Abstract
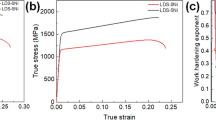
The effects of the microalloying element niobium (Nb) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the hot stamped steel 38MnB5 were investigated. The impact of Nb addition on the microstructure was studied through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The experimental results indicated that the microstructures of the steel containing Nb were finer than those of the steel without Nb. Moreover, Nb mainly presented as a second-phase particle in 38MnB5 steel, and the particles included Nb carbonitrides. In addition, the tensile strength and elongation of the hot rolled and hot stamped steels were also measured, and they demonstrated that the appropriate addition of Nb was beneficial to the mechanical properties of 38MnB5. Under the same conditions, the tensile strength of 38MnB5Nb was higher than that of 38MnB5, which increased from 2011 to 2179 MPa. The yield strength also increased from 1316 to 1476 MPa, and the elongation increased from 5.92% to 6.64%. Overall, Nb had a positive effect on the performance of the hot stamped steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.S. Chen, Discussion of the modern electronic technology application and future development trend on automobile, Appl. Mech. Mater., 155–156(2012), p. 627.
Y.X. Li, Z.Q. Lin, A.Q. Jiang, and G.L. Chen, Experimental study of glass–fiber mat thermoplastic material impact properties and lightweight automobile body analysis, Mater. Des., 25(2004), No. 7, p. 579.
T. Taylor, G. Fourlaris, P. Evans, and G. Bright, New generation ultrahigh strength boron steel for automotive hot stamping technologies, Mater. Sci. Technol., 30(2014), No. 7, p. 818.
R. Kurji, O. Lavigne, and R. Ghomashchi, Micromechanical characterisation of weld metal susceptibility to hydrogen–assisted cold cracking using instrumented indentation, Weld. World, 60(2016), No. 5, p. 883.
X.H. Han, Y.Y. Zhong, S.L. Tan, Y.N. Ding, and J. Chen, Microstructure and performance evaluations on Q&P hot stamping parts of several UHSS sheet metals, Sci. China: Technol. Sci., 60(2017), No. 11, p. 1692.
Y. Chang, X.D. Li, K.M. Zhao, C.Y. Wang, G.J. Zheng, P. Hu, and H. Dong, Influence of stress on martensitic transformation and mechanical properties of hot stamped AHSS parts, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 629(2015), p. 1.
C.C. Kinney, K.R. Pytlewski, A.G. Khachaturyan, and J.W. Morris Jr, The microstructure of lath martensite in quenched 9Ni steel, Acta Mater., 69(2014), p. 372.
T. Niino, J. Inoue, M. Ojima, S. Nambu, and T. Koseki, Effects of solute carbon on the work hardening behavior of lath martensite in low–carbon steel, ISIJ Int., 57(2017), No. 1, p. 181.
Z.J. Luo, L.P. Wang, W. Meng, J.C. Shen, and S.U. Hang, Effect of lath martensite/bainite microstructure on strength and toughness of a low carbon martensite steel, Trans. Mater. Heat Treat., 33(2012), No. 2, p. 85.
S.C. Li, G.M. Zhu, and Y.L. Kang, Effect of substructure on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of lath martensite in 0.1C–1.1Si–1.7Mn steel, J. Alloys Compd., 675(2016), p. 104.
P. Gong, E.J. Palmiere, and W.M. Rainforth, Dissolution and precipitation behavior in steels microalloyed with niobium during thermomechanical processing, Acta Mater., 97(2015), p. 392.
M. Zaeimi, A. Basti, and M. Alitavoli, Effect of martensite volume fraction on forming limit diagrams of dual–phase steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 24(2015), No. 5, p. 1781.
V.I. Izotov, N.A. Komkov, and G.A. Filippov, Kinetics and crystal geometry of precipitation of vanadium carbides at the interphase boundary upon pearlitic transformation of steel, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 114(2013), No. 3, p. 256.
A. Ostapovets and A. Serra, Slip dislocation and twin nucleation mechanisms in hcp metals, J. Mater. Sci., 52(2017), No. 1, p. 533.
H.W. Yen, P.Y. Chen, C.Y. Huang, and J.R. Yang, Interphase precipitation of nanometer–sized carbides in a titanium–molybdenum–bearing low–carbon steel, Acta Mater., 59(2011), No. 16, p. 6264.
Y.L. Fang, Z.Y. Liu, W.Y. Xue, H.M. Song, and L.Z. Jiang, Precipitation of secondary phases in lean duplex stainless steel 2101 during isothermal ageing, ISIJ Int., 50(2010), No. 2, p. 286.
V. Homolová, J. Janovec, P. Záhumenský, and A. Výrostková, Influence of thermal–deformation history on evolution of secondary phases in p91 steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 349(2003), No. 1–2, p. 306.
S. Wu, X. Li, J. Zhang, and C. Shang, Effect of Nb on transformation and microstructure refinement in medium carbon steel, Acta Metall. Sin., 50(2014), No. 4, p. 400.
J.H. Li, W.L. Zhang, C. Yuan, X.Q. Bao, and X.X. Gao, Inhibition force of precipitates for promoting abnormal grain growth in magnetostrictive Fe83Ga17–(B,NbC) alloy sheets, Rare Met., 36(2017), No. 5, p. 1.
S. Roy, D. Chakrabarti, and G.K. Dey, Austenite grain structures in Ti and Nb–containing high–strength low–alloy steel during slab reheating, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 44(2013), No. 2, p. 717.
H.Y. Wang, Effect of Rare Earth on NbC Dissolution and Precipitation Behaviors in Microalloy Steels [Dissertation], University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, 2017, p. 64.
B. Wang, Y.W. Hu, X.F. Yang, X.W. Cai, Y. Jiang, and J.Q. Luo, Microstructure and properties of Nb–bearing high–strength low–alloy surfacing layers, Met. Sci. Technol., 33(2016), No. 8, p. 1004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Li, Bs., Zhu, Gm. et al. Effects of Nb on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 38MnB5 steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25, 1181–1190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1670-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1670-z