Abstract
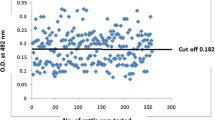
The diagnosis of Trypanosoma evansi in animals with low parasitaemia is hampered by low diagnostic sensitivity of traditional detection methods. The present study was undertaken with an objective to improve the diagnostic tools for detection of antibodies against T. evansi infection using indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in bovines. The optimum concentration of antigen, test sera and conjugate were determined as 5 µg per well, 1:10 and 1: 6,000 dilutions, respectively. Among 320 cattle and 382 buffaloes examined in different parts of Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh for T. evansi infection, 36.12 and 31.87 percent were found positive by indirect ELISA, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baghel AK, Manohar GS, Kumar D, Bhan AK (1996) Comparative evaluation of various parasitological and immunodiagnostic techniques in buffalo calves experimentally infected with Trypanosoma evansi. J Vet Parasitol 10:39–45
Desquesnes M, Bossard G, Thevenon S, Patrel O, Lepetitcolin E, Hollzmuller P, Berthier D, Jacquiet P, Cuny G (2009) Development and application of an antibody-ELISA to follow up a Trypanosoma evansi outbreak in a dromedary camel herd in France. Vet Parasitol 162:214–220
Jithendran KP, Rao JR, Mishra AK (1997) Evaluation of antigenic preparations for the diagnosis of experimental Trypanosoma evansi infection in bovine calves. J Vet Parasitol 11(1):17–21
Lanham SM, Godfrey GD (1970) Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other animals using DEAE- cellulose. Exp Parasitol 28:521–534
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall R (1951) Protein estimation with the folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Molina JM, Ruiz A, Juste MC, Corbera JA, Amador R, Gutierrez C (2000) Seroprevalence of Trypanosoma evansi in dromedaries (Camelus dromedarius) from the Canary Islands (Spain) using an antibody Ab-ELISA. Prev Vet Med 47:53–59
O.I.E., Deborah Surra E (2004) Trypanosoma evansi. In: Deborah E (ed) Manual of standards for diagnostic tests and vaccines, 5th edn. Office International des Epizooties, Paris, pp 891–900
Shahardar RA, Rao JR, Mishra AK, Tewari AK (2008) Detection of antibodies against Trypanosoma evansi in dromedary camels by ELISA using purified antigens. J Vet Parasitol 22(2):47–51
Singh V, Chhabra MB (1993) Counter immune-electrophoresis for rapid detection of circulating antigens of Trypanosoma evansi. Indian J Anim Sci 63(6):625–627
Singh V, Singh A, Chhabra MB (1994) Polypeptide profile of whole cell lysate of Trypanosoma evansi stocks from northern India. Indian J Anim Sci 64:14–17
Sinha BS, Verma SP, Mallik KP, Samantary S, Kumar B, Kumar RP (2006) Study on epidemiological aspects of bovine Trypanosomiasis in some districts of Bihar. J Vet Parasitol 20(1):69–71
Sivajothi S, Rayulu VC, Sujatha K, Sudhakara Reddy B, Amaravathi P (2013a) Histopathological observations in rabbits experimentally infected with Trypanosoma evansi. J Adv Vet Res 3:122–126
Sivajothi S, Rayulu VC, Malakondaiah P, Sreenivasulu D (2013b) Colloidal dye immunobinding assay for detection of Trypanosoma evansi antibodies in Animals. Int J Livest Res 3(3):48–56
Sivajothi S, Rayulu VC, Sudhakara Reddy B (2013c) Haematological and biochemical changes in experimental Trypanosoma evansi infection in rabbits. J Parasit Dis 37(2):173–176. doi:10.1007/s12639-013-0321-6
Verloo D, Holland W, My LN, Thanh NG, Tam PT, Goddeeris B, Vercruysse J, Busher P (2000) Comparison of serological tests for Trypanosoma evansi natural infections is water buffaloes from north Vietnam. Vet Parasitol 92:87–96
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the authorities of Sri Venkateswara Veterinary University, Tirupati for providing facilities to carry out this research. Authors are also thankful to the field veterinarians who assisted in collection of blood samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivajothi, S., Rayulu, V.C., Malakondaiah, P. et al. Diagnosis of Trypanosoma evansi in bovines by indirect ELISA. J Parasit Dis 40, 141–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0465-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0465-z