed that the adhesion quality of Ni/Au/ITO contacts was superior to annealed Ni/Au contacts. It was found that electroluminescence intensity was higher (7.5%) for LED chip with Ni/Au/ITO p-contacts than LED chip with Ni/Au contacts. The forward voltages (VF) of LEDs with Ni/Au and Ni/Au/ITO contacts at 20 mA current injection were found 2.8 V and 2.91 V, respectively. These results indicate that Ni/Au/ITO may be used as transparent p-contacts for fabrication of high-performance GaN LEDs due to their better optical and adhesive properties compared to the conventional Ni/Au (5/5 nm) contacts on p-GaN.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C M Lee, C C Chuo, I L Chen, J C Chang and J I Chyi IEEE Electron. Dev. Lett.24 156 (2003)
W S Wong, T Sands, N W Cheung, M Kneissl, D P Bour, P Mei, L T Romano and N M Johnson Appl. Phys. Lett. 77 2822 (2000)
Y C Lin, S J Chang, Y K Su, T Y Tsai, C S Chang, S C Shei, S J Hsu, C H Liu, U H Liaw, S C Chen and B R Huang IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett.14 1668 (2002)
Y C Lin, S J Chang, Y K Su, T Y Tsai, C S Chang, S C Shei, C W Kuo and S C Chen Solid-State Electron.47 849 (2003)
R-H Horng, D-S Wuu, Y-C Lien and W-H Lan Appl. Phys. Lett.79 2925 (2001)
C-S Chang, S-J Chang, Y-K Su, Y-Z Chiou, Y-C Lin, Y-P Hsu, S-C Shei, H-M Lo, J-C Ke, S-C Chen and C-H Liu Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.42 3324 (2003)
S Zhou, S Yuan, Y Liu, L J Guo, S Liu and H Ding Appl. Surf. Sci.355 1013 (2015)
C H Lin, D L Hibbard, A Au, H P Lee, Z J Dong, F J Szalkowski, J Chen and C Chen Mater. Res. Soc. Symp.639 G4.8.1 (2001)
K-M Chang, J-Y Chu and C-C Cheng IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett.16(8) 1807 (2004)
S-H Su, C-C Hou, M Yokoyama, S-M Chen Solid-State Electron.49 1905 (2005)
J-O Song, K-K Kim, H Kim, Y-K Kim, H-G Hong, H Na and T-Y Seong Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.10 211(2007)
S-P Jung, C-H Lin, H M Chan, Z Fan, J G Lu, H P Lee Phys. Stat. Solidi. (a)201 2827 (2004)
J K Sheu, Y K Su, G C Chi, P L Koh, M J Jou, C M Chang, C C Liu, and W C Hung Appl. Phys. Lett.74 2340 (1999)
C Gui, X Ding, S Zhou, Y Gao, X Liu and S Liu Opt. Laser Technol.104 112 (2018)
W Hou, C Stark, S You, L Zhao, T Detchprohm and C Wetzel Appl. Opt.51(23) 5596 (2012)
J Y Moon, J H Kim, H S Lee, C H Ahn, H K Cho, J Y Lee and H S Kim J Korean Phys. Soc.53 3681 (2008)
T W Kang, C S Chi, S Park and T W Kim Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.39 1062 (2000)
L-C Chen, J-K Ho, F-R Chen, J-J Kai, L Chang, C-S Jong, C C. Chiu, C-N Huang and K-K Shih Phys. Stat. Sol. (a)176 773 (1999)
J S Kwak and Y Park J Korean Phys Soc45 988 (2004)
S Y Kim, H W Jang and J-Lam Lee Phys. Stat. Sol. (c)1 214 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, under network programme (PSC-0102). Authors are thankful to members of Optoelectronics and MOEMS Group for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K., Chauhan, A., Mathew, M. et al. Electrical and optical properties of InGaN/GaN MQWs light-emitting diodes with Ni/Au/ITO transparent p-contacts. Indian J Phys 94, 183–187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01472-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01472-0