Abstract
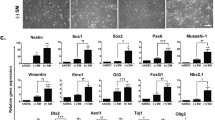
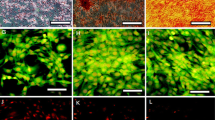
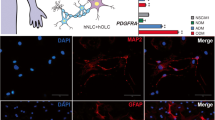
Conversion of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) into neuron-like cells (NLC) is a feasible cell therapy strategy for replacing lost neurons in neuronal disorders. In this study, adipose-derived MSC (ADMSC) were converted into neural stem cells (NSC) via neurosphere. The resulting NSC were then differentiated into NLC by transduction with microRNA-218, using a lentiviral vector. ADMSC, NSC, and NLC were first characterized by flow cytometry, RT-PCR, and immunocytochemistry. The functionality of the NLC was evaluated by qRT-PCR and patch clamp recording. Immunophenotyping of ADMSC showed their immunoreactivity to MSC markers CD90, CD73, CD105, and CD49d, but not to CD31 and CD45. RT-PCR results demonstrated the expression of nestin, neurogenin, neurod1, neurofilament light, and GAP43 genes in NSC while NLC expressed synaptophysin, neurofilament heavy, and GAP43. In addition, NSC morphology changed into multipolar with long processes after transduction with miR-218. Moreover, using qRT-PCR, the expression levels of miR-218 and functionality genes CACNA1C, SNAP25, KCNH1, KCNMA1, and SCN9A were significantly increased in NLC, compared with NSC, and ADMSC at 3 weeks and 5 months post-transduction. Furthermore, the generated NLC expressed significantly higher protein levels of neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NFh) and enolase 2 (Eno2) neuronal markers, compared with ADMSC and NSC. Finally, action potentials were successfully recorded by the generated NLC, using patch clamp. In summary, ADMSC-derived NSC differentiated into functional NLC by transduction with miR-218. The generated NLC expressed functional SNAP25, CACNA1C, KCNH1, KCNMA1, and SCN9A and produced an action potential, which provides useful insights into the generation of functional neuronal cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADMSC:
-
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- NS:
-
neurospheres
- NSC:
-
neural stem cells
- NLC :
-
neural-like cells
- Mir-218:
-
microRNA-218
- CD90:
-
thy-1 cell surface antigen
- CD73:
-
5′ecto-nucleotidase
- CD49d:
-
integrin subunit alpha 4
- CD105:
-
endoglin
- CD31:
-
platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1
- CD45:
-
protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C
- Syp:
-
synaptophysin
- NFl:
-
neurofilament light
- NFh:
-
neurofilament heavy
- Nes:
-
nestin
- Sox2:
-
SRY-box transcription factor 2
- Oct4:
-
POU class 5 homeobox 1
- Neurog1:
-
neurogenin
- Neurod1:
-
neuronal differentiation 1
- GAP43:
-
growth-associated protein 43
- SNAP25:
-
synaptosome-associated protein 25
- CACNA1C:
-
calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 C
- KCNH1:
-
potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1
- KCNMA1:
-
potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M alpha 1
- SCN9A:
-
sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 9
References
Abematsu M, Tsujimura K, Yamano M, Saito M, Kohno K, Kohyama J, Namihira M, Komiya S, Nakashima K (2010) Neurons derived from transplanted neural stem cells restore disrupted neuronal circuitry in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. J Clin Invest 120:3255–3266. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci42957
Agasse F, Bernardino L, Kristiansen H, Christiansen SH, Ferreira R et al (2008) Neuropeptide Y promotes neurogenesis in murine subventricular zone. Stem Cells 26:1636–1645
Ahmadi N, Razavi S, Kazemi M, Oryan S (2012) Stability of neural differentiation in human adipose derived stem cells by two induction protocols. Tissue Cell 44:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2011.11.006
Amin ND, Bai G, Klug JR, Bonanomi D, Pankratz MT et al (2015) Loss of motoneuron-specific microRNA-218 causes systemic neuromuscular failure. Science 350:1525–1529. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad2509
Bloch M, Ousingsawat J, Simon R, Schraml P, Gasser TC et al (2007) KCNMA1 gene amplification promotes tumor cell proliferation in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 26:2525–2534. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210036
Cai C, Grabel L (2007) Directing the differentiation of embryonic stem cells to neural stem cells. Dev Dyn 236:3255–3266
Daniunaite K, Serenaite I, Misgirdaite R, Gordevicius J, Unguryte A et al (2015) Epigenetic regulation of human adipose-derived stem cells differentiation. Mol Cell Biochem 410:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2543-7
Darabi S, Tiraihi T, Delshad A, Sadeghizadeh M (2013a) A new multistep induction protocol for the transdifferentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells into GABAergic neuron-like cells. Iran Biomed J 17:8–14. https://doi.org/10.6091/IBJ.1112.2012
Darabi S, Tiraihi T, Ruintan A, Abbaszadeh HA, Delshad A et al (2013b) Polarized neural stem cells derived from adult bone marrow stromal cells develop a rosette-like structure. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 49:638–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-013-9628-y
Darvishi M, Tiraihi T, Mesbah-Namin SA, Delshad A, Taheri T (2017) Motor neuron transdifferentiation of neural stem cell from adipose-derived stem cell characterized by differential gene expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:275–289
Dekmak A, Mantash S, Shaito A, Toutonji A, Ramadan N et al (2018) Stem cells and combination therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Behav Brain Res 340:49–62
Dharmadasa T, Matamala JM, Kiernan MC (2016) Treatment approaches in motor neurone disease. Curr Opin Neurol 29:581–591
Enderami SE, Soleimani M, Mortazavi Y, Nadri S, Salimi A (2018) Generation of insulin-producing cells from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on PVA scaffold by optimized differentiation protocol. J Cell Physiol 233:4327–4337. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26266
Fiore R, Khudayberdiev S, Saba R, Schratt G (2011) MicroRNA function in the nervous system. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 102:47–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-415795-8.00004-0
Ghasemi Z, Naderi N, Shojaei A, Ahmadirad N, Raoufy MR et al (2018) Low frequency electrical stimulation attenuated the epileptiform activity-induced changes in action potential features in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Cell J 20:355–360. https://doi.org/10.22074/cellj.2018.5443
Grierson AJ, Johnson GV, Miller CC (2001) Three different human tau isoforms and rat neurofilament light, middle and heavy chain proteins are cellular substrates for transglutaminase. Neurosci Lett 298:9–12
Han C, Hoeijmakers JG, Liu S, Gerrits MM, te Morsche RH et al (2012) Functional profiles of SCN9A variants in dorsal root ganglion neurons and superior cervical ganglion neurons correlate with autonomic symptoms in small fibre neuropathy. Brain 135:2613–2628. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws187
Hassan MQ, Maeda Y, Taipaleenmaki H, Zhang W, Jafferji M, Gordon JAR, Li Z, Croce CM, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2012) miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem 287:42084–42092
He X, Dong Y, Wu CW, Zhao Z, Ng SS et al. (2013) MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol Med 18:1491-1498 doi:https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2012.00304
Hecker N, Seemann SE, Silahtaroglu A, Ruzzo WL, Gorodkin J (2017) Associating transcription factors and conserved RNA structures with gene regulation in the human brain. Sci Rep 7:5776. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06200-4
Heo DN, Acquah N, Kim J, Lee SJ, Castro NJ et al (2018) Directly induced neural differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells using three-dimensional culture system of conductive microwell with electrical stimulation. Tissue Eng A 24:537–545. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2017.0150
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T et al (2004) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131:2791–2801
Hu F, Sun B, Xu P, Zhu Y, Meng X-H et al (2017) MiR-218 induces neuronal differentiation of ASCs in a temporally sequential manner with fibroblast growth factor by regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7:39427
Inestrosa NC, Varela-Nallar L (2015) Wnt signalling in neuronal differentiation and development. Cell Tissue Res 359:215–223
Iwamoto N, Fukui S, Takatani A, Shimizu T, Umeda M et al (2018) Osteogenic differentiation of fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis is induced by microRNA-218 through a ROBO/slit pathway. Arthritis Res Ther 20:189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1703-z
Jalali H, Parivar K, Soleimani M, Nabiuni M, Aghaee-Bakhtiari H (2016) Ex-vivo gene therapy using lentiviral mediated gene transfer into umbilical cord blood derived stem cells. Zahedan J Res Med Sci 18:e5991. https://doi.org/10.17795/zjrms-5991
Kiefer K, Clement J, Garidel P, Peschka-Suss R (2004) Transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity of nonviral gene transfer reagents in human smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Pharm Res 21:1009–1017
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S (2019) miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D155–d162. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1141
Lange C, Mix E, Rateitschak K, Rolfs A (2006) Wnt signal pathways and neural stem cell differentiation. Neurodegen Dis 3:76–86
Lee AS, De Jesús-Cortés H, Kabir ZD, Knobbe W, Orr M et al. (2016) The neuropsychiatric disease-associated gene cacna1c mediates survival of young hippocampal neurons. eNeuro 3:ENEURO.0006-0016.2016 https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0006-16.2016
Marei HES, El-Gamal A, Althani A, Afifi N, Abd-Elmaksoud A et al (2018) Cholinergic and dopaminergic neuronal differentiation of human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol 233:936–945. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25937
Mastrangelo M, Scheffer IE, Bramswig NC, Nair LD, Myers CT et al (2016) Epilepsy in KCNH1-related syndromes epileptic disorders. Int Epilepsy J Videotape 18:123–136. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2016.0830
McGinley L, McMahon J, Strappe P, Barry F, Murphy M, O'Toole D, O'Brien T (2011) Lentiviral vector mediated modification of mesenchymal stem cells & enhanced survival in an in vitro model of ischaemia. Stem Cell Res Ther 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt53
Moore TJ, Abrahamse H (2014) Neuronal differentiation of adipose derived stem cells: progress so far. Int J Photoenergy 2014:8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/827540
Moradi S, Asgari S, Baharvand H (2014) Concise review: harmonies played by microRNAs in cell fate reprogramming. Stem Cells 32:3–15
Muroyama Y, Kondoh H, Takada S (2004) Wnt proteins promote neuronal differentiation in neural stem cell culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:915–921
Naderi M, Tehrani H, Soleimani M, Shabani I, Hashemi SM (2014) A home-brew real-time PCR assay for reliable detection and quantification of mature miR-122. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 23. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000125
Nafissi S, Kazemi H, Tiraihi T, Beladi-Moghadam N, Faghihzadeh S et al (2016) Intraspinal delivery of bone marrow stromal cell-derived neural stem cells in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a safety and feasibility study. J Neurol Sci 362:174–181
Nasser M, Ballout N, Mantash S, Bejjani F, Najdi F et al (2018) Transplantation of embryonic neural stem cells and differentiated cells in a controlled cortical impact (CCI) model of adult mouse somatosensory cortex. Front Neurol 9:895
Naujock M, Stanslowsky N, Reinhardt P, Sterneckert J, Haase A et al (2014) Molecular and functional analyses of motor neurons generated from human cord-blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 23:3011–3020. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2014.0180
Nazir FH, Becker B, Brinkmalm A, Höglund K, Sandelius Å et al (2018) Expression and secretion of synaptic proteins during stem cell differentiation to cortical neurons. Neurochem Int 121:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2018.10.014
Nguyen LH, Diao HJ, Chew SY (2015) MicroRNAs and their potential therapeutic applications in neural tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 88:53–66
Nishioka M, Shimada T, Bundo M, Ukai W, Hashimoto E et al (2013) Neuronal cell-type specific DNA methylation patterns of the Cacna1c gene. Int J Dev Neurosci 31:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.11.007
Peng S, Zhou Y-L, Song Z-Y, Lin S (2017, 2017) Effects of neuropeptide Y on stem cells and their potential applications in disease therapy. Stem Cells Int
Qian DX, Zhang HT, Ma X, Jiang XD, Xu RX (2010) Comparison of the efficiencies of three neural induction protocols in human adipose stromal cells. Neurochem Res 35:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-0101-y
Salmon P, Trono D (2007) Production and titration of lentiviral vectors current protocols in human genetics. Chapter 12:Unit 12.10 https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142905.hg1210s54
Sasaki R, Aoki S, Yamato M, Uchiyama H, Wada K et al (2010) A protocol for immunofluorescence staining of floating neurospheres. Neurosci Lett 479:126–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.05.042
Segev A, Garcia-Oscos F, Kourrich S (2016) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in brain slices. J Visual Exp:54024. https://doi.org/10.3791/54024
Sensenbrenner M, Lucas M, Deloulme J-C (1997) Expression of two neuronal markers, growth-associated protein 43 and neuron-specific enolase, in rat glial cells. J Mol Med 75:653–663
Song J-L, Zheng W, Chen W, Qian Y, Ouyang Y-M et al (2017) Lentivirus-mediated microRNA-124 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes the repair of spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Mol Med 49:e332–e332
Sun P, Liu DZ, Jickling GC, Sharp FR, Yin K-J (2018) MicroRNA-based therapeutics in central nervous system injuries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38:1125–1148
Terashima M, Kobayashi M, Motomiya M, Inoue N, Yoshida T et al (2010) Analysis of the expression and function of BRINP family genes during neuronal differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cells. J Neurosci Res 88:1387–1393
Thiebes KP, Nam H, Cambronne XA, Shen R, Glasgow SM et al (2015) miR-218 is essential to establish motor neuron fate as a downstream effector of Isl1-Lhx3. Nat Commun 6:7718. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8718
Tomasoni R, Repetto D, Morini R, Elia C, Gardoni F et al (2013) SNAP-25 regulates spine formation through postsynaptic binding to p140Cap. Nat Commun 4:2136. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3136
Upadhya D, Hattiangady B, Castro OW, Shuai B, Kodali M et al (2019) Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived MGE cell grafting after status epilepticus attenuates chronic epilepsy and comorbidities via synaptic integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1814185115
Uzbas F, May ID, Parisi AM, Thompson SK, Kaya A et al (2015) Molecular physiognomies and applications of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Rev 11:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9578-0
Venkataraman S, Birks DK, Balakrishnan I, Alimova I, Harris PS, Patel PR, Handler MH, Dubuc A, Taylor MD, Foreman NK, Vibhakar R (2013) MicroRNA 218 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting multiple cancer phenotype-associated genes in medulloblastoma. J Biol Chem 288:1918–1928. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.396762
Wang W, Wang F, Liu J, Zhao W, Zhao Q, He M, Qian BJ, Xu Y, Liu R, Liu SJ, Liu W, Liu J, Zhou XF, Wang TH (2014) SNAP25 ameliorates sensory deficit in rats with spinal cord transection. Mol Neurobiol 50:290–304
Wang Q, Wang Y, Ji W, Zhou G, He K et al (2015) SNAP25 is associated with schizophrenia and major depressive disorder in the Han Chinese population. J Clin Psychiatry 76:e76–e82. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.13m08962
Xin H, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang X, Shang X et al (2013) MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched extracellular particles. Stem Cells 31:2737–2746
Yoshimura K, Shigeura T, Matsumoto D, Sato T, Takaki Y et al (2006) Characterization of freshly isolated and cultured cells derived from the fatty and fluid portions of liposuction aspirates. J Cell Physiol 208:64–76
Zhang HT, Luo J, Sui LS, Ma X, Yan ZJ et al (2009) Effects of differentiated versus undifferentiated adipose tissue-derived stromal cell grafts on functional recovery after spinal cord contusion. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9424-0
Zhang Y, Wang J, Huang W, Cai J, Ba J et al (2018) Nuclear nestin deficiency drives tumor senescence via lamin A/C-dependent nuclear deformation. Nat Commun 9:3613–3613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05808-y
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the help and advice of the laboratory members at Stem Cell Technology Research Center, Tehran, Iran.
Funding
The project was funded by Tarbiat Modares University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Taki Tiraihi; formal analysis: Wissam Khalil; investigation: Wissam Khalil; methodology: Wissam Khalil; project administration: Taki Tiraihi; resources: Masoud Soleimani and Nafiseh Baheiraei; supervision: Taki Tiraihi; validation: Taki Tiraihi, Masoud Soleimani, and Kazem Zibara; visualization: Wissam Khalil; writing—original draft: Wissam Khalil; writing—review and editing: Taki Tiraihi, Kazem Zibara, and Nafiseh Baheirae.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All the applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The protocols performed in this study were approved by the ethical committee of the Faculty of Medical Sciences at Tarbiat Modares University (IRB NO. IR.TMU.REC.1394.279), and the experiments were done according to the principles expressed in the declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalil, W., Tiraihi, T., Soleimani, M. et al. Conversion of Neural Stem Cells into Functional Neuron-Like Cells by MicroRNA-218: Differential Expression of Functionality Genes. Neurotox Res 38, 707–722 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00244-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00244-7