Abstract
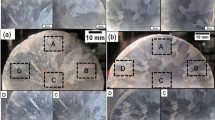
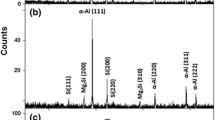
The microstructural characteristics and microhardness of nanostructured Al−4.6Cu−Mn ribbons produced by melt spinning were investigated using field-emission gun scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and hardness testing, and the results were compared to those of similar ribbons manufactured by direct-chill casting. It is shown that the nanostructure of the as-melt-spun ribbons consists of α-Al dendrites with a secondary dendrite arm spacing of approximately 0.55−0.80 μm and ultrafine eutectic crystals of a nanosized scale of approximately 100−200 nm on dendritic boundaries. The solidification time and cooling rate of 46-μm-thick ribbons were estimated to be 1.3 × 10−6 s and 4.04 × 106 K·s−1, respectively. At an aging temperature of 190°C, the coherent θ″ phase in aged ribbons gradually transforms into nanoscale θ′-phase platelets as the aging time is extended from 2 to 8 h; the rod-like morphology of the T (Al20Cu2Mn3) dispersoid with 120−160-nm diameter also forms, which results in peak aging hardness. The precipitation behaviors of aged ribbons cannot be changed at the high cooling rates of as-cast ribbons. However, a finer and more uniformly distributed microstructure and a supersaturated solid solution at a high cooling rate can shorten the time required to obtain a certain aging hardness before peak hardness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Okayasu, Y. Ohkura, S. Takeuchi, S. Takasu, H. Ohfuji, and T. Shiraishi, A study of the mechanical properties of an Al-Si-Cu alloy (ADC12) produced by various casting processes, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 543(2012), p. 185.
B.P. Reis, R.P. França, J.A. Spim, A. Garcia, E.M. da Costa, and C.A. Santos, The effects of dendritic arm spacing (as-cast) and aging time (solution heat-treated) of Al–Cu alloy on hardness, J. Alloys Compd., 549(2013), p. 324.
D.G. Eskin, Suyitno, and L. Katgerman, Mechanical properties in the semi-solid state and hot tearing of aluminium alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 49(2004), No. 5, p. 629.
Suyitno, D.G. Eskin, and L. Katgerman, Structure observations related to hot tearing of Al-Cu billets produced by direct-chill casting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 420(2006), No. 1-2, p. 1.
D. Eskin, Q. Du, D. Ruvalcaba, and L. Katgerman, Experimental study of structure formation in binary Al-Cu alloys at different cooling rates, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 405(2005), No. 1-2, p. 1.
L.A. Jacobson, Rapid solidification processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 11(1994), No. 8, p. 355.
R. Trivedi, F. Jin, and I.E. Anderson, Dynamical evolution of microstructure in finely atomized droplets of Al-Si alloys, Acta Mater., 51(2003), No. 2, p. 289.
I. Lichioiu, I. Peter, B. Varga, and M. Rosso, Preparation and structural characterization of rapidly solidified Al-Cu alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 30(2014), No. 4, p. 394.
Z.W. Chen, J. Zhao, and P. Chen, Microstructure and mechanical properties of nanostructured A8006 ribbons, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 552(2012), p. 189.
Z.W. Chen, Y.M. Lei, and H.F. Zhang, Structure and properties of nanostructured A357 alloy produced by melt spinning compared with direct chill ingot, J. Alloys Compd., 509(2011), No. 27, p. 7473.
E. Karaköse and M. Keskin, Structural investigations of mechanical properties of Al based rapidly solidified alloys, Mater. Des., 32(2011), No. 10, p. 4970.
L. Bourgeois, C. Dwyer, M. Weyland, J.F. Nie, and B.C. Muddle, Structure and energetics of the coherent interface between the θ' precipitate phase and aluminium in Al-Cu, Acta Mater., 59(2011), No. 18, p. 7043.
S.Y. Hu, M.I. Baskes, M. Stan, and L.Q. Chen, Atomistic calculations of interfacial energies, nucleus shape and size of θ' precipitates in Al-Cu alloys, Acta Mater., 54(2006), No. 18, p. 4699.
A. Guinier, Structure of age-hardened aluminium-copper alloys, Nature, 142(1938), p. 569.
G.D. Preston, Response to the letter of A. Guinier (Ref.14), Nature, 142(1938), p. 570.
S.C. Wang and M.J. Starink, Precipitates and intermetallic phases in precipitation hardening Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) based alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 50(2005), No. 4, p. 193.
A. Guinier, Heterogeneities in solid solutions, Solid State Phys., 9(1959), p. 293.
W.J. Huang, Z.Y. Liu, M. Lin, X.W. Zhou, L. Zhao, A.L. Ning, and S.M. Zeng, Reprecipitation behavior in Al-Cu binary alloy after severe plastic deformation-induced dissolution of θ' particles, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 546(2012), p. 26.
L. Bourgeois, C. Dwyer, M. Weyland, J.F. Nie, and B.C. Muddle, The magic thicknesses of θ' precipitates in Sn-microalloyed Al-Cu, Acta Mater., 60(2012), No. 2, p. 633.
R. Yoshimura, T.J. Konno, E. Abe, and K. Hiraga, Transmission electron microscopy study of the evolution of precipitates in aged Al-Li-Cu alloys: the θ' and T1 phases, Acta Mater., 51(2003), No. 14, p. 4251.
W.W. Zhang, B. Lin, D.T. Zhang, and Y.Y. Li, Microstructures and mechanical properties of squeeze cast Al-5.0Cu-0.6Mn alloys with different Fe content, Mater. Des., 52(2013), p. 225.
N.A. Belov, A.N. Alabin, and I.A. Matveeva, Optimization of phase composition of Al-Cu-Mn-Zr-Sc alloys for rolled products without requirement for solution treatment and quenching, J. Alloys Compd., 583(2014), p. 206.
H. Jones, Cooling rates during rapid solidification from a chill surface, Mater. Lett., 26(1996), No. 3, p. 133.
V.I. Tkatch, S.N. Denisenko, and O.N. Beloshov, Direct measurements of the cooling rates in the single roller rapid solidification technique, Acta Mater., 45(1997), No. 7, p. 2821.
A. Guinier, The precipitation mechanism of a metal solid solution crystal: case of aluminium copper and aluminium silver system, J. Phys. Radium, 3(1942), No. 7, p. 124.
H. Yoshida, Some aspects on the structure of Guinier-Preston zones in Al-Cu alloys based on high resolution electron microscope observations, Scripta Metall., 22(1988), No. 7, p. 947.
K. Robinson, The unit cell and Brillouin zones of Ni4Mn11Al60 and belated compounds, Philos. Mag. Ser., 43(1952), No. 342, p. 775.
S.C. Wang, C.Z. Li, and M.G. Yan, Study of the new Frank–Kasper phases in Al-Li-Cu-Mg alloys, Acta Metall. Mater., 41(1993), No. 10, p. 2949.
B.C. Muddle and I.J. Polmear, The precipitate O phase in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys, Acta Metall., 37(1989), No. 3, p. 777.
Z.W. Chen, P. Chen, and S.S. Li, Effect of Ce addition on microstructure of Al20Cu2Mn3 twin phase in an Al-Cu-Mn casting alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 532(2012), p. 606.
S.P. Ringer and K. Hono, Microstructural evolution and age hardening in aluminium alloys: atom probe field-Ion microscopy and transmission electron microscopy studies, Mater. Charact., 44(2000), No. 1-2, p. 101.
J.B.M. Nuyten, Quenched structures and precipitation in Al-Cu alloys with and without trace additions of Cd, Acta Metall., 15(1967), p. 1765.
B. Klobes, O. Balarisi, M. Liu, T.E.M. Staab, and K. Maier, The effect of microalloying additions of Au on the natural ageing of Al-Cu, Acta Mater., 58(2010), No. 19, p. 6379.
C.R. Hutchinson and S.P. Ringer, Precipitation processes in Al-Cu-Mg alloys microalloyed with Si, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 31(2000), No. 11, p. 2721.
Z.H. Bai, F. Qiu, X.X. Wu, Y.Y. Liu, and Q.C. Jiang, Age hardening and creep resistance of cast Al-Cu alloy modified by praseodymium, Mater. Charact., 86(2013), p. 185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Zw., Fan, Qy. & Zhao, K. Microstructure and microhardness of nanostructured Al−4.6Cu−Mn alloy ribbons. Int J Miner Metall Mater 22, 860–867 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1143-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1143-6