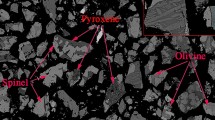
Abstract
A sodium modification–direct reduction coupled process was proposed for the simultaneous extraction of V and Fe from vanadium- bearing titanomagnetite. The sodium oxidation of vanadium oxides to water-soluble sodium vanadate and the transformation of iron oxides to metallic iron were accomplished in a single-step high-temperature process. The increase in roasting temperature favors the reduction of iron oxides but disfavors the oxidation of vanadium oxides. The recoveries of vanadium, iron, and titanium reached 84.52%, 89.37%, and 95.59%, respectively. Moreover, the acid decomposition efficiency of titanium slag reached 96.45%. Compared with traditional processes, the novel process provides several advantages, including a shorter flow, a lower energy consumption, and a higher utilization efficiency of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Chen, C.P. Guan, Y. Wang, Y.M. Zhou, and X.J. Tang, Experimental research on improving the recovery of vanadium titanomagnetite ore in Hongge mining areas in Panzhihua, Sichuan Nonferrous Met., No. 2, (2011),p. 17.
X.Q. Wang, Blast Furnace Process for Vanadium-bearing Titanomagnetite, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1994.
K.J. Hu, G. Xi, J. Yao, and X. Xi Status quo of manufacturing techniques of titanium of titanium slag in the world, World Nonferrous Met., No. 12, (2006),p. 26.
Z.J. Liu, G.Q. Yang, Q.G. Xue, J.L. Zhang, and T.J. Yang, Research on direct reduction of coal-containing pellets of vanadic-titanomagnetite by rotary hearth furnace, Chin. J. Process Eng., 9(2009), Suppl. 1, p. 51.
J. Deng, X. Xue, and G.G. Liu, Current situation and development of comprehensive utilization of vanadiumbearing titanomagnetite at PANGANG, J. Mater. Metall., 6(2007, No. 2, 83.
B.C. Jena, W. Dresler, and I.G. Reilly, Extraction of titanium, vanadium and iron from titanomagnetite deposits at pipestone lake, Manitoba, Canada, Miner. Eng., 8(1995, No. 1–2), 159.
E. Hukkanen and H. Walden, The production of vanadium and steel from titanomagnetites, Int. J. Miner. Process., 15(1985, No. 1–2), 89.
L.H. Zhou, D.P. Tao, M.X. Fang, F.H. Zeng, and X. Pu, Carbothermic reduction of V–Ti magnetite ore, Chin. J. Rare Met., 33(2009, No. 3, 406.
L. Hong, Y.H. Ding, and H.E. Xie, Prospect of comprehensive utilization of V-rearing titanomagnetite by rotary hearth furnace process, Met. Mine, No. 5, (2007),p. 10.
X. Xue, Research on direct reduction of vanadic titanomagnetite, Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 28(2007, No. 3, 37.
R.R. Moskalyk and A.M. Alfantazi, Processing of vanadium: a review, Miner. Eng., 16(2003, No. 9, 793.
Y.X. Qin, Comparison of direct reduction by rotary hearth furnace-electric furnace smelting process and blast furnace process, Jiangsu Metall., 32(2004, No. 2, 9.
W.C. Song, K. Li, Q. Zheng, and H. Li, A novel process of vanadium extraction from molten vanadium bearing slag, Waste Biomass Valorization, 5(2014, No. 3, 327.
D.S. Chen, L.S. Zhao, T. Qi, G.P. Hu, H.X. Zhao, J. Li, and L.N. Wang, Desilication from titanium–vanadium slag by alkaline leaching, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 23(2013, No. 10, 3076.
L. Zhang, L.N. Zhang, M.Y. Wang, G.Q. Li, and Z.T. Sui, Dynamic oxidation of the Ti-bearing blast furnace, ISIJ Int., 46(2006, No. 3, 458.
L. Zhang, L.N. Zhang, M.Y. Wang, G.Q. Li, and Z.T. Sui, Recovery of titanium compounds from molten Ti-bearing blast furnace slag under the dynamic oxidation condition, Miner. Eng., 20(2007, No. 7, 684.
H.Y. Sun, X.J. Dong, X.F. She, Q.G. Xue, and J.S. Wang, Solid state reduction of titanomagnetite concentrate by graphite, ISIJ Int., 53(2013, No. 4, 564.
D.S. Chen, B. Song, L.N. Wang, T. Qi, Y. Wang, and W.J. Wang, Solid state reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with pulverized coal, Miner. Eng., 24(2011, No. 8, 864.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Nos. 2013CB632601 and 2013CB632604), the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Nos. 51125018 and 51504230), the Key Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KGZD-EW-201-2), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51374191 and 2110616751104139), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2012M510552 and 2013T60175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Ym., Yi, Ly., Wang, Ln. et al. A novel process for the recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite: sodium modification–direct reduction coupled process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24, 504–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1431-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1431-4