Abstract
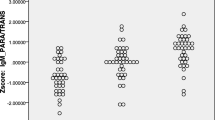
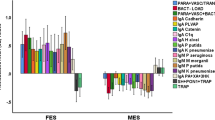
Increased gut permeability (leaky gut) with increased translocation of Gram-negative bacteria plays a role in the gut-brain axis through effects on systemic immune-inflammatory processes. Deficit schizophrenia is characterized by an immune-inflammatory response combined with a deficit in natural IgM antibodies to oxidative-specific epitopes (OSEs), which are a first-line defense against bacterial infections. This study measured plasma IgA/IgM responses to 5 Gram-negative bacteria in association with IgM responses to malondialdehyde (MDA) and azelaic acid in 80 schizophrenia patients (40 with the deficit syndrome and 40 without) and in 38 healthy controls. Deficit schizophrenia was characterized by significantly increased IgA responses to Hafnei alvei, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Morganella morganii, and Klebsiella pneumoniae as compared with non-deficit schizophrenia. The presence of deficit schizophrenia was highly predicted by increased IgA responses to Pseudomonas putida and IgM responses to all five Gram-negative bacteria and lowered natural IgM to MDA and azelaic acid with a bootstrap area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.960 (2000 random curves). A large proportion of the variance (41.5%) in the negative subscale score of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale was explained by the regression on IgA responses to K. pneumoniae and IgM responses to the five enterobacteria coupled with lowered IgM antibodies to azelaic acid. There were significant associations between IgA levels to Gram-negative bacteria and Mini-Mental State Examination, Boston naming test, Verbal Fluency, and Word List Memory test scores. These findings provide further evidence that deficit schizophrenia is a distinct phenotype of schizophrenia, which is characterized by an increased impact of Gram-negative commensal bacteria coupled with a deficit in natural IgM, pointing to aberrations in B1 cells. It is concluded that increased bacterial translocation and deficits in the compensatory immune-regulatory system (CIRS) may drive negative symptoms and neurocognitive impairments, which are hallmarks of deficit schizophrenia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand D, Chaudhuri A (2016) Bacterial outer membrane vesicles: new insights and applications. Mol Membr Biol 33:125–137
Anderson G, Maes M (2013) Schizophrenia: linking prenatal infection to cytokines, the tryptophan catabolite (TRYCAT) pathway, NMDA receptor hypofunction, neurodevelopment and neuroprogression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 42:5–19
Arai H, Furuya T, Yasuda T, Miura M, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2004) Neurotoxic effects of lipopolysaccharide on nigral dopaminergic neurons are mediated by microglial activation, interleukin-1beta, and expression of caspase-11 in mice. J Biol Chem 279:51647–51653
Aziz M, Holodick NE, Rothstein TL, Wang P (2015) The role of B-1 cells in inflammation. Immunol Res 63:153–166
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 57:289–300
Binder CJ (2012) Naturally occurring IgM antibodies to oxidation-specific epitopes. Adv Exp Med Biol 750:2–13
Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Tóth M, Korecka A, Bakocevic N, Ng LG, Kundu P, Gulyás B, Halldin C, Hultenby K, Nilsson H, Hebert H, Volpe BT, Diamond B, Pettersson S (2014) The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med 6(263):263ra158
Cepeda-Carrion GA, Nitzl C, Roldan JL (2018) Mediation analyses in partial least squares structural equation modeling: guidelines and empirical examples. Chapter 9. Partial least squares structural equation modeling: basic concepts, methodological issues and applications. In: Latan H, Noonan R (eds) . Springer, Heidelberg, pp 173–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64069-3_8
CERAD (1986) CERAD—an overview: the consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s disease. https://sites.duke.edu/centerforaging/cerad/. Accessed 7 Dec 2018
Chan ED, Riches DW (2001) IFN-gamma + LPS induction of iNOS is modulated by ERK, JNK/SAPK, and p38(mapk) in a mouse macrophage cell line. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 280:C441–C450
Check J, Byrd CL, Menio J, Rippe RA, Hines IN, Wheeler MD (2010) Src kinase participates in LPS-induced activation of NADPH oxidase. Mol Immunol 47(4):756–762
Davis J, Moylan S, Harvey BH, Maes M, Berk M (2014) Neuroprogression in schizophrenia: pathways underpinning clinical staging and therapeutic corollaries. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 48:512–529
Davis J, Eyre H, Jacka FN, Dodd S, Dean O, McEwen S, Debnath M, McGrath J, Maes M, Amminger P, McGorry PD, Pantelis C, Berk M (2016) A review of vulnerability and risks for schizophrenia: beyond the two hit hypothesis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 65:185–194
Díaz-Zaragoza M, Hernández-Ávila R, Viedma-Rodríguez R, Arenas-Aranda D, Ostoa-Saloma P (2015) Natural and adaptive IgM antibodies in the recognition of tumor-associated antigens of breast cancer (review). Oncol Rep 34:1106–1114
Ellis TN, Kuehn MJ (2010) Virulence and immunomodulatory roles of bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:81–94
Ellis TN, Leiman SA, Kuehn MJ (2010) Naturally produced outer membrane vesicles from Pseudomonas aeruginosa elicit a potent innate immune response via combined sensing of both lipopolysaccharide and protein components. Infect Immun 78:3822–3831
Grigoleit JS, Kullmann JS, Wolf OT, Hammes F, Wegner A, Jablonowski S, Engler H, Gizewski E, Oberbeck R, Schedlowski M (2011) Dose-dependent effects of endotoxin on neurobehavioral functions in humans. PLoS One 6(12):e28330
Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, Dobrzanski P, Stoehr JD, Wenk GL (1998) Chronic neuroinflammation in rats reproduces components of the neurobiology of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 780:294–303
Hoppe S, Bier FF, von Nickisch-Rosenegk M (2012) Microarray-based method for screening of immunogenic proteins from bacteria. J Nanobiotechnol 10:12
Kalayasiri R, Kraijak K, Mutirangura A, Maes M (2018) Paranoid schizophrenia and methamphetamine-induced paranoia are both characterized by a similar LINE-1 partial methylation profile, which is more pronounced in paranoid schizophrenia. BioRxiv 403535. https://doi.org/10.1101/403535
Kanchanatawan B, Sriswasdi S, Thika S, Sirivichayakul S, Carvalho AF, Geffard M, Kubera M, Maes M (2018a) Deficit schizophrenia is a discrete diagnostic category defined by neuro-immune and neurocognitive features: results of supervised machine learning. Metab Brain Dis 33:1053–1067
Kanchanatawan B, Sriswasdi S, Thika S, Stoyanov D, Sirivichayakul S, Carvalho AF, Geffard M, Maes M (2018b) Towards a new classification of stable phase schizophrenia into major and simple neuro-cognitive psychosis: results of unsupervised machine learning analysis. J Eval Clin Pract 24:879–891
Kanchanatawan B, Thika S, Sirivichayakul S, Carvalho AF, Geffard M, Maes M (2018c) In schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, and physiosomatic symptoms are strongly related to psychotic symptoms and excitation, impairments in episodic memory, and increased production of neurotoxic tryptophan catabolites: a multivariate and machine learning study. Neurotox Res 33:641–655
Kaparakis-Liaskos M, Ferrero RL (2015) Immune modulation by bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol 15:375–387
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Kirkpatrick B, Buchanan RW, McKenney PD, Alphs LD, Carpenter WT Jr (1989) The schedule for the deficit syndrome: an instrument for research in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 30:119–123
Kittirathanapaiboon P, Khamwongpin M (2005) The validity of the mini international neuropsychiatric interview (M.I.N.I.) Thai version. J Mental Health Thail 13(3):125–135
Kwa SF, Beverley P, Smith AL (2006) Peyer's patches are required for the induction of rapid Th1 responses in the gut and mesenteric lymph nodes during an enteric infection. J Immunol 176:7533–7541
Lewis CE, McCarthy SP, Lorenzen J, McGee JO (1990) Differential effects of LPS, IFN-gamma and TNF alpha on the secretion of lysozyme by individual human mononuclear phagocytes: relationship to cell maturity. Immunology 69:402–408
Lin WN, Lin CC, Cheng HY, Yang CM (2011) Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 gene expression by lipopolysaccharide through the RNA-binding protein HuR: involvement of NADPH oxidase, reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Br J Pharmacol 163(8):1691–1706
Lucas K, Maes M (2013) Role of the toll like receptor (TLR) radical cycle in chronic inflammation: possible treatments targeting the TLR4 pathway. Mol Neurobiol 48:190–204
Maes M, Carvalho AF (2018) The compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in depression and bipolar disorder. Mol Neurobiol 55:8885–8903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1016-x
Maes M, Bosmans E, Ranjan R, Vandoolaeghe E, Meltzer HY, De Ley M, Berghmans R, Stans G, Desnyder R (1996) Lower plasma CC16, a natural anti-inflammatory protein, and increased plasma interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in schizophrenia: effects of antipsychotic drugs. Schizophr Res 21:39–50
Maes M, Bosmans E, Kenis G, De Jong R, Smith RS, Meltzer HY (1997a) In vivo immunomodulatory effects of clozapine in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 26:221–225
Maes M, Delange J, Ranjan R, Meltzer HY, Desnyder R, Cooremans W, Scharpé S (1997b) Acute phase proteins in schizophrenia, mania and major depression: modulation by psychotropic drugs. Psychiatry Res 66:1–11
Maes M, Mihaylova I, Leunis JC (2007) Increased serum IgA and IgM against LPS of enterobacteria in chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS): indication for the involvement of gram-negative enterobacteria in the etiology of CFS and for the presence of an increased gut-intestinal permeability. J Affect Disord 99:237–240
Maes M, Kubera M, Leunis JC (2008) The gut-brain barrier in major depression: intestinal mucosal dysfunction with an increased translocation of LPS from gram negative enterobacteria (leaky gut) plays a role in the inflammatory pathophysiology of depression. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 29:117–124
Maes M, Twisk FN, Kubera M, Ringel K, Leunis JC, Geffard M (2012) Increased IgA responses to the LPS of commensal bacteria is associated with inflammation and activation of cell-mediated immunity in chronic fatigue syndrome. J Affect Disord 136:909–917
Maes M, Kubera M, Leunis JC, Berk M, Geffard M, Bosmans E (2013a) In depression, bacterial translocation may drive inflammatory responses, oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS), and autoimmune responses directed against O&NS-damaged neoepitopes. Acta Psychiatr Scand 127:344–354
Maes M, Ringel K, Kubera M, Anderson G, Morris G, Galecki P, Geffard M (2013b) In myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, increased autoimmune activity against 5-HT is associated with immuno-inflammatory pathways and bacterial translocation. J Affect Disord 150:223–230
Maes M, Kanchanatawan B, Sirivichayakul S, Carvalho AF (2018) In Schizophrenia, low natural IgM antibody titers to oxidative specific epitopes and higher IgM responses to Nitrated and nitrosylated proteins strongly predict negative symptoms, neurocognitive impairments and the deficit syndrome. Preprints 2018100083. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints201810.0083.v2)
McMahon M, Skaggs B (2016) Autoimmunity: do IgM antibodies protect against atherosclerosis in SLE? Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:442–444
Meyer U (2014) Prenatal poly(i:C) exposure and other developmental immune activation models in rodent systems. Biol Psychiatry 75:307–315
Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B (2011) Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 70:663–671
Muraca M, Putignani L, Fierabracci A, Teti A, Perilongo G (2015) Gut microbiota-derived outer membrane vesicles: under-recognized major players in health and disease? Discov Med 19:343–348
Noto MN, Maes M, Nunes SO, Ota VK, Rossaneisf AC, Verri Jr WA, Cordeiro Q, Belangero SI, Gadelha A, Bressan RA, Noto C (2018) Activation of the immune-inflammatory response system and the compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system in antipsychotic naive first episode psychosis. Preprints Preprints2018090314.v2
O'Dwyer DN, Dickson RP, Moore BB (2016) The lung microbiome, immunity, and the pathogenesis of chronic lung disease. J Immunol 196:4839–4847
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Pai K, Sodhi A (1991) Effect of cisplatin, rIFN-Y, LPS and MDP on release of H2O2, O2- and lysozyme from human monocytes in vitro. Indian J Exp Biol 29:910–915
Pasternak BA, d'Mello S, Jurickova II, Han X, Willson T, Flick L, Petiniot L, Uozumi N, Divanovic S, Traurnicht A, Bonkowski E, Kugathasan S, Karp CL, Denson LA (2010) Lipopolysaccharide exposure is linked to activation of the acute phase response and growth failure in pediatric Crohn's disease and murine colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16:856–869
Peng T, Lu X, Feng Q (2005) NADH oxidase signaling induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression during lipopolysaccharide stimulation in cardiomyocytes. FASEB J 19:293–295
Ringle CM, da Silva D, Bido D (2014) Structural equation modeling with the SmartPLS. Braz J Mark 13(2)
Roomruangwong C, Kanchanatawan B, Sirivichayakul S, Anderson G, Carvalho AF, Duleu S, Geffard M, Maes M (2017, 2017) IgA/IgM responses to gram-negative bacteria are not associated with perinatal depression, but with physio-somatic symptoms and activation of the tryptophan catabolite pathway at the end of term and postnatal anxiety. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527316666170407145533
Roomruangwong C, Barbosa DS, de Farias CC, Matsumoto AK, THL B, Morelli NR, Kanchanatawan B, Duleu S, Geffard M, Maes M (2018a) Natural regulatory IgM-mediated autoimmune responses directed against malondialdehyde regulate oxidative and nitrosative pathways and coupled with IgM responses to nitroso adducts attenuate depressive and physiosomatic symptoms at the end of term pregnancy. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 72:116–130
Roomruangwong C, Noto C, Kanchanatawan B, Anderson G, Kubera M, Carvalho AF, Maes M (2018b) The role of aberrations in the immune-inflammatory response system (IRS) and the compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in different phenotypes of schizophrenia: the IRS-CIRS theory of schizophrenia. Preprint. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints201809.0289.v1
Rothstein TL, Griffin DO, Holodick NE, Quach TD, Kaku H (2013) Human B-1 cells take the stage. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1285:97–114
Shen Y, Giardino Torchia ML, Lawson GW, Karp CL, Ashwell JD, Mazmanian SK (2012) Outer membrane vesicles of a human commensal mediate immune regulation and disease protection. Cell Host Microbe 12:509–520
Sirivichayakul S, Kanchanatawan B, Thika S, Carvalho AF, Maes M (2018a) Eotaxin, an endogenous cognitive deteriorating chemokine (ECDC), is a major contributor to cognitive decline in Normal people and to executive, memory, and sustained attention deficits, formal thought disorders, and psychopathology in schizophrenia patients. Neurotox Res 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9937-8
Sirivichayakul S, Kanchanatawan B, Thika S, Carvalho A, Maes M (2018b) A new schizophrenia model: immune activation is associated with induction of the tryptophan catabolite pathway and increased eotaxin levels which together determine memory impairments and schizophrenia symptom dimensions. BioRxiv 393173. https://doi.org/10.1101/393173
Skelly DT, Griffin ÉW, Murray CL, Harney S, O'Boyle C, Hennessy E, Dansereau MA, Nazmi A, Tortorelli L, Rawlins JN, Bannerman DM, Cunningham C (2018) Acute transient cognitive dysfunction and acute Brain Inj induced by systemic inflammation occur by dissociable IL-1-dependent mechanisms. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0075-8
Smith RS, Maes M (1995) The macrophage-T-lymphocyte theory of schizophrenia: additional evidence. Med Hypotheses 45:135–141
Thiagarajan D, Frostegård AG, Singh S, Rahman M, Liu A, Vikström M, Leander K, Gigante B, Hellenius ML, Zhang B, Zubarev RA, de Faire U, Lundström SL, Frostegård J (2016) Human IgM antibodies to malondialdehyde conjugated with albumin are negatively associated with cardiovascular disease among 60-year-olds. J Am Heart Assoc 20(5):12
Todar K (2018) Todar’s online textbook of bacteriology. http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/. Accessed 11 Dec 2018
Valero J, Mastrella G, Neiva I, Sánchez S, Malva JO (2014) Long-term effects of an acute and systemic administration of LPS on adult neurogenesis and spatial memory. Front Neurosci 8:83
Weismann D, Binder CJ (2012) The innate immune response to products of phospholipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:2465–2475
Wiest R (2005) Bacterial translocation. Biosci Microflora 24:61–90
Xu Y, Zhou H, Zhu Q (2017) The impact of microbiota-gut-brain Axis on diabetic cognition impairment. Front Aging Neurosci 9:106
Zakaria R, Wan Yaacob WM, Othman Z, Long I, Ahmad AH, Al-Rahbi B (2017) Lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in rats: a model of Alzheimer's disease. Physiol Res 66:553–565
Zhu F, Zheng Y, Ding YQ, Liu Y, Zhang X, Wu R, Guo X, Zhao J (2014) Minocycline and risperidone prevent microglia activation and rescue behavioral deficits induced by neonatal intrahippocampal injection of lipopolysaccharide in rats. PLoS One 9(4):e93966
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Asahi Glass Foundation, Chulalongkorn University Centenary Academic Development Project, and Ratchadapiseksompotch Funds, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, grant numbers RA60/042 (to BK) and RA61/050 (to MM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the contributing authors have participated in the manuscript. MM and BK designed the study. BK recruited patients and completed diagnostic interviews and rating scale measurements. MM carried out the statistical analyses. All authors (BK, MM, SS, and AC) contributed to interpretation of the data and writing of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maes, M., Kanchanatawan, B., Sirivichayakul, S. et al. In Schizophrenia, Increased Plasma IgM/IgA Responses to Gut Commensal Bacteria Are Associated with Negative Symptoms, Neurocognitive Impairments, and the Deficit Phenotype. Neurotox Res 35, 684–698 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9987-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9987-y