Abstract
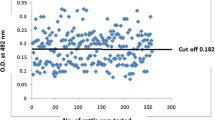
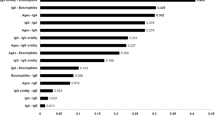
The present study was performed to compare the soluble, whole and excretory/secretary antigens of Toxoplasma gondii (RH strain) in diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by ELISA method. Tachyzoites of T. gondii, RH strain were injected in intra-peritoneal cavity of BALB/c mice, after 4 days tachyzoites were harvested by peritoneal washing of the mice. For soluble antigen, exudates were centrifuged and sediment sonicated and then centrifuged at 4 °C, 1 h, supernatant collected and density of protein determined by Bradford method. For whole antigen after collecting, washing and centrifuging of peritoneal fluid the tachyzoites sediment was counted. In excretory/secretary antigen 1.5 × 108 tachyzoites were transferred in 1 ml tube of saline and incubated under mild agitation and after centrifuging, supernatant was collected and protein density determined by Bradford method. 176 human serum samples were evaluated for T. gondii IgG antibody with prepared antigens, and finally serum samples were evaluated by commercial ELISA kit (Trinity, USA) which was considered as gold standard method. In this study sensitivity and specificity of prepared antigens compared with commercial kit in ELISA method. Sensitivity and specificity of soluble antigen was 91.4 and 74.5 %, in whole antigen these parameters were 77.1 and 77.3 % and in excretory/secretary antigen were 28.5 and 74.5 % respectively. Soluble antigen had high levels of sensitivity and specificity in ELISA method and the results were rather resemble to commercial kit (Trinity, USA).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyle JP, Radke JR (2009) A history of studies that examine the interactions of Toxoplasma with its host cell: emphasis on in vitro models. Int J Parasitol 39(8):903–914
Candolfi E, Pastor R, Huber R, Filisetti D, Villard O (2007) IgG avidity assay firms up the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis on the first serum sample in immunocompetent pregnant women. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 58:83–88
Chen R, Lu S, Lou D, Lin A, Zeng X, Ding Z, Wen L, Ohta N, Wang J, Fu C (2008) Evaluation of a rapid ELISA technique for detection of circulating antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol Immunol 52:180–187
Dubey JP (2010) Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Grant IH, Gold WM, Rosenblum M, Niedzwieki D, Armstrong D (1990) Toxoplasma gondii serology in HIV infected patients: the development of central nervous system toxoplasmosis in AIDS. AIDS 4:519–521
Hafid J, Raberin H, Tran Manh Sung R (2001) Comparison of PCR, capture-ELISA and immunoblotting for detection of Toxoplasm gondii in infected mice. J Med Microbiol 50:1100–1104
Montoya J, Liesenfeld O (2004) Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 363(9425):1965–1976
Rahbari AH, Keshavarz H, Shojaee S, Mohebali M, Rezaeian M (2012) IgG avidity ELISA test for diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis in humans. Korean J Parasitol 50:99–102
Remington JS, Thulliez P, Montoya JG (2004) Recent developments for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol 42:941–945
Silva NM, Lourenco EV, Silva DAO, Mineo JR (2002) Optimization of cut-off titres in Toxoplasma gondii specific ELISA and IFAT in dog sera using immunoreactivity to SAG-1 antigens as a molecular marker of infection. Vet J 163:94–98
Son ES, Nam HW (2001) Detection and characterization of secretory/excretory proteins of Toxoplasma gondii by monoclonal antibodies. Korean J Parasitol 39:49–56
Weiss LM, Dubey JP (2009) Toxoplasmosis: a history of clinical observations. Int J Parasitol 39(8):895–901
Yamamoto YI, Mineo JR, Meneghisse CS, Guimaraes AC, Kawarabayashi M (1998) Detection in human sera of IgM, IgG, and IgA, to excreted/secreted antigens from Toxoplasma gondii by use of dot -ELISA and immunoblot assay. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 92(1):23–30
Acknowledgments
This study has done as MSPH thesis and the authors gratefully acknowledge the school of Public Health of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pishkari, S., Shojaee, S., Keshavarz, H. et al. Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii soluble, whole and excretory/secretary antigens for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by ELISA test. J Parasit Dis 41, 289–291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0794-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0794-1