Abstract
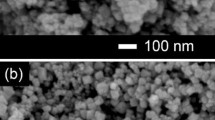
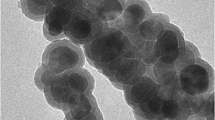
The essential goal of this work is to produce an eco-friendly and economically nano-adsorbent that may separate organic dye, especially, cationic dye, from polluted water prior to making use of this adsorbent in industrial field. This work suggests a way of fabricating magnetite and silica. The proposed approach concerned three steps: the preparation of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by co-precipitation method, then of silica using sodium silicate prepared from silica sand, and finally a magnetite coating of silica Fe3O4/SiO2. The nanocomposites were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The XRD characterization displayed that silica formed an amorphous phase and that magnetite shaped a spinel phase. To optimize the diverse experimental variables affecting the elimination performance of the CV, the effects of experimental parameters including solution pH, adsorbent dose, contact time, initial dye concentration and temperature were evaluated. Adsorption kinetic disclosed that pseudo-second-order is the best model (R2 > 0.99, qe = 5.68 mg g−1). Adsorption isotherm represented that Langmuir is the best model with Qmax = 200 mg g−1. The negative ΔH° and ΔG° values exhibited the exothermic and spontaneous nature of CV sorption on the nanoparticles, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information are available by request.
References
Zangeneh H, Zinatizadeh AAL, Habib M, Akia M, Hasnain Isa M (2015) Photo-catalytic oxidation of organic dyes and pollutants in waste water using different modified titanium dioxides: a comparatives review. J Ing Eng Chem 26:1–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.10.043
Roca AG, Morales MP, O'Grady K (2006) Structural and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite nanoparticles prepared by high temperature decomposition of organic precursors. Nanotechnol 17:2783–2788. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/11/010
Maity D, Choo SG, Yi J, Ding J, MinXue J (2009) Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles via a solvent-free thermal decomposition route. J MagnMagn Mater 321:1256–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.11.013
Salem ANM, Ahmed MA, El-Shahat MF (2016) Selective adsorption of amaranth dye onFe3O4/MgO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 219:780–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.03.084
Han X, Chu L, Liu S, Chen T, Ding C, Yan J, Cui L, Quan G (2015) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using porous biochar obtained by KOH activation of peanut shell biochar. Bio Resour 10:2836–2849. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.10.2.2836-2849
Joshiba GJ, Kumar PS, Christopher FC, Pooja G, Kumar VV (2020) Fabrication of novel amine-functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles for toxic metals: kinetic and isotherm modelling. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:27202–27210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05186-y
Ismail AM, Menazea AA, Ali H (2021) Selective adsorption of cationic azo dyes onto zeolite nanorod-based membranes prepared via laser ablation. J Mater Sci Electron 32:19352–19367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06453-w
Chaari I, Medhioub M, Jamoussi F, Hamzaoui AH (2020) Acid-treated clay materials (southwestern Tunisia) for removing sodium leuco-vat dye: characterization, adsorption study and activation mechanism. J Mol Struct 1223:128944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128944
Ghorbani F, Kamari S (2019) Core–shell magnetic nanocomposite of Fe3O4@SiO2@NH2 as an efficient and highly recyclable adsorbent of methyl red dye from aqueous environments. Environ Technol Innov 14:100333
Zhang Z, Kong J (2011) Novel magneticfe3O4@C nanoparticles as adsorbents for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 193:325–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.033
Hariani PL, Faizal M, Marsi R, Setiabudidaya D (2013) Synthesis and properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation method to removal Procion dye. Int J Environ Sci Dev 4. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJESD.2013.V4.366
Takai ZI, Mustafa MK, Asman S, Khairunnadim AS (2019) Preparation and characterization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by sol-gel method. In J Nanoelectron Mater 12:37–46
Ge S, Shi X, Sun K, Li C, Uher C, Baker JR, Banaszak Holl MM, Orr BG (2009) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Iron oxide nanoparticles with tunable magnetic properties. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interface 113:13593–13599. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp902953t
Morales F, Márquez G, Sagredo V, Torres TE, Denardin JC (2019) Structural and magnetic properties of silica-coated magnetite nanoaggregates. Phys B Condens Matter 572:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.08.007
Huang J, Liu W, Liang Y, Li L, Duan L, Chen J, Zhu F, Lai Y, Zhu W, You W, Jia Z, Xiong J, Wang D (2018) Preparation and biocompatibility of diphasic magnetic nanocomposite scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C 87:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.02.003
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew ChemInt EdEng 46:1222–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
Zhang L, Shao HP, Zheng H, Lin T, Guo ZM (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic composite nanoparticles by a one-pot process. Int J Miner Metall Matter 23:1112–1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1329-6
Lee HJ, Lu Q, Lee JY, Jin Choi H (2019) Polymer-MagneticCompositeParticles of Fe3O4/poly (o-anisidine) and their suspension characteristics under applied magnetic fields. Polym 11:219. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020219
Kakvandi B, Jonidi A, Kalantary RR (2013) Synthesis and Propertiesof Fe3O4-activated carbon magnetic nanoparticles for Remova lof aniline from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Irn J Environ Health Sci Eng 10:19
Shah KH, Ali S, Shah F (2018) Magnetic oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) impregnated bentonite clay as a potential adsorbent for Cr (III) adsorption. Mater Res Express 5:096102. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad50e
Ahmad ARD, Imam SS, Oh WD (2020) Fe3O4-zeolite hybrid material as hetero-Fenton catalyst for enhanced degradation of aqueous Ofloxacin solution. Catalysts 10:1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111241
Zhao Y, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang S, Huang Y, Wu X, Wang X (2014) Synthesis of amidoximme-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic for highly efficient sorptionof U(VI). Chem Eng J 235:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.034
Furlan PY, Furlan AY, Kisslinger K (2019) Water as the solvent in the Stober process for forming ultrafine silica shells on magnetite nanoparticles. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:15578–15584. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b03554
Taufiq A, Nikmah A, Hidayat A, Sunaryono S, Mufti N, Susanto N (2020) Synthesis of magnetite/silica from sand to create a delivery vehicle. Heliyon 6:e03784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03784
Huang C, Hu B (2008) Silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with γ- mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane for fast and selective solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Cd,Cu,Hg, and Pb in environmental and biological samples prior to their determination by inductively coupled plasma massspectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 63:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2007.12.010
Kakavandi B, Jahangiri-rad M, Rafiee M, Esfahani AR, Babaei AA (2016) Develpement of response surface methodology for optimization of pheneol and p-chlorophenol adsorption on magnetic recoverable carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 231:192–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.05.033
Grass RN, Athanassiou EK, Stark WJ (2007) Covalently functionalized cobalt nanoparticles as a platform for magnetic separations in organic synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:4909–4912. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200700613
Ding BJ, Chen WM, Fan LW, Zheng YH, Lv D, Lu ZX (2014) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic catalyst support. Inorg Chem Ind 46:62
Kazemzadeh H, Ataie A, Rashchi F (2012) In situ synthesis of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles by reverse Coprecipitation method. J Supercond Nov Magn 25:2803–2808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-011-1270-x
Yoshino H, Kamiya K, Nasu HIR (1990) Study on the structural evolution of sol-gel derived SiO2gels in the early stage of conversion to glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 126:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(90)91024-L
Hameed B, El-kaiary M (2008) Remval of basic dye from aqueous medium using a novel agricultural waste material. Pumpkin seed hullJ Hasard Mater 155:601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.102
Subhan F, Aslam S, Yan Z, Khan M, Etim UI, Naeem M (2019) Effective adsorptive performance of Fe3O4@SiO2 core shell spheres for methylene blue: kinetics,isotherm and mechanism. J Porous Mater 26:1465–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00744-8
Deng H, Lu J, Li G, Zang G, Wang X (2011) Adsorption of methylene blue on adsorbent materials produced from cotton stalk. Chem Eng J 172:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.06.013
Abu Auwal M, Hossen J, Rakib-uz-Zaman M (2018) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution using tamarind seed powder as adsorbent. J Env Sci Toxi Fod Tech 12:41–48. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-1203014148
Arnata W, Suprihatin FF, Richana N, Candra Sunarti T (2019) Adsorption of anionic Congo red dye by using cellulose from sago frond. Pollut Res 38:557–567
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-calledadsorption of substances Kungliga Svenska Vetenskaps akademiens. Handlingar Band 24:1–39
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0923-0467(98)00076-1
Langmuir I (1918) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-0032(17)90938-X
Freundlich HMF (1906) Uber die adsorption ilosungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Noori M, Tahmasebpoor M, Nami SH (2022) Adsorption removal of crystal violet in single and binary systems onto low-costiron oxide nanoparticles coated clinoptilolite powders/granules. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1727993/v1
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, El-Sonbati AZ, Hawas AR (2017) Magnetic alginate beads with high basic dye removal potential and excellent regeneration ability. Can J Chem 95:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2016-0641
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Peighambardoust SH, Pateiro M, Lorenzo JM (2021) Adsorption of CrystalViolet dye using activated carbon of Lemn wood and activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite from AqueousSolutions: a kinetic equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Mole 26:2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082241
Du Y, Pei M, He Y, Yu F, Guo W, Wang L (2014) Preparation, characterization and application of magnetic Fe3O4-CS for the adsorption of Orange I from aqueous solutions. PLoS One 9:e108647. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108647
Mohebali S, Bastani D, Shayesteh H (2019) Equilibrium kinetic and thermodynamic studies of a low-cost biosorbent for the removal of Congo red dye: acid and CTAB-acid modified celery Apium graveolens. J Mol Struct 1176:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.08.068
Scheufele FB, Staudt J, Ueda MH, Caroline R, Steffen V, Borba CE, M’odenes AN, Kroumov AD (2020) Biosorption of direct black dye by cassavaroot husks: Kinetics,equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism assessment. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103533
Alqadami AA, Naushad M, Abdalla MA, Khan MR, Alothman ZA (2016) Adsorptive removal of toxic dye using Fe3O4–TSC nanocomposite: equilibrium kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Chem Eng Data 61:3806–3813. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.6b00446
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Mr. Mounir Hajji from Centre National de Recherches en Sciences des Materiaux for his help with synthesis of sodium silicate.
Funding
The study was fnancially supported by National Center of Research in Material Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Andolsi Amal, Chaari Islem, Hamzaoui Ahmad Hichem: prepared the research, and interpret household survey data and wrote research report draft. Hamzaoui Ahmad Hichem, Chaari Islem: conceptualization and methodology. All authors edit and revised the manuscript and approved it to send to the journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have non relevant financial or non-financial to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Consent for Publications
All the authors of the manuscript mutually agree on submission and publication in the journal.
Consent to Participate All
Authors contributed to the work and revised the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Andolsi, A., Chaari, I. & Hamzaoui, A.H. Surface Modification of Magnetite Using Silica Coating: Spectroscopic, Structural, Morphological Characterization and Interaction with Crystal Violet Dye. Silicon 15, 6257–6268 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02488-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02488-2