Abstract
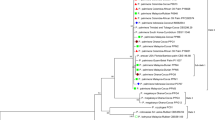
Legume crop cultivation is widespread in Greece and contributes significantly to the agricultural economy of the country. In contrast to pea, Pea seed-borne mosaic virus (PSbMV) detection and pathotype characterization in lentil is limited. The aim of this study was the molecular characterization of the first reported lentil isolate of PSbMV in Greece. Specific primers against three genes of PSbMV, namely the coat protein (CP) and the P1 and HC-Pro proteases have been designed and tested in RT-PCR detection and quantitation of the virus in lentil. Phylogenetic and recombination analysis of the Greek CP and HC-Pro amplicons was performed with the aim of detecting sequence variability indicative of pathotype classification. Moreover, the identified point mutations of the Greek HC-Pro sequence were further exploited in RT-RFLP protocols that together with the phylogenetic analysis lead to the classification of the Greek PSbMV isolate into pathogroup 1.




Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Alconero, R., Provvidenti, R., & Gonsalves, D. (1986). Three Pea seed-borne mosaic virus pathotypes from pea and lentil germ plasm. Plant Disease, 70, 783–786.
Aleman-Verdaguer, M. E., Goudou-Urbino, C., Dubern, J., Beachy, R. N., & Fauquet, C. (1997). Analysis of the sequence diversity of the P1, HC, P3, NIb and CP genomic regions of several yam mosaic potyvirus isolates: implications for the intraspecies molecular diversity of potyviruses. Journal of General Virology, 78, 1253–1264.
Ali, A., & Randles, J. W. (1997). Early season survey of pea viruses in Pakistan and the detection of two new pathotypes of pea seedborne mosaic potyvirus. Plant Disease, 81, 343–347.
Ali, A., & Randles, J. W. (2001). Genomic heterogeneity in Pea seed-borne mosaic virus isolates from Pakistan, the centre of diversity of the host species, Pisum sativum. Archives of Virology, 146, 1855–1870.
Andersen, K., & Johansen, I. E. (1998). A single conserved amino acid in the coat protein gene of pea seed-borne mosaic potyvirus modulates the ability of the virus to move systemically in Chenopodium quinoa. Virology, 241, 304–311.
Andrejeva, J., Puurand, U., Merits, A., Rabenstein, F., Järvekülg, L., & Valkonen, J. P. (1999). Potyvirus helper component-proteinase and coat protein (CP) have coordinated functions in virus–host interactions and the same CP motif affects virus transmission and accumulation. Journal of General Virology, 80, 1133–1139.
Blanc, S., Ammar, E. D., Garcia-Lampasona, S., Dolja, V. V., Llave, C., Baker, J., et al. (1998). Mutations in the potyvirus helper component protein: effects on interactions with virions and aphid stylets. Journal of General Virology, 79, 3119–3122.
Chatzivassiliou, Ε. Κ., Boubourakas, H., Winter, S., Lesemann, D. E., Avgelis, A. D., & Katis, N. I. (2002). Viruses infecting pea (Pisum sativum L.) crops in Greece. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 45, 82.
Chatzivassiliou, Ε. Κ., Kargiotidou, A., Tokatlidis, I., Kumari, S. G., & Makkouk, K. M. (2010). The incidence of viruses in lentil crops and breeding perspectives in Greece. 15th Hellenic Phytopathological Congress. Corfu, Greece. Abstracts p. 105 (in Greek).
Chung, B. Y., Miller, W. A., Atkins, J. F., & Firth, A. E. (2008). An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. PNAS, 105, 5897–5902.
Coutts, B. A., Prince, R. T., & Jones, R. A. C. (2009). Quantifying effects of seedborne inoculum on virus spread, yield losses, and seed infection in the Pea seed-borne mosaic virus–field pea pathosystem. Phytopathology, 99, 1156–1167.
Goodell, J. J., & Hampton, R. O. (1984). Ecological characteristics of the lentil strain of pea seedborne mosaic virus. Plant Disease, 68, 148–150.
Hampton, R. O. (1982). Incidence of the lentil strain of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus as a contaminant of Lens culinaris germ plasm. Phytopathology, 72, 695–698.
Hampton, R. O., Mink, G. I., Bos, L., Inouye, T., Musil, M., & Hagedorn, D. J. (1981). Host differentiation and serological homology of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus isolates. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology, 87, 1–10.
Hampton, R. O., Kraft, J. M., & Muehlbauer, F. J. (1993). Minimizing the threat of seedborne pathogens in crop germplasm: elimination of Pea seedborne mosaic virus from the USDA-ARS germ plasm collection of Pisum sativum. Plant Disease, 77, 220–224.
Hjulsager, C. K., Lund, O. S., & Johansen, I. E. (2002). A new pathotype of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus explained by properties of the P3-6k1- and viral genome-linked protein (VPg)-coding regions. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 15, 169–171.
Johansen, E., Rasmussen, F., Heide, M., & Borkhardt, B. (1991). The complete nucleotide sequence of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus RNA. Journal of General Virology, 72, 2625–2632.
Johansen, I. E., Keller, K. E., Dougherty, W. G., & Hampton, R. O. (1996). Biological and molecular properties of a pathotype P-1 and a pathotype P-4 isolate of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus. Journal of General Virology, 77, 1329–1333.
Jones, R. A. C. (2004). Using epidemiological information to develop effective integrated virus disease management strategies. Virus Research, 100, 5–30.
Kargiotidou, A., Chatzivassiliou, E. K., Tzantarmas, C., & Tokatlidis, I. S. (2015). Seed propagation at low density facilitates the selection of healthy plants to produce seeds with a reduced virus load in a lentil landrace. Seed Science and Technology, 43, 31–39.
Kasschau, K. D., & Carrington, J. C. (1998). A counterdefensive strategy of plant viruses: suppression of posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell, 95, 461–470.
Kavallieratos, N., Tomanović, Ž., Sarlis, P. G., Vayias, B. J., Žikić, V., & Emmanouel, N. E. (2007). Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea) on cultivated and self-sown plants in Greece. Biologia, 62, 335–344.
Khetarpal, R. K., & Maury, Y. (1987). Pea seed-borne mosaic virus: a review. Agronomie, 7, 215–224.
Khetarpal, R. K., Maury, Y., Cousin, R., Burghofer, A., & Varma, A. (1990). Study on resistance of pea to Pea seed-borne mosaic virus and new pathotypes. Annals of Applied Biology, 116, 297–304.
Kohnen, P. D., Johansen, I. E., & Hampton, R. O. (1995). Characterization and molecular detection of the P-4 pathotype of Pea seed-borne mosaic potyvirus. Phytopathology, 85, 789–793.
Lee, K. C., & Wong, S. M. (1998). Variability of P1 protein of Zucchini yellow mosaic virus for strain differentiation and phylogenetic analysis with other potyviruses. DNA Sequence, 9, 275–293.
Makkouk, K. M., Kumari, S. G., & Bos, L. (1993). Pea seed-borne mosaic virus: occurrence in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) and lentil (Lens culinaris Med.) in West Asia and North Africa, and further information on host range, purification, serology, and transmission characteristics. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology, 99, 115–124.
Makkouk, K. M., Kumari, S. G., van Leur, J. A. G., & Jones, R. A. C. (2014). Control of plant virus diseases in cool-season grain legume crops. Advances in Virus Research, 90, 207–254.
Musil, M. (1966). Uber das Vorkommen des Virus des Blattrollens der Erbse in der Slowakei (Vorlaufige Mitteilung). Biologia (Bratislava), 21, 133–138.
Olmos, A., Bertolini, E., Gil, M., & Cambra, M. (2005). Real-time assay for quantitative detection of non-persistently transmitted Plum pox virus RNA targets in single aphids. Journal of Virological Methods, 128, 151–155.
Resuehr, D., & Spiess, A.-N. (2003). A real-time polymerase chain reaction-based evaluation of cDNA synthesis priming methods. Analytical Biochemistry, 322, 287–291.
Revers, F., & García, J. A. (2015). Molecular biology of potyviruses. Advances in Virus Research, 92, 101–199.
Roudet-Tavert, G., German-Retana, S., Delaunay, T., Delecolle, B., Candresse, T., & Le Gall, O. (2002). Interaction between potyvirus helper component-proteinase and capsid protein in infected plants. Journal of General Virology, 83, 1765–1770.
Shiboleth, Y. M., Haronsky, E., Leibman, D., Arazi, T., Wassenegger, M., Whitham, S. A., Gaba, V., & Gal-On, A. (2007). The conserved FRNK box in HC-Pro, a plant viral suppressor of gene silencing, is required for small RNA binding and mediates symptom development. Journal of Virology, 81, 13135–13148.
Soitamo, A. J., Jada, B., & Lehto, K. (2011). HC-Pro silencing suppressor significantly alters the gene expression profile in tobacco leaves and flowers. BMC Plant Biology. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-68.
Syller, J. (2005). The roles and mechanisms of helper component proteins encoded by potyviruses and caulimoviruses. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 67, 119–130.
Torok, V. A., & Randles, J. W. (2007). Discriminating between isolates of PSbMV using nucleotide sequence polymorphisms in the HC-Pro coding region. Plant Disease, 91, 490–496.
Tsitsipis, J. A., Kati, N. I., Margaritopoulos, J. T., Lykouressis, D. P., Avgelis, A. D., Gargalianou, I., Zarpas, K. D., Perdikis, D. C., & Papapanayotou, A. (2007). A contribution to the aphid fauna of Greece. Bulletin of Instectology, 60, 31–38.
van Leur, J. A. G., Freeman, A. E., Aftab, M., Spackman, M., Redden, B., & Materne, M. (2013). Identification of seed-borne Pea seed-borne mosaic virus in lentil (Lens culinaris) germplasm and strategies to avoid its introduction in commercial Australian lentil fields. Australasian Plant Disease Notes. doi:10.1007/s13314-013-0099-5.
Vijayapalani, P., Maeshima, M., Nagasaki-Takekuchi, N., & Miller, W. A. (2012). Interaction of the trans-frame potyvirus protein P3N-PIPO with host protein PCaP1 facilitates potyvirus movement. PLoS Pathogens, 8, e1002639.
Wen, R. H., & Hajimorad, M. R. (2010). Mutational analysis of the putative pipo of soybean mosaic virus suggests disruption of PIPO protein impedes movement. Virology, 400, 1–7.
Wylie, S. J., Coutts, B. A., & Jones, R. A. C. (2011). Genetic variability of the coat protein sequence of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus isolates and the current relationship between phylogenetic placement and resistance groups. Archives of Virology, 156, 1287–1290.
Acknowledgements
This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund – ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program "Education and Lifelong Learning" of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF) ‐ Research Funding Program: THALES (Investing in knowledge society through the European Social Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giakountis, A., Skoufa, A., Paplomatas, E.I. et al. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of a Greek lentil isolate of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus . Phytoparasitica 43, 615–628 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-015-0495-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-015-0495-9