Abstract
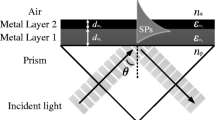
A prism coupler based plasmonic sensor consisting of a prism, gold (Au) metal film and dielectric sample has been investigated with the use of admittance loci method in wavelength interrogation mode. Prism materials namely fused silica, chalcogenide (2S2G) and silicon have been used to study their effect on surface plasmon sensing in wavelength interrogation mode by admittance loci plots and by corresponding surface plasmon sensing curves. The performance of the plasmonic sensor under wavelength interrogation mode based on the choice of the prism material has been discussed and validated by the dynamic range and sensitivity plots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otto A (1968) Excitation of nonradiative surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection. Z Phys 216:398–410
Kretschmann E, Raether H (1968) Radiative decay of non-radiative surface plasmons excited by light. Z Naturforsch 23A:2135–2136
Liedberg B, Nylander C, Lunström I (1983) Surface plasmon resonance for gas detection and biosensing. Sens Actuators 4:299–304
Homola J, Koudela I, Yee SS (1999) Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on diffraction gratings and prism couplers: sensitivity comparison. Sens Actuators B 54:16–24
Person Le J, Colas F, Compère C, Lehaitre M, Anne LM, Boussard-Plèdel C, Bureau B, Adam LJ, Deputier S, Guilloux-Viry M (2008) Surface plasmon resonance in chalcogenide glass-based optical system. Sens Actuators B 130:771–776
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2013) Modelling of chalcogenide glass based plasmonic structure for chemical sensing using near infrared light. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 124(21):5170–5176
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2013) Performance of admittance loci based design of plasmonic sensor at infrared wavelength. Opt Eng 52(8):087112-1-8
Palik DE (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic Press, New York
Patskovsky S, Kabashin VA, Meunier M, Luong THJ (2004) Near-infrared surface plasmon resonance sensing on a silicon platform. Sens Actuators B 97:409–414
Patskovsky S, Kabashin VA, Meunier M, Luong THJ (2003) Properties and sensing characteristics of surface plasmon resonance in infrared light. J Opt Soc Am A 20(8):1644–1650
Macleod AH (2010) Thin-Film Optical Filters, 4th edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, New York
Lin WC, Chen PK, Su CM, Lee KC, Yang CC (2005) Bio-plasmonics: Nano/micro structure of surface plasmon resonance devices for biomedicine. Opt Quantum Electron 37:1423–1437
Lin WC, Chen PK, Su CM, Hsiao CT, Lee SS, Lin S, Shi JX, Lee KC (2006) Admittance loci design method for multilayer surface plasmon resonance devices. Sens Actuators B 117:219– 229
Jen JY, Lakhtakia A, Yu WC, Chan YT (2009) Multilayered structures for p- and s-polarized long-range surface- plasmon-polariton propagation. J Opt Soc Am A 26(6):2600–2606
Brahmachari K, Ghosh S, Ray M (2013) Surface plasmon resonance based sensing of different chemical and biological samples using admittance loci method. Photonic Sens 3(2):159–167
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2013) Effect of prism material on design of surface plasmon resonance sensor by admittance loci method. Front Optoelectron 6(2):185–193, Brahmachari K, Ray M (2013) Erratum to: Effect of prism material on design of surface plasmon resonance sensor by admittance loci method. Front Optoelectron 6(1):353
Gupta G, Kondoh J (2007) Tuning and sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens Actuators B 122:381–388
Fontana E (2006) Thickness optimization of metal films for the development of surface-plasmon-based sensors for nonabsorbing media. Appl Opt 45(29):7632–7642
Sharma KA, Mohr JG (2008) On the performance of surface plasmon resonance based fibre optic sensor with different bimetallic nanoparticle alloy combinations. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:0551061-7
Sharma KN (2012) Performances of different metals in optical fiber-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Pramana J Phys 78(1):417–427
Shalabney A, Abdullahim I (2010) Electromagnetic fields distribution in multilayer thin film structures and the origin of sensitivity enhancement in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Sens Actuators A 159:24–32
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2013) Admittance loci based design of a plasmonic structure using Ag-Au bimetallic alloy film. ISRN Optics 2013:946832-1-7
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2014) Design of nanocomposite film based plasmonic device for gas sensing. (in press)
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2014) Effect of different plasmon active metals on admittance loci based design of a plasmonic sensor. Sens Imaging 15(1):89-1-13
Brahmachari K, Ray M (2014) Admittance loci based design of nanoplasmonic sensor using ceramic and chalcogenide materials. Sens. Actuators A 212:102–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brahmachari, K., Ray, M. Admittance Loci Based Design of Plasmonic Sensor Working in Wavelength Interrogation Regime. Silicon 8, 33–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-014-9219-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-014-9219-x