Abstract
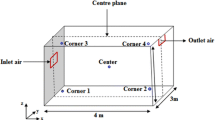
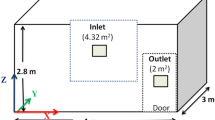
Inhalation of radon (222Rn) and its decay products are a major source of natural radiation exposure. It is known from recent surveys in many countries that radon and its progeny contribute significantly to total inhalation dose and it is fairly established that radon when inhaled in large quantity causes lung disorder. In recent times, numerical modelling has become the cost effective replacement of experimental methods for the prediction and visualization of indoor pollutant distribution. The aim of this study is to implement the Finite Volume Method (FVM) for studying the radon distribution indoor. The findings show that the radon concentration which is distributed in a non-homogeneous way in the room is due to the difference in the radon concentration of different sources (wall, floor and ceiling). Moreover, the radon concentration is much larger near walls, and decreases in the middle of the room because of the effect of air velocity. We notice that the simulation results of radon concentration are in agreement with the results of other experimental studies. The annual effective dose of radon in the model room has been also investigated.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c:
-
Concentration of radon (Bqm−3)
- ci :
-
Concentration of radon (Bqm−3) in inlet
- L:
-
Height of the room (m)
- p:
-
Pressure (Nm−2)
- Pr:
-
Prandtl numbre
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number
- Sh:
-
Sherwood number
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number
- Ri:
-
Richardson number
- Le:
-
Lewis number
- N:
-
Buoyancy ratio
- \({\bar{\varepsilon }}_{\text{c}}\) :
-
Overall effectiveness coefficient for contaminant distribution
- Caverage :
-
Average concentration of (222Rn) inside the room (Bqm−3)
- Coutlet :
-
Average concentration of 222Rn at the outlet (Bqm−3)
- Cinlet :
-
Average concentration of 222Rn at the inlet (Bqm−3)
- u:
-
Velocity vector (ms−1)
- w:
-
Height of the opening (m)
- x,y:
-
Cartesian coordinates
- ρ:
-
Mixture density (Air-222Rn), Kg m−3
- λ:
-
222Rn decay constant (s−1)
- D:
-
Radon diffusivity in air (m−2 s−1)
- βc :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient, K−1
- g:
-
Gravitational acceleration (m−2 s−1)
References
F Steinhausler Environ. Intern. 22 (Suppl. 1) S1111 (1996)
Q Guo, J Sun and W Zhuo J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 37 716 (2000)
K K Dwivedi et al. Radiat. Meas. 33 7 (2001)
P C Deka, H Sarma, S Sarkar, T D Goswami and B K Sarma Indian J. Phys. 83 1025 (2009)
M S Kandari and R C Ramola Indian J. Phys. 83 1019 (2009)
R S Saini, M Nain, R P Chauhan. N Kishore and S K Chakarvarti Indian J. Phys. 83 1197 (2009)
F Bochicchio, F Forastiere, D Abeni and E Rapiti Radiat. Protect. Dosim. 78 33 (1998)
R W Field et al. Am. J. Epidemiol. 151 1091 (2000)
J Ma, H Yonehara, T Aoyama, M Doi, S Kobayashi and M Sakanoue Health Phys. 72 86 (1997)
W Jacobi Health Phys. 22 441 (1972)
J Postendorfer, A Wicke and A Schraub Health Phys. 34 465 (1978)
W Zhuo, T Iida, J Moriizumi, T Aoyagi and I Takahashi Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 93 357 (2001)
V Urosevic, D Nikezic, and S Vulovic J. Environ. Radioact. 99 1829 (2008)
B Zhao and J Wu J. Hazard. Mater. 147 439 (2007)
D Xie, H Wang and K J Kearfott Atmos. Environ. 60 453 (2012)
K Akbari, J Mahmoudi and M Ghanbari J. Environ. Radioact. 116 166 (2013)
H Elharfi, M Naïmi, M Lamsaadi, A Raji and M Hasnaoui Int. Schol. Research Netw. 2012 16 (2012)
J A Rabi and A A Mohamad Appl. Mathem. Modell. 30 1546 (2006)
M Corcione, S Grignaffini and A Quintino Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81 811 (2015)
M M Rahman, M A Alim, M A H Mamun, M K Chowdhury and A K M S Islam ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2 2 (2007)
R S Kaluri and T Basak Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54 2578 (2011)
B M Moharram, M N Suliman, N F Zahran, S E Shennawy and A R El Sayed Annals of Nucl. Energ. 45 138 (2012)
UNSCEAR United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources, effects and risk of ionizing radiation (New York: United Nations) (2000)
L Oufni, M A Misdaq and M Amrane Radiat. Measur. 40 118 (2005)
International Commission on Radiological Protection, Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection. Annals of the ICRP Vol 45 No. 1S (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabi, R., Oufni, L. A theoretical investigation of the distribution of indoor radon concentrations. Indian J Phys 91, 471–479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0932-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0932-8