Abstract
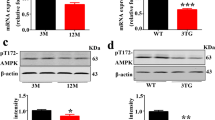
Our previous study indicated that inhibition of NLRP1-dependent pyroptosis could decrease intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of a protein kinase A (PKA) agonist– or streptozotocin (STZ)-induced hyperphosphorylated tau. In this study, we used a glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) overactivation rat model to reconfirm our previous results. ICV injection of wortmannin (WT, a PI3K inhibitor) and GF-109203X (GFX, a PKC inhibitor) was used to induce overactivation of GSK-3β in rats. We injected NLRP1 siRNA together with WT/GFX to evaluate the effect of the inhibition of NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis on hyperphosphorylated tau. Our results indicated that ICV injection of NLRP1 siRNA prevented ICV-WT/GFX-induced neuronal death, further improving the spatial memory of the rats in the Morris water maze test. ICV injection of NLRP1 siRNA downregulated the expression of ASC, caspase-1, and GSDMD and the contents of IL-1β and IL-18 in rat brains. ICV injection of NLRP1 siRNA also decreased hyperphosphorylated tau and the activity of GSK-3β. Thus, these results support our previous study that NLRP1-dependent pyroptosis could enhance hyperphosphorylation of tau protein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abey A, Davies D, Goldsbury C, Buckland M, Valenzuela M, Duncan T (2021) Distribution of tau hyperphosphorylation in canine dementia resembles early Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Brain Pathol 31:144–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12893
Alfonso-Loeches S, Ureña-Peralta J, Morillo-Bargues MJ, Gómez-Pinedo U, Guerri C (2016) Ethanol-induced TLR4/NLRP3 neuroinflammatory response in microglial cells promotes leukocyte infiltration across the BBB. Neurochem Res 41:193–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1760-5
Arendt T, Stieler JT, Holzer M (2016) Tau and tauopathies. Brain Res Bull 126:238–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.08.018
Chen CM, Yen CY, Chen WL, Lin CH, Wu YR, Chang KH, Lee-Chen GJ (2021) Pathomechanism characterization and potential therapeutics identification for Parkinson’s disease targeting neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci 22:1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031062
de Brito Toscano EC, Rocha NP, Lopes BNA, Suemoto CK, Teixeira AL (2021) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: focus on NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes. Curr Protein Pept Sci 22:584–598. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203722666210916141436
Dempsey C, Rubio Araiz A, Bryson KJ, Finucane O, Larkin C, Mills EL, Robertson AAB, Cooper MA, O’Neill LAJ, Lynch MA (2017) Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 promotes non-phlogistic clearance of amyloid-β and cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav Immun 61:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.014
Ebeid MA, Habib MZ, Mohamed AM, Faramawy YE, Saad SST, El-Kharashi OA, El Magdoub HM, Abd-Alkhalek HA, Aboul-Fotouh S, Abdel-Tawab AM (2021) Cognitive effects of the GSK-3 inhibitor “lithium” in LPS/chronic mild stress rat model of depression: Hippocampal and cortical neuroinflammation and tauopathy. Neurotoxicology 83:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2020.12.016
Han C, Yang Y, Guan Q, Zhang X, Shen H, Sheng Y, Wang J, Zhou X, Li W, Guo L, Jiao Q (2020) New mechanism of nerve injury in Alzheimer’s disease: β-amyloid-induced neuronal pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med 24:8078–8090. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15439
Gong H, Wan X, Zhang Y, Liang S (2021) Downregulation of HOTAIR reduces neuronal pyroptosis by targeting miR-455-3p/NLRP1 axis in propofol-treated neurons in vitro. Neurochem Res 46:1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03249-6
Huang B, Liu J, Meng T, Li Y, He D, Ran X, Chen G, Guo W, Kan X, Fu S, Wang W, Liu D (2018) Polydatin prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced Parkinson’s disease via regulation of the AKT/GSK3β-Nrf2/NF-κB signaling axis. Front Immunol 9:2527. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02527
Hyman BT, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Carrillo MC, Dickson DW, Duyckaerts C, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Mirra SS, Nelson PT, Schneider JA, Thal DR, Thies B, Trojanowski JQ, Vinters HV, Montine TJ (2012) National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.10.007
Jiang X, Tian Q, Wang Y, Zhou XW, Xie JZ, Wang JZ, Zhu LQ (2011) Acetyl-L-carnitine ameliorates spatial memory deficits induced by inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase C. J Neurochem 118:864–878. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07355.x
Kaushal V, Dye R, Pakavathkumar P, Foveau B, Flores J, Hyman B, Ghetti B, Koller BH, LeBlanc AC (2015) Neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome activation of Caspase-1 coordinately regulates inflammatory interleukin-1-beta production and axonal degeneration-associated Caspase-6 activation. Cell Death Differ 22:1676–1686. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.16
Kim JY, Paton JC, Briles DE, Rhee DK, Pyo S (2015) Streptococcus pneumoniae induces pyroptosis through the regulation of autophagy in murine microglia. Oncotarget 6:44161–44178. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6592
Lauckner J, Frey P, Geula C (2003) Comparative distribution of tau phosphorylated at Ser262 in pre-tangles and tangles. Neurobiol Aging 24:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00228-2
Lauretti E, Dincer O, Praticò D (2020) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867:118664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118664
Li X, Lu F, Tian Q, Yang Y, Wang Q, Wang JZ (2006) Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer-like tau hyperphosphorylation in rat hippocampus slices in culture. J Neural Transm (vienna) 113:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0303-7
Li Y, Xu P, Shan J, Sun W, Ji X, Chi T, Liu P, Zou L (2020) Interaction between hyperphosphorylated tau and pyroptosis in forskolin and streptozotocin induced AD models. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109618
Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Gong CX (2002) Involvement of aberrant glycosylation in phosphorylation of tau by cdk5 and GSK-3beta. FEBS Lett 530:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03487-7
Liu P, Zou L, Jiao Q, Chi T, Ji X, Qi Y, Xu Q, Wang L (2013) Xanthoceraside attenuates learning and memory deficits via improving insulin signaling in STZ-induced AD rats. Neurosci Lett 543:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.065
Liu SJ, Zhang AH, Li HL, Wang Q, Deng HM, Netzer WJ, Xu H, Wang JZ (2003) Overactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase C leads to hyperphosphorylation of tau and impairment of spatial memory. J Neurochem 87:1333–1344. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02070.x
Meng XF, Wang XL, Tian XJ, Yang ZH, Chu GP, Zhang J, Li M, Shi J, Zhang C (2014) Nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome mediates neuron injury under high glucose. Mol Neurobiol 49:673–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8551-2
Morales I, Jiménez JM, Mancilla M, Maccioni RB (2013) Tau oligomers and fibrils induce activation of microglial cells. J Alzheimers Dis 37:849–856. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-131843
Peng JH, Zhang CE, Wei W, Hong XP, Pan XP, Wang JZ (2007) Dehydroevodiamine attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation and spatial memory deficit induced by activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:1521–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.02.008
Prince M, Wimo A, Guerchet M, Ali GC, Wu YT, Prina M (2015) World Alzheimer Report 2015: The global impact of dementia: an analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2015/. Accessed 21 Sep 2015.
Richetin K, Steullet P, Pachoud M, Perbet R, Parietti E, Maheswaran M, Eddarkaoui S, Bégard S, Pythoud C, Rey M, Caillierez R, Do Q, K, Halliez S, Bezzi P, Buée L, Leuba G, Colin M, Toni N, Déglon N (2020) Tau accumulation in astrocytes of the dentate gyrus induces neuronal dysfunction and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci 23:1567–1579. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00728-x
Sandberg M, Patil J, D'Angelo B, Weber SG, Mallard C (2014) NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 79:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.004
Saxena G, Patro IK, Nath C (2011) ICV STZ induced impairment in memory and neuronal mitochondrial function: a protective role of nicotinic receptor. Behav Brain Res 224:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.039
Schöll M, Lockhart SN, Schonhaut DR, O’Neil JP, Janabi M, Ossenkoppele R, Baker SL, Vogel JW, Faria J, Schwimmer HD, Rabinovici GD, Jagust WJ (2016) PET Imaging of Tau Deposition in the Aging Human Brain. Neuron 89:971–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.028
Tan CC, Zhang JG, Tan MS, Chen H, Meng DW, Jiang T, Meng XF, Li Y, Sun Z, Li MM, Yu JT, Tan L (2015) NLRP1 inflammasome is activated in patients with medial temporal lobe epilepsy and contributes to neuronal pyroptosis in amygdala kindling-induced rat model. J Neuroinflammation 12:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0233-0
Tan MS, Tan L, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Jia CD, Yu JT (2014) Amyloid-β induces NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis 5:e1382. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.348
Timmers M, Tesseur I, Bogert J, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Börjesson-Hanson A, Baquero M, Boada M, Randolph C, Tritsmans L, Van Nueten L, Engelborghs S, Streffer JR (2019) Relevance of the interplay between amyloid and tau for cognitive impairment in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 79:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.03.016
Wang C, Pan Y, Zhang QY, Wang FM, Kong LD (2012) Quercetin and allopurinol ameliorate kidney injury in STZ-treated rats with regulation of renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation. PLoS ONE 7:e38285. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038285
Wang HB, Li T, Ma DZ, Zhi H (2018) ERα36 gene silencing promotes tau protein phosphorylation, inhibits cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. FASEB J 22:fj201701386. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201701386
Wang SN, Li Q, Jing MH, Alba E, Yang XH, Sabaté R, Han YF, Pi RB, Lan WJ, Yang XB, Chen JK (2016) Natural xanthones from Garcinia mangostana with multifunctional activities for the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 41:1806–1817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1896-y
Wang Y, Zhang JX, Du XX, Zhao L, Tian Q, Zhu LQ, Wang SH, Wang JZ (2008) Temporal correlation of the memory deficit with Alzheimer-like lesions induced by activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Neurochem 106:2364–2374. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05578.x
Xu GG, Deng YQ, Liu SJ, Li HL, Wang JZ (2005) Prolonged Alzheimer-like tau hyperphosphorylation induced by simultaneous inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase C in N2a cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (shanghai) 37:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00050.x
Xu H, Li J, Wang Z, Feng M, Shen Y, Cao S, Li T, Peng Y, Fan L, Chen J, Gu C, Yan F, Wang L, Chen G (2017) Methylene blue attenuates neuroinflammation after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through the Akt/GSK-3β/MEF2D signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun 65:125–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.04.020
Yang C, Li X, Gao W, Wang Q, Zhang L, Li Y, Li L, Zhang L (2018) Cornel iridoid glycoside inhibits tau hyperphosphorylation via regulating cross-talk between GSK-3β and PP2A signaling. Front Pharmacol 9:682. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00682
Yang C, Li X, Zhang L, Li Y, Li L, Zhang L (2019) Cornel iridoid glycoside induces autophagy to protect against tau oligomer neurotoxicity induced by the activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. J Nat Med 73:717–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-019-01318-3
Yang CC, Kuai XX, Li YL, Zhang L, Yu JC, Li L, Zhang L (2013) Cornel iridoid glycoside attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibition of PP2A demethylation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:108486. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/108486
Yang W, Liu Y, Xu QQ, Xian YF (2020) Lin ZX (2020) Sulforaphene ameliorates neuroinflammation and hyperphosphorylated tau protein via regulating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway in experimental models of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:4754195. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4754195.eCollection
Zhang H, Wang X, Xu P, Ji X, Chi T, Liu P, Zou L (2020) Tolfenamic acid inhibits GSK-3beta and PP2A mediated tau hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease models. J Physiol Sci 70:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12576-020-00757-y
Funding
This work was supported by the University Students’ Innovative Undertaking Program of Liaoning Province (No. S202010163029) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: X. L., W. S., P. L. Methodology: X. L., Y. Y. Formal analysis and investigation: J. S., X. S., X. Y. Writing—original draft preparation: X. L., W. S., H. W. Writing—review and editing: P. L. Funding acquisition: P. L. Resources: P. L., L. Z. Supervision: P. L., L. Z.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The animal study conformed to the regulations on the administration of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (Authorization number: SYPU-IACUC-2020–08.19–006).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Song, W., Yu, Y. et al. Inhibition of NLRP1-Dependent Pyroptosis Prevents Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Overactivation–Induced Hyperphosphorylated Tau in Rats. Neurotox Res 40, 1163–1173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00554-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00554-y