Abstract
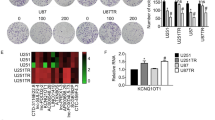
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most prevalent primary cerebral tumor in adults with high aggressiveness. Temozolomide (TMZ) is considered as the most widely used chemotherapy for GBM patients. Accumulating studies have proved that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in the pathogenesis of tumors. The aim of our study is to disclose the role of mir-99a-let-7c cluster host gene (MIR99AHG) in GBM. MIR99AHG expression was discovered to be elevated in GBM cells through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis. Loss-of-function experiments demonstrated that MIR99AHG silencing enhanced TMZ sensitivity of GBM both in vitro and in vivo. RNA pull down, RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP), and luciferase reporter assays were implemented to unveil the underlying mechanism of MIR99AHG in GBM. The results of the mechanism assays implied that MIR99AHG interacted with microRNA-204-5p (miR-204-5p) and enhanced thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) expression to inactivate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. MIR99AHG/miR-204-5p/TXNIP regulatory axis was verified by rescue experiments in GBM. To summarize, MIR99AHG plays a promoting role in the TMZ resistance of GBM cells. The findings in this study might provide novel sight for the treatment for GBM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Arora A, Somasundaram K (2019) Glioblastoma vs temozolomide: can the red queen race be won? Cancer Biol Ther 20(8):1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1599662
Campos B, Olsen LR, Urup T, Poulsen HS (2016) A comprehensive profile of recurrent glioblastoma. Oncogene 35(45):5819–5825. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.85
Cao J, Han X, Qi X, Jin X, Li X (2018) miR-204-5p inhibits the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting Runx2. Int J Mol Med 42(5):2560–2568. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3811
Cao W, Zhou G (2020) LncRNA SNHG12 contributes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells by absorbing miRNA-320b. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20200805
Chavda V, Patel V, Yadav D, Shah J, Patel S, Jin JO (2020) Therapeutics and research related to glioblastoma: advancements and future targets. Curr Drug Metab 21(3):186–198. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200221666200408083950
Chen Q, Liu T, Bao Y, Zhao T, Wang J, Wang H, Wang A, Gan X, Wu Z, Wang L (2020) CircRNA cRAPGEF5 inhibits the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via the miR-27a-3p/TXNIP pathway. Cancer Lett 469:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.017
Chen S, Li K (2020) HOXD-AS1 facilitates cell migration and invasion as an oncogenic lncRNA by competitively binding to miR-877-3p and upregulating FGF2 in human cervical cancer. BMC Cancer 20(1):924. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07441-9
Chi Y, Wang D, Wang J, Yu W, Yang J (2019) Long non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of cancers. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091015
Chu Y, Jiang M, Du F, Chen D, Ye T, Xu B, Li X, Wang W, Qiu Z, Liu H, Nie Y, Liang J, Fan D (2018) miR-204-5p suppresses hepatocellular cancer proliferation by regulating homeoprotein SIX1 expression. FEBS Open Bio 8(2):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12363
Duffau H (2017) Glioblastoma in 2017. Revue Infirm 66(228):16–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.revinf.2016.12.002
Emmrich S, Streltsov A, Schmidt F, Thangapandi VR, Reinhardt D, Klusmann JH (2014) LincRNAs MONC and MIR100HG act as oncogenes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Mol Cancer 13:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-171
Han C, Li H, Ma Z, Dong G, Wang Q, Wang S, Fang P, Li X, Chen H, Liu T, Xu L, Wang J, Wang J, Yin R (2021) MIR99AHG is a noncoding tumor suppressor gene in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis 12(5):424. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03715-7
Jiapaer S, Furuta T, Tanaka S, Kitabayashi T, Nakada M (2018) Potential strategies overcoming the temozolomide resistance for glioblastoma. Neurol Med Chir 58(10):405–421. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.ra.2018-0141
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J, Baer-Dubowska W (2017) The Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway: an update on its regulation and possible role in cancer prevention and treatment. Pharmacol Rep 69(3):393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.12.011
Liang C, Yang Y, Guan J, Lv T, Qu S, Fu Q, Zhao H (2018) LncRNA UCA1 sponges miR-204-5p to promote migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells via upregulation of ZEB1. Pathol Res Pract 214(9):1474–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.07.036
Liang Y, Wang H, Chen B, Mao Q, Xia W, Zhang T, Song X, Zhang Z, Xu L, Dong G, Jiang F (2021) circDCUN1D4 suppresses tumor metastasis and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma by stabilizing TXNIP expression. Mol Ther−nucleic Acids 23:355–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.11.012
Marosi C (2006) Chemotherapy for malignant gliomas. Wien Med Wochenschr 156(11–12):346–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-006-0307-4
Meng Q, Wang X, Xue T, Zhao Q, Wang W, Zhao K (2020) Long noncoding RNA MIR99AHG promotes gastric cancer progression by inducing EMT and inhibiting apoptosis via miR577/FOXP1 axis. Cancer Cell Int 20:414. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01510-6
Nishikawa R (2010) Standard therapy for glioblastoma–a review of where we are. Neurol Med Chir 50(9):713–719. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.50.713
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2013) The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clinical Cancer Res 19(4):764–772. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-3002
Omuro A, DeAngelis LM (2013) Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 310(17):1842–1850. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.280319
Palkina N, Komina A, Aksenenko M, Moshev A, Savchenko A, Ruksha T (2018) miR-204-5p and miR-3065-5p exert antitumor effects on melanoma cells. Oncol Lett 15(6):8269–8280. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8443
Shen J, Xiong J, Shao X, Cheng H, Fang X, Sun Y, Di G, Mao J, Jiang X (2020) Knockdown of the long noncoding RNA XIST suppresses glioma progression by upregulating miR-204-5p. J Cancer 11(15):4550–4559. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.45676
Shou J, Gao H, Cheng S, Wang B, Guan H (2021) LncRNA HOXA-AS2 promotes glioblastoma carcinogenesis by targeting miR-885-5p/RBBP4 axis. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01690-1
Soomro SH, Ting LR, Qing YY, Ren M (2017) Molecular biology of glioblastoma: classification and mutational locations. JPMA J Pak Med Assoc 67(9):1410–1414
Tang G, Luo L, Zhang J, Zhai D, Huang D, Yin J, Zhou Q, Zhang Q, Zheng G (2021) lncRNA LINC01057 promotes mesenchymal differentiation by activating NF-κB signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett 498:152–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.047
Tian Y, Su Y, Ye Q, Chen L, Yuan F, Wang Z (2020) Silencing of TXNIP alleviated oxidative stress injury by regulating MAPK-Nrf2 axis in ischemic stroke. Neurochem Res 45(2):428–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02933-y
Wu Y, Qian Z (2019) Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs regulatory pathways in the tumorigenesis and pathogenesis of glioma. Discov Med 28(153):129–138
Xia Z, Liu F, Zhang J, Liu L (2015) Decreased expression of MiRNA-204-5p contributes to glioma progression and promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0132399. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132399
Xie M, Xie R, Xie S, Wu Y, Wang W, Li X, Xu Y, Liu B, Zhou Y, Wang T, Gao L, Pan T (2020) Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) acts as a tumor suppressor in human prostate cancer. Cell Biol Int 44(10):2094–2106. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11418
Yang B, Shen J, Xu L, Chen Y, Che X, Qu X, Liu Y, Teng Y, Li Z (2019) Genome-wide identification of a novel eight-lncRNA signature to improve prognostic prediction in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol 9:898. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00898
Yang S, Chen B, Zhang B, Li C, Qiu Y, Yang H, Huang Z (2020) miR-204-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting HER-2. Mol Med Rep 22(4):2645–2654. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11367
Zhao JL, Wang CL, Liu YL, Zhang GY (2019) Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 enhances migration and invasion of ovarian cancer by upregulating DGCR8. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(23):10226–10233 https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19659
Zottel A, Šamec N, Videtič Paska A, Jovčevska I (2020) Coding of glioblastoma progression and therapy resistance through long noncoding RNAs. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071842
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
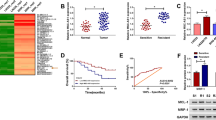
MIR99AHG silencing inhibits TMZ sensitivity of GBM in vivo. (A) The excised tumors in sh-NC or sh-MIR99AHG#1 groups were displayed. (B-C) The volume and weight of tumors in two groups were shown. ** P<0.01. (TIF 633 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Ma, J. MIR99AHG/miR-204-5p/TXNIP/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway Decreases Glioblastoma Temozolomide Sensitivity. Neurotox Res 40, 1152–1162 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00536-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00536-0