Abstract
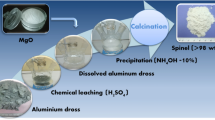
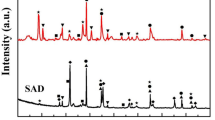
The feasibility of aluminum recovery from secondary aluminum dross by extraction with NaOH solution and the subsequent synthesis of MgAl2O4 spinel by sintering the extracted slag were studied. The extraction percentage of soluble aluminum from the dross reached 80% at a temperature of 353 K, liquid-to-solid ratio of 12 mL·g−1, stirring speed of 300 r·min−1, and an extraction time of 15 min; the hydrolysis percentage of AlN reached 40% with an extraction time of 30 min. The activation energies of the soluble aluminum and AlN extracted from the dross were 7.15 and 8.98 kJ·mol−1, respectively, indicating that their kinetics were controlled by outer diffusion without a product layer. The extracted slag was sintered in the temperature range 1373–1773 K; MgAl2O4 spinel with a compressive strength as high as 69.4 MPa was produced in the sample sintered at 1673 K for 3 h. This value exceeds the threshold (40 MPa) prescribed by the National Standard for the Magnesia and Magnesia−alumina Refractory Bricks of China (GB/T 2275–2007). These results establish the effectiveness of aluminum recovery from secondary aluminum dross and subsequent MgAl2O4 spinel synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Hong, J. Wang, H.Y. Chen, B.D. Sun, J.J. Li, and C. Chen, Process of aluminum dross recycling and life cycle assessment for Al-Si alloys and brown fused alumina, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 20(2010), No. 11, p. 2155.
A. López-Delgado, H. Tayibi, C. Pérez, F.J. Alguacil, and F.A. López, A hazardous waste from secondary aluminium metallurgy as a new raw material for calcium aluminate glasses, J. Hazard. Mater., 165(2009), No. 1–3, p. 180.
J.A.S. Tenorio and D.C.R. Espinosa, Effect of salt/oxide interaction on the process of aluminum recycling, J. Light Met., 2(2002), No. 2, p. 89.
P.E. Tsakiridis, Aluminum salt slag characterization and utilization-A review, J. Hazard. Mater., 217–218(2012), p. 3.
M.C. Shinzato and R. Hypolito, Solid waste from aluminum recycling process: characterization and reuse of its economically valuable constituents, Waste Manage., 25(2005), No. 1, p. 37.
P.E. Tsakiridis, P. Oustadakis, and S. Agatzini-Leonardou, Aluminum recovery during black dross hydrothermal treatment, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 1(2013), No. 1–2, p. 23.
G.V. Calder and T.D. Stark, Aluminum reactions and problems in municipal solid waste landfills, Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manage., 14(2010), No. 4, p. 258.
J.Y. Hwang, X. Huang, and Z. Xu, Recovery of metals from aluminum dross and salt cake, J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng., 5(2006), No. 1, p. 47.
B. Dash, B.R. Das, B.C. Tripathy, I.N. Bhattacharya, and S.C. Das, Acid dissolution of alumina from waste aluminum dross, Hydrometallurgy, 92(2008), No. 1–2, p. 52.
M. Davies, P. Smith, W.J. Bruckard, and J.T. Woodcock, Treatment of salt cakes by aqueous leaching and Bayer-type digestion, Miner. Eng., 21(2008), No. 8, p. 605.
K. Taehyung, K. Donghyun, and K. Shinhoo, Effect of additives on the sintering of MgAl2O4, J. Alloys Compd., 587(2014), p. 594.
H.N. Yoshimura, A.P. Abreu, A.L. Molisani, A.C. de Camargo, J.C.S. Portela, and N.E. Narita, Evaluation of aluminum dross waste as raw material for refractories, Ceram. Int., 34(2008), No. 3, p. 581.
F. Tavangarian and R. Emadi, Synthesis and characterization of pure nanocrystalline magnesium aluminate spinel powder, J. Alloys Compd., 489(2010), No. 2, p. 600.
I. Ganesh, G.J. Reddy, G. Sundararajan, S.M. Olhero, P.M.C. Torres, and J.M.F. Ferreira, Influence of processing route on microstructure and mechanical properties of MgAl2O4 spinel, Ceram. Int., 36(2010), No. 2, p. 473.
Z.Y. Yu, N.Q. Zhao, E.Z. Liu, C.S. Shi, X.W. Du, and J. Wang, Fabrication of aluminum matrix composites with enhanced mechanical properties reinforced by in situ generated MgAl2O4 whiskers, Composites Part A, 43(2012), No. 4, p. 631.
I. Ganesh, Fabrication of magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) spinel foams, Ceram. Int., 37(2011), No. 7, p. 2237.
G. Bonnefont, G. Fantozzi, S. Trombert, and L. Bonneau, Fine-grained transparent MgAl2O4 spinel obtained by spark plasma sintering of commercially available nanopowders, Ceram. Int., 38(2012), No. 1, p. 131.
F. Zhu, J.X. Liao, S.G. Xue, W. Hartley, Q. Zhou, and H. Wu, Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography, Sci. Total Environ., 573(2016), p. 157.
M. Li, B. Peng, L.Y. Chai, N. Peng, H. Yan, and D.K. Hou, Recovery of iron from zinc leaching residue by selective reduction roasting with carbon, J. Hazard. Mater., 237–238(2012), p. 323.
Y. Zhang, Z.H. Guo, Z.Y. Han, and X.Y. Xiao, Effect of rare earth oxides doping on MgAl2O4 spinel obtained by sintering of secondary aluminium dross, J. Alloys Compd., 735(2018), p. 2597.
Z.Y. Han, Z.H. Guo, Y. Zhang, X.Y. Xiao, Z. Xu, and Y. Sun, Adsorption-pyrolysis technology for recovering heavy metals in solution using contaminated biomass phytoremediation, Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 129(2018), p. 20.
X.F. Kong, M. Li, S.G. Xue, W. Hartley, C.R. Chen, C. Wu, X.F. Li, and Y.W. Li, Acid transformation of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics, J. Hazard. Mater., 324(2017), Part B, p. 382.
H.G. Li, Metallurgical Principle, Science Press, Beijing, 2005, p. 300.
R.C. Wang, Y.C. Zhai, Z.Q. Ning, and P.H. Ma, Kinetics of SiO2 leaching from Al2O3 extracted slag of fly ash sodium hydroxide solution, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 24(2014), No. 6, p. 1928.
H.D. Chandler, Activation entropy and anomalous temperature dependence of viscosity in aqueous suspensions of Fe2O3, Powder Technol., 305(2017), p. 572.
X.B. Li, W.J. Lv, G.T. Feng, G.H. Liu, Z.H. Peng, Q.S. Zhou, and Y. Meng, The applicability of Debye-Hückel model in NaAl(OH)4-NaOH-H2O system, Chin. J. Process Eng., 5(2005), No. 5, p. 525.
S. Wang, Preparation and Properties of Spinel Composites From Secondary Aluminium Dross [Dissertation], Central South University, Changsha, 2016, p. 6.
X.F. Kong, Y. Guo, S.G. Xue, W. Hartley, C. Wu, Y.Z. Ye, and Q.Y. Cheng, Natural evolution of alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue, J. Cleaner Prod., 143(2017), p. 224.
X.L. Jia, H.J. Zhang, Y.J. Yan, and Z.J. Liu, Effect of the citrate sol-gel synthesis on the formation of MgAl2O4 ultrafine powder, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 379(2004), No. 1–2, p. 112.
H.B. Bafrooei and T. Ebadzadeh, MgAl2O4 nanopowder synthesis by microwave assisted high energy ball-milling, Ceram. Int., 39(2013), No. 8, p. 8933.
J.J. Guo, H. Lou, H. Zhao, X.G. Wang, and X.M. Zheng, Novel synthesis of high surface area MgAl2O4 spinel as catalyst support, Mater. Lett., 58(2004), No. 12–13, p. 1920.
M.F. Zawrah, H. Hamaad, and S. Meky, Synthesis and characterization of nano MgAl2O4 spinel by co-precipitated method, Ceram. Int., 33(2007), No. 6, p. 969.
N. Van Minh and I.S. Yang, A Raman study of cation disorder transition temperature of natural MgAl2O4 spinel, Vib. Spectrosc., 35(2004), No. 1–2, p. 93.
P. Barpanda, S.K. Behera, P.K. Gupta, S.K. Pratihar, and S. Bhattacharya, Chemically induced order disorder transition in magnesium aluminum spinel, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 26(2006), No. 13, p. 2603.
M.L. Bouchetou, J.P. Ildefonse, J. Poirier, and P. Daniellou, Mullite grown from fired andalusite grains: the role of impurities and of the high temperature liquid phase on the kinetics of mullitization and consequences on thermal shocks resistance, Ceram. Int., 31(2005), No. 7, p. 999.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21577176) and the Environment Protection Scientific Research Project of Hunan Province, China (No. [2016]59–3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Guo, Zh., Han, Zy. et al. Feasibility of aluminum recovery and MgAl2O4 spinel synthesis from secondary aluminum dross. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 309–318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1739-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1739-3