Abstract
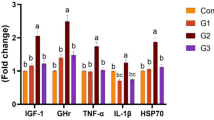
An effective alternative approach to combat aquaculture challenges is the strategic application of bioresources, which not only mitigate disease ailment but also optimize fish growth. Hence, current research was undertaken to highlight the synergic role of bioresources such as plant immunostimulant Ocimum sanctum along with potent gut-derived probiotic Bacillus cereus strain SL1 (Gen Bank Accession Number: FJ627945.1) on mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigala) growth, antioxidant status, gut histopathology, and immune response. For 90 days, fingerlings (average weight 6.8 ± 0.5 g) were fed on diets having varying concentrations of O. sanctum and B. cereus. After the completion of the feeding trial, various growth, immunity, and histological and antioxidant metrics were evaluated according to standard procedures. In comparison to the control and other treatment groups, T3 group showed a significant (P < 0.05) increase in growth parameters, antioxidant enzymatic activity, and hematological and immunological parameters. In addition to it, supplementation of both B. cereus and O. sanctum also upregulated the antioxidant-related gene expressions, such as hepatic catalase gene by 1.89–3.00 folds, hepatic SOD-1 by 4.46–7.52 folds, and GPx-1of the liver by 1.56–1.95 folds. For 10 days, fingerlings were challenged with the pathogenic bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila (MTCC-1739), and maximum survival rate (77.77%) was reported in fingerlings of T3 treatment. Further histopathological studies of gut tissues affirm that O. sanctum and B. cereus play a synergic role in the protection of digestive organs from the pathogenic bacterium A. hydrophila. These results suggest that O. sanctum and B. cereus synergically improved the growth performance, immunity, antioxidant status, and gut histology of C. mrigala leading to its sustainable culture.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2016) FAOSTAT database, FAO. 1 December 2016; https://www.fao.org/faostat
Delgado CL, Wada N, Rosegrant MW, Meijer S, Ahmed M (2003) Fish to 2020: supply and demand in changing global markets. Penang (Malaysia): World Fish Center.
Stickney RR, McVey JP (2002) Responsible marine aquaculture. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Megbowon I, Adejonwo OA, Adeyemi YB, Kolade OY, Adetoye AAA, Edah B, Okunade OA, Adedeji AK (2013) Effect of garlic on growth performance, nutrient utilization and survival of an Ecotype Cichlid, ‘Wesafu.’ IOSR J Agric Vet Sci 6(3):10–13
El-Dakar AY, Hassanien GD, Gad SS, Sakr SE (2008) Use of dried basil leaves as a feeding attractant for hybrid tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus, fingerlings. J Mediterr Aquacult 1(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.21608/maj.2008.2662
Bhatnagar A, Lamba R (2018) Immunomodulatory and growth promoting effect of dietary administration of Indian herbs Allium sativum (garlic) and Ocimum sanctum (tulsi) on Cirrhinus mrigala. Int J Recent Sci Res 9(4):26217–26226
Tovar-Ramırez D, Infante JZ, Cahu C, Gatesoupe FJ, Vázquez-Juárez R (2004) Influence of dietary live yeast on European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larval development. Aquaculture 234(1–4):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.028
Balcázar JL, De Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Cunningham D, Vendrell D, Múzquiz JL (2006) The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet microbial 114(3–4):173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.01.009
Kuebutornye FK, Abarike ED, Lu Y (2019) A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish shellfish immunol 87:820–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.010
Verschuere L, Rombaut G, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2000) Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol Mol Boil Rev 64(4):655–671. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.64.4.655-671
Nayak S (2010) Probiotics and immunity: a fish perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29(1):2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.02.017
Bhatnagar A, Raparia S, Kumari S (2012) Influence of isolated Bacillus coagulans on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of Catla catla. JANSET 6(3):225–235
Bhatnagar A, Raparia S (2014) Optimum dietary inclusion level of Bacillus coagulans for growth and digestibility improvement for Catla catla (Hamilton). Int J Curr Res Rev 6(7):1–10
Bhatnagar A, Lamba R (2017) Molecular characterization and dosage application of autochthonous potential probiotic bacteria in Cirrhinus mrigala. J Fish Sci 11(2):46
Bhatnagar A, Dhillon O (2019) Characterization, screening, and application of bacteria with probiotic properties isolated from the gut of Labeo calbasu (Hamilton). Fisheries & Aquatic Life 27:178–189. https://doi.org/10.2478/aopf-2019-0020
Bhatnagar A, Saluja S (2019) Synergistic effects of autochthonous probiotic bacterium and Mentha piperita diets in Catla catla (Hamilton, 1822) for enhanced growth and immune response. JFAS 22(1):1–16
Bhatnagar A, Raparia S (2020) Evaluation of probiotic adequacy, immunomodulatory effects and dosage application of Bacillus coagulans in formulated feeds for Catla catla (Hamilton 1822). Inte J Aquat Biol 8(3):194–208
Hall KC, Bellwood DR (1995) Histological effects of cyanide, stress and starvation on the intestinal mucosa of Pomacentrus coelestis, a marine aquarium fish species. J Fish Biol 47:438–454. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1995.tb01913.x
Green BS, McCornik MI (1999) Influence of larval feeding history on the body condition of Amphiprion melanopus. J Fish Biol 55:1273–1289. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1999.tb02075.x
Dayal R, Srivastva PP, Lakra WS, Bhatnagar A, Chowdhary S, Yadav AK, Srivatsa SM (2013) Histological changes in the intestine of Channa Striatus grow out fed with different fat sources: effect of dietry manipulation. Asian J Exp Biol Sci 4(4):561–566
Takashima F, Hibiya T (1982) An atlas of fish history: normal and pathological features Kodansha, distributed by Fischer, G., Tokyo.
Roberts RJ (1989) The mycology of teleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish Pathology, 2nd edn. Bailliere Tindall, London, pp 320–336
El-Houseiny W, Mansour MF, Mohamed WA, Al-Gabri NA, El-Sayed AA, Altohamy DE, Ibrahim RE (2021) Silver nanoparticles mitigate Aeromonas hydrophila-induced immune suppression, oxidative stress, and apoptotic and genotoxic effects in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 535:736430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736430.
Shao JZ, Liu J, Xiang LX (2004) Aeromonas hydrophila induces apoptosis in Carassius auratus lymphocytes in vitro. Aquaculture 229:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00364-8
Cavalcante RB, Telli GS, Tachibana L, de Carla DD, Oshiro E, Natori MM, Ranzani-Paiva MJ (2020) Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics for nile tilapia: growth performance and protection against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Aquac Rep 17:100343
Quarterly aquatic animal disease report (Asia and Pacific region). FAO, NACA; 2003.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization), Resistance management and integrated parasite control in ruminants – guidelines, module 1 – ticks: acaricide resistance: diagnosis, management and prevention, Food and Agriculture Organization, Animal Production and Health Division, Rome, 2004, pp. 25–77.
Bhatnagar A, Saluja S (2021) Role of Zingiber officinale and autochthonous probiotic Bacillus coagulans in feeds of Catla catla (Hamilton, 1822) for growth promotion, immunostimulation, histoprotection, and control of DNA damage. Fish Physiol Biochem 47(6):2081–2100
Bhatnagar A, Lamba R (2015) Antimicrobial ability and growth promoting effects of feed supplemented with probiotic bacterium isolated from gut microflora of Cirrhinus mrigala. J Integr Agric 14(3):583–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60836-4
Garg SK, Bhatnagar A, Kalla A, Johal MS (2002) Experimental ichthyology CBS publications and distributors New Delhi, India.
Cho CY, Slinger Bayley SJ (1982) Bioenergetics of salmonid fishes: energy intake, expenditure and productivity. Comp Biochem Physiol 73(1): 25–41 https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(82)90198-5
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (1995) Official methods of analysis Association of Official Analytical Chemists Incorporation Arlington, USA 684.
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water 20 American Public Health Association New York.
Walter HE (1984) Probionases: methods with haemoglobin, casein and azocoll as substrates. In: Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, (ed. by H. U. Bergmeyer), pp. 270–277.
Sawhney SK, Singh R (2000) Introductory practical biochemistry. Narosa Publishing House, p 452
Sadasivam S, Manickam A (1996) Biochemical methods. 2nd Edn. New Age Interantional Publishers, pp. 107–109.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement in the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Dacie JV, Lewis SH (1963) Practical hematology J and A Churchill Ltd. London.
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP, Rumsey GL (1994) Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 4:125–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2427(94)90062-0
Park KH, Do Jeong H (1996) Enhanced resistance against Edwardsiella tarda infection in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by administration of protein-bound polysaccharide. Aquaculture 143(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(95)01224-9
Anderson DP, Siwicki AK (1995) Basic haematology and serology for fish health programs. In: Diseases in Asian Aquaculture II (ed. by M. Shariff, J. R. Arthur and R.P. Subasinghe). Manila, Philippines: Philippines Fish Health Section, Asian Fisheries Society, pp 185.
Kulow H (1967) Eine Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung der Serumproteine von Satzkarpfen (a rapid method of finding the serum proteins in young common carp). Dt Fischerei-Ztg 14:241–149
Parry RM Jr, Chandan RC, Shahani KM (1965) A rapid and sensitive assay of muramidase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 119(2):384–386. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-119-30188
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. In Methods in enzymology. 105:21–126. Academic press https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J biochem 47(3):469–474
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra W (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179(4073):588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Austin B, Stuckey LF, Robertson PAW, Effendi I, Griffith DRW (1995) A probiotic strain of Vibrio alginolyticus effective in reducing disease caused by Aeromonas salmonicida, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio ordalii. J Fish Dis 18(1):9396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1995.tb01271
Sahoo SK, De TK, Ghosh PK, Maitra A (1998) pH and thermo-sensitive hydrogel nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 206(2):361–368. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1998.5692
Nandeesha MC, Gangadhar B, Varghese TJ, Keshavanath P (1998) Effect of feeding Spirulina platensis on the growth, proximate composition and organoleptic quality of common carp. Cyprinus carpio L Aquac Res 29(5):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.1998.00163.x
Saluja S, Bhatnagar A (2023) Dietary administration of probiotic Bacillus coagulans and Mentha piperita can protect histological architecture and DNA damage in Catla catla (Hamilton, 1822). Fish Aquac J https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaf.2023.02.002
Sun YZ, Yang HL, Ma RL, Lin WY (2010) Probiotic applications of two dominant gut Bacillus strains with antagonistic activity improved the growth performance and immune responses of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish shellfish immunol 29(5):803–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.07.018
Ringo E, Sperstad S, Myklebust R, Refstie S, Krogdahl A (2006) Characterisation of the microbiota associated with intestine of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): the effect of fish meal, standard soybean meal and a bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 261(3):829–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.06.030
Uberschar B (1993) Measurement of proteolytic enzyme activity: significance and application in larval fish research. University of Bergen pp-233–239.
Platel K, Srinivasan K (2004) Digestive stimulant action of spices: a myth or reality? Indian J Med Res 119(5):167
Jasim SA, Hafsan H, Saleem HD, Kandeel M, Khudhair F, Yasin G, Iswanto AH, Mohammed HT, Izzat SE, Dadras M (2022) The synergistic effects of the probiotic (Lactobacillus fermentum) and cinnamon, Cinnamomum sp. powder on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, immunity, antioxidant defence and resistance to Yersinia ruckeri infection in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high rearing density. Aquac Res 53(17):5957–5970. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.16064
Kumar A, Bhatnagar A, Garg SK (2009) Growth performance, carcass composition and digestive enzyme activity of pearlspot, Etroplus suratensis (Bloch) reared in inland saline groundwater ponds providing substrate or feed. Livest. Res. Rural. Dev. 21(10):180. Retrieved August 6, 2010, from http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd21/10/kuma21180.htm
Jana SN, Sudesh GSK, Sabhlok VP, Bhatnagar A (2012) Nutritive evaluation of lysine- and methionine-supplemented raw vs heat-processed soybean to replace fishmeal as a dietary protein source for grey mullet, Mugil cephalus, and milkfish. Chanos chanos J Appl Aquacult 24(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454438.2012.652032
Bhatnagar A, Lamba R (2016) Immunostimulating and growth promoting activity of dietary levamisole on Cirrhinus mrigala fingerlings. J Aquacult Mar Bio 4(6):00102
Soltan MA, El-Laithy SM (2008) Effect of probiotics and some spices as feed additives on the performance and behaviour of the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egy J Aqua Bio Fish 12(2):63–80. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejabf.2008.1992
Nahak G, Sahu RK (2014) Immunomodulatory activity of aqueous leaf extracts of Ocimum basilicum Linn in Clarias batrachus. Int J Phar Pharmaceut Sci 6(6):433–440
Shoemaker CA, Klesius PH (1997) Protective immunity against enteric septicaemia in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), following controlled exposure to Edwardsiella ictaluri. J Fish Dis 20(5):361–368. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2761.1997.00310.x
Chakrabarti R, Vasudeva RY (2006) Achyranthes aspera stimulates the immunity and enhances the antigen clearance in Catla catla. Int J Immunopharmacol 6(5):782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2005.11.020
Gopalakannan A, Arul V (2006) Immunomodulatory effects of dietary intake of chitin, chitosan and levamisole on the immune system of Cyprinus carpio and control of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in ponds. Aquaculture 255(1–4):179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.01.012
Rao YV, Chakrabarti R (2005) Dietary incorporatinon of Achyranthes aspera seed influences the immunity of common carp Cyprinus carpio. Indian J Anim Sci 75(9):1097
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP, Rumsey GL (1994) Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against frunculosis. Vet Immunol Immunop 41:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2427(94)90062-0
Anderson DP, Jeney G (1992) Immunostimulants added to injected Aeromonas salmonicida bacterin enhance the defense mechanisms and protection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vet immunol immunopathol 34(3–4):379–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2427(92)90177-R
Shafqatullah M, Khurram A, Khaliqurrehman Khan FA (2013) Comparative analyses of Ocimum sanctum stem and leaves for phytochemicals and inorganic constituents. Middle-East J Sci Res 13(2):236–240
Rao YV, Das BK, Jyotyrmayee P, Chakrabarti R (2006) Effect of Achyranthes aspera on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20(3):263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.04.006
Sahu S, Das BK, Mishra BK, Pradhan J, Sarangi N (2007) Effect of Allium sativum on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. J Appl Ichthyol 23:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00785.x
Sahu S, Das BK, Pradhan J, Mohapatra BC, Mishra BK, Sarangi N (2007) Effect of Magnifera indica kernel as a feed additive on immunity and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Labeo rohita fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2006.09.009
Martínez-Álvarez RM, Morales AE, Sanz A (2005) Antioxidant defenses in fish: biotic and abiotic factors. Rev Fish Biol Fish 15:75–88
Srikanth K, Pereira E, Duarte A, Ahmad I (2013) Glutathione and its dependent enzymes’ modulatory responses to toxic metals and metalloids in fish—a review. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:2133–2149
Soni RA, Sudhakar K, Rana RS (2017) Spirulina – from growth to nutritional product:a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 69:157–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.09.010
Hoseini morteza Yousefi SM, (2018) Beneficial effects of thyme (Thymus vulgaris) extract on oxytetracycline-induced stress response, immunosuppression, oxidative stress enzymatic changes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Nutr 24(1):625–632. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12853
Abdel-Latif HMR, Abdel-Tawwab M, Khafaga AF, Dawood MAO (2020) Dietary origanum essential oil improved antioxidative status, immune-related genes, and resistance of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 104:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.05.056
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77(3):591–625. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1997.77.3.591
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations JASA 53(282):457–481
Sun Z, Tan X, Ye H, Zou C, Ye C, Wang A (2018) Effects of dietary Panax notoginseng extract on growth performance, fish composition, immune responses, intestinal histology and immune related genes expression of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatusc× Epinephelus fuscoguttatusd) fed high lipid diets. Fish shellfish immunol 73:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.11.007
Cerezuela R, Fumanal M, Tapia‐Paniagua ST, Meseguer J, Moriñigo MÁ, Esteban MÁ (2013) Changes in intestinal morphology and micro‐ biota caused by dietary administration of inulin and Bacillus subtilis in gilt‐ head sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) specimens. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34(5):1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.01.015
Gisbert E, Castillo M, Skalli A, Andree K, Badiola I (2013) Bacillus cereus var. toyoi promotes growth, affects the histological organization and microbiota of the intestinal mucosa in rainbow trout finger‐ lings. Anim Sci J 91(6):2766–2774
Han B, Long WQ, He JY, Liu YJ, Si YQ, Tian LX (2015) Effects of dietary Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immunological parameters, intestinal morphology and resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 46(2):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.06.018
Lotfy A (2015) Studies on the rearing of some marine fish larvae using breeding and natural food. Ph.D. Theses, Faculty of Agriculture (Saba-Basha). Alexandria University, Egypt.
Acknowledgements
DM is sincerely thankful to The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, India, for providing Research Fellowship in the form of JRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anita Bhatnagar: conceptualized and designed the experiments and participated in the preparation of the manuscript Deepika Mann: carried out the experiment and analyzed the samples/data, participated in manuscript drafting
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Ethical Guidelines for the use of Animal Care were followed. Approval from Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) has been obtained prior to experimentation (Project No. IPS/IAES/313/22). All of the tests were carried out in accordance with ethical standards.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatnagar, A., Mann, D. The Synergic Effect of Gut-Derived Probiotic Bacillus cereus SL1 And Ocimum sanctum on Growth, Intestinal Histopathology, Innate Immunity, and Expression of Enzymatic Antioxidant Genes in Fish, Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton, 1822). Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10143-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10143-w