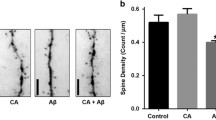
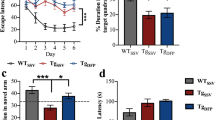
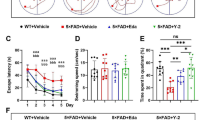
Abstract
Oxidative stress is a key factor in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders and is involved in the accumulation of amyloid beta plaques and Tau inclusions. Edaravone (EDR) is a free radical scavenger that is approved for motor neuron disease and acute ischemic stroke. EDR alleviates pathologies and cognitive impairment of AD via targeting multiple key pathways in transgenic mice. Herein, we aimed to study the effect of EDR on Tau pathology in P301L mice; an animal model of frontotemporal dementia (FTD), at two age time points representing the early and late stages of the disease. A novel EDR formulation was utilized in the study and the drug was delivered orally in drinking water for 3 months. Then, behavioral tests were conducted followed by animal sacrifice and brain dissection. Treatment with EDR improved the reference memory and accuracy in the probe trial as evaluated in Morris water maze, as well as novel object recognition and significantly alleviated motor deficits in these mice. EDR also reduced the levels of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and 3-nitrotyrosine adducts. In addition, immunohistochemistry showed that EDR reduced tau phosphorylation and neuroinflammation and partially rescued neurons against oxidative neurotoxicity. Moreover, EDR attenuated downstream pathologies involved in Tau hyperphosphorylation. These results suggest that EDR may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of FTD.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data that were generated and analyzed in this study are included in this article.
References:
Aggarwal NT, Wilson RS, Beck TL, Bienias JL, Bennett DA (2006) Motor dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 63:1763–1769
Ahsan H (2013) 3-Nitrotyrosine: a biomarker of nitrogen free radical species modified proteins in systemic autoimmunogenic conditions. Hum Immunol 74:1392–1399
Alavi Naini SM, Soussi-Yanicostas N (2015) Tau hyperphosphorylation and oxidative stress, a critical vicious circle in neurodegenerative tauopathies? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:151979
Albers DS, Augood SJ, Martin DM et al (1999) Evidence for oxidative stress in the subthalamic nucleus in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurochem 73:881–884
Banno M, Mizuno T, Kato H et al (2005) The radical scavenger edaravone prevents oxidative neurotoxicity induced by peroxynitrite and activated microglia. Neuropharmacology 48:283–290
Barber SC, Shaw PJ (2010) Oxidative stress in ALS: key role in motor neuron injury and therapeutic target. Free Radical Biol Med 48:629–641
Burrell JR, Kiernan MC, Vucic S, Hodges JR (2011) Motor Neuron dysfunction in frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134:2582–2594
Cente M, Filipcik P, Pevalova M, Novak M (2006) Expression of a truncated tau protein induces oxidative stress in a rodent model of tauopathy. Eur J Neurosci 24:1085–1090
Cherry JD, Tripodis Y, Alvarez VE et al (2016) Microglial neuroinflammation contributes to tau accumulation in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:112–112
Cook C, Dunmore JH, Murray ME et al (2014) Severe amygdala dysfunction in a MAPT transgenic mouse model of frontotemporal dementia. Neurobiol Aging 35:1769–1777
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Dalleau S, Baradat M, Guéraud F, Huc L (2013) Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress:4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance. Cell Death Differ 20:1615–1630
David DC, Hauptmann S, Scherping I et al (2005) Proteomic and functional analyses reveal a mitochondrial dysfunction in P301L tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 280:23802–23814
Dias-Santagata D, Fulga TA, Duttaroy A, Feany MB (2007) Oxidative stress mediates tau-induced neurodegeneration in Drosophila. J Clin Invest 117:236–245
DuBoff B, Götz J, Feany MB (2012) Tau promotes neurodegeneration via DRP1 mislocalization in vivo. Neuron 75:618–632
Dumont M, Stack C, Elipenahli C et al (2011) Behavioral deficit, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction precede tau pathology in P301S transgenic mice. FASEB J 25:4063–4072
Dutschmann M, Menuet C, Stettner GM et al (2010) Upper airway dysfunction of Tau-P301L mice correlates with tauopathy in midbrain and ponto-medullary brainstem nuclei. J Neurosci 30:1810–1821
Elipenahli C, Stack C, Jainuddin S et al (2012) Behavioral improvement after chronic administration of coenzyme Q10 in P301S transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 28:173–182
Feng S, Yang Q, Liu M, et al. (2011) Edaravone for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, Cd007230
Gabbita SP, Scheff SW, Menard RM et al (2005) Cleaved-tau: a biomarker of neuronal damage after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 22:83–94
Gamblin TC, King ME, Kuret J, Berry RW, Binder LI (2000) Oxidative regulation of fatty acid-induced tau polymerization. Biochemistry 39:14203–14210
Goedert M, Hasegawa M, Jakes R et al (1997) Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau by stress-activated protein kinases. FEBS Lett 409:57–62
Good PF, Werner P, Hsu A, Olanow CW, Perl DP (1996) Evidence of neuronal oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 149:21–28
Götz J, Chen F, Barmettler R, Nitsch RM (2001) Tau filament formation in transgenic mice expressing P301L tau. J Biol Chem 276:529–534
Götz J, Halliday G, Nisbet R (2019) Molecular Pathogenesis of the Tauopathies. Ann Rev Pathol 14:239
Götz J, Ittner LM (2008) Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:532–544
Hampton AL, Hish GA, Aslam MN et al (2012) Progression of ulcerative dermatitis lesions in C57BL/6Crl mice and the development of a scoring system for dermatitis lesions. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 51:586–593
Haque MM, Murale DP, Kim YK, Lee J-S (2019) Crosstalk between oxidative stress and tauopathy. Int J Mol Sci 20:1959
Hernandez F, Lucas JJ, Avila J (2013) GSK3 and tau: two convergence points in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33(Suppl 1):S141-144
Jiao S-S, Yao X-Q, Liu Y-H et al (2015) Edaravone alleviates Alzheimer’s disease-type pathologies and cognitive deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:5225–5230
Kashon ML, Ross GW, O’Callaghan JP et al (2004) Associations of cortical astrogliosis with cognitive performance and dementia status. J Alzheimers Dis 6:595–604
Köhler C, Dinekov M, Götz J (2013) Active glycogen synthase kinase-3 and tau pathology-related tyrosine phosphorylation in pR5 human tau transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 34:1369–1379
Lee K-Y, Koh S-H, Noh MY et al (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β activity plays very important roles in determining the fate of oxidative stress-inflicted neuronal cells. Brain Res 1129:89–99
Lewis J, McGowan E, Rockwood J et al (2000) Neurofibrillary tangles, amyotrophy and progressive motor disturbance in mice expressing mutant (P301L) tau protein. Nat Genet 25:402–405
Lovell MA, Xiong S, Xie C, Davies P, Markesbery WR (2004) Induction of hyperphosphorylated tau in primary rat cortical neuron cultures mediated by oxidative stress and glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Alzheimers Dis 6:659–671
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival*. J Cell Physiol 192:1–15
Mecocci P, Polidori MC (2012a) Antioxidant clinical trials in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:631–638
Mecocci P, Polidori MC (2012b) Antioxidant clinical trials in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:631–638
Mondragón-Rodríguez S, Perry G, Zhu X et al (2013) Phosphorylation of tau protein as the link between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and connectivity failure: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:940603–940603
Morris RG, Garrud P, Rawlins JN, O’Keefe J (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297:681–683
Nakashima H, Ishihara T, Yokota O et al (2004) Effects of alpha-tocopherol on an animal model of tauopathies. Free Radical Biol Med 37:176–186
National Health and Medical Research Council (2013) Australian code for the care and use of animals for scientific purposes, 8 edn. NHMRC, Canberra
Onyike CU, Diehl-Schmid J (2013) The epidemiology of frontotemporal dementia. Int Rev Psychiatry (abingdon, England) 25:130–137
Orr ME, Sullivan AC, Frost B (2017) A brief overview of tauopathy: causes, consequences, and therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:637–648
Parikh A, Kathawala K, Li J et al (2018a) Self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion of edaravone: part II: in vivo assessment of efficacy against behavior deficits and safety in Alzheimer’s disease model. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:2111–2128
Parikh A, Kathawala K, Tan CC, Garg S, Zhou X-F (2018b) Self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion of edaravone: part I - oral bioavailability improvement. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:2051–2069
Pennanen L, Wolfer DP, Nitsch RM, Götz J (2006) Impaired spatial reference memory and increased exploratory behavior in P301L tau transgenic mice. Genes Brain Behav 5:369–379
Pérez M, Cuadros R, Smith MA, Perry G, Avila J (2000) Phosphorylated, but not native, tau protein assembles following reaction with the lipid peroxidation product, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. FEBS Lett 486:270–274
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E et al (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43:815–825
Rajasekar N, Dwivedi S, Tota SK et al (2013) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on okadaic acid induced memory impairment in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 715:381–394
Ramsden M, Kotilinek L, Forster C et al (2005) Age-dependent neurofibrillary tangle formation, neuron loss, and memory impairment in a mouse model of human tauopathy (P301L). J Neurosci 25:10637–10647
Rong W-T, Lu Y-P, Tao Q et al (2014) Hydroxypropyl-sulfobutyl-β-cyclodextrin improves the oral bioavailability of Edaravone by modulating drug efflux pump of enterocytes. J Pharm Sci 103:730–742
Rudenko LK, Wallrabe H, Periasamy A et al (2019) Intraneuronal tau misfolding induced by extracellular amyloid-β oligomers. J Alzheimers Dis 71:1125–1138
Sancheti H, Kanamori K, Patil I et al (2014) Reversal of metabolic deficits by lipoic acid in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: a 13C NMR study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:288–296
Shamma RN, Basha M (2013) Soluplus®: A novel polymeric solubilizer for optimization of Carvedilol solid dispersions: Formulation design and effect of method of preparation. Powder Technol 237:406–414
Sies H (1997) Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol 82:291–295
Silva MC, Haggarty SJ (2020) Tauopathies: deciphering disease mechanisms to develop effective therapies. Int J Mol Sci 21:8948
Sinha M, Hk A, Juyal R et al (2009) Edaravone in acute ischemic stroke, an Indian experience. Neurol Asia 14:7–10
Smith CD, Carney JM, Starke-Reed PE et al (1991) Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:10540–10543
Stadtman ER (1992) Protein oxidation and aging. Science 257:1220–1224
Stamer K, Vogel R, Thies E, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow E-M (2002) Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress. J Cell Biol 156:1051–1063
Su B, Wang X, Nunomura A et al (2008) Oxidative stress signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 5:525–532
Subbarao KV, Richardson JS, Ang LC (1990) Autopsy samples of Alzheimer’s cortex show increased peroxidation in vitro. J Neurochem 55:342–345
Thangavel R, Stolmeier D, Yang X, Anantharam P, Zaheer A (2012) Expression of glia maturation factor in neuropathological lesions of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:572–581
Wang L, Jiang Q, Chu J et al (2013) Expression of tau40 induces activation of cultured rat microglial cells. PLoS ONE 8:e76057
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2016) Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:5–21
Watanabe K, Tanaka M, Yuki S, Hirai M, Yamamoto Y (2018) How is edaravone effective against acute ischemic stroke and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? J Clin Biochem Nutr 62:20–38
Watanabe T, Tahara M, Todo S (2008) The novel antioxidant Edaravone: from bench to bedside. Cardiovasc Ther 26:101–114
Watanabe T, Yuki S, Egawa M, Nishi H (1994) Protective effects of MCI-186 on cerebral ischemia: possible involvement of free radical scavenging and antioxidant actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1597–1604
Wolf A, Bauer B, Abner EL, Ashkenazy-Frolinger T, Hartz AM (2016) A comprehensive behavioral test battery to assess learning and memory in 129S6/Tg2576 mice. PLoS ONE 11:e0147733
Yamamoto Y, Kuwahara T, Watanabe K, Watanabe K (1996) Antioxidant activity of 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one. Redox Rep 2:333–338
Yamamoto T, Yuki S, Watanabe T et al (1997) Delayed neuronal death prevented by inhibition of increased hydroxyl radical formation in a transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 762:240–242
Yarchoan M, Toledo JB, Lee EB et al (2014) Abnormal serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 is associated with tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol 128:679–689
Yoshida H, Yanai H, Namiki Y et al (2006) Neuroprotective effects of Edaravone: a novel free radical scavenger in cerebrovascular injury. CNS Drug Rev 12:9–20
Yoshino H (2019) Edaravone for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother 19:185–193
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support provided to S. Kelliny by Commonwealth Research and Training scholarship and Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education. We would like to thank Mr. Andrew Beck for suggestions regarding histological techniques and imaging. The authors would also like to acknowledge H Md Morshed Alam (BASF Australia Ltd) for providing samples of Soluplus, and Suzhou Auzone Biotech for the Edaravone formulation.
Funding
This study was supported by National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Grants (1020567, 1021409) and supporting Grant from the University of South Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LB and XFZ contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, experiments, data collection and analysis were performed by SK. JX collaborated in animal studies. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. LB and XFZ supervised the study. All the authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
XFZ is one of the inventors of Chinese patent 200610149832.9. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Ethical approval
All procedures were compliant with the approved protocol (U17-14, U13-18) from Animal Ethics Committee of the University of South Australia and the South Australia animal welfare act and the “Australian code of practice and use of animals for scientific purposes”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelliny, S., Xiong, J., Bobrovskaya, L. et al. Preclinical validation of a novel oral Edaravone formulation for treatment of frontotemporal dementia. Neurotox Res 39, 1689–1707 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00405-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00405-2