Abstract
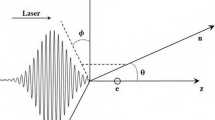
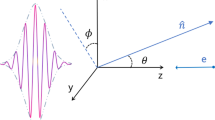
Based on Thomson scattering classical theory and single electron model, numerical simulation of Thomson scattering X-ray source is completed with the help of MATLAB software. We discuss the influence of waist radius and initial phase of few-cycle laser pulse on maximum radiation energy, maximum radiation power, radiation angle distribution and spectrum when the collision center is at or away from the focus. It is found that the initial z-axis position of the electron has no effect on the overall change trend. The influence ability of waist radius appears a “watershed” phenomenon at \({b}_{0}=4{\lambda }_{0}\). When \({b}_{0}=1\sim 3{\lambda }_{0}\), with the increase in the waist radius, the maximum radiation energy and the maximum radiation power increase, and the collimation of laser and the monochromaticity of the spectrum become worse. When \({b}_{0}\ge 4{\lambda }_{0}\), the change in waist radius has no effect on these parameters. In addition, when the initial phase of few-cycle laser pulse increases in the range of 0–360°, the maximum radiation direction rotates counterclockwise, and the values of the maximum radiation energy and the instantaneous power of the maximum radiation energy and the peak value of the spectrum fluctuate only in a small range.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Mourou, T. Tajima et al., Optics in the relativistic regime. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78(2), 309 (2006)
D. Strickland, G. Mourou, Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 56(3), 219 (1985)
A. Dubietis, G. Jonusauskas et al., Powerful femtosecond pulse generation by chirped and stretched pulse parametric amplification in BBO crystal. Opt. Commun. 88(4), 437 (1992)
P. Maine, D. Strickland, P. Bado et al., Generation of ultrahigh peak power pulses by chirped pulse amplification. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 24(2), 398 (1988)
T. Eidam, S. Handf, E. Seise et al., Femtosecond fiber CPA system emitting 830 W average output power. Opt. Lett. 35(2), 94 (2010)
I.N. Ross, P. Matousek et al., The prospects for ultrashort pulse duration and ultrahigh intensity using optical parametric chirped. Opt. Commun. 144(1), 125 (1997)
M.D. Perry, G. Mourou, Terawatt to Petawatt sub-picosecond lasers. Science 264(5161), 917 (1994)
G.A. Mourou, C.P.J. Barry, M.D. Perry, Ultrahigh-intensity lasers: physics of the extreme on a tabletop. Phys. Today 51(1), 22 (1998)
P.B. Corkum, F. Krausz, Attosecond science. Nat. Phys. 3(6), 381 (2007)
F. Krausz, M. Ivanov, Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(1), 163 (2009)
W. Thomlinson, Medical applications of synchrotron radiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 319(1), 295 (1992)
K. Lee, S.Y. Chung, S.H. Park et al., Effects of high-order fields of a tightly focused laser pulse on relativistic nonlinear Thomson scattered radiation by a relativistic electron. Europhys. Lett. 89(6), 613 (2010)
Z. Chi, Y. Du, W. Huang et al., Linearly polarized X-ray fluorescence computed tomography based on a Thomson scattering light source: a Monte Carlo study. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 27(3), 737 (2020)
A. Baltuska, T. Udem, M. Uiberacker et al., Attosecond control of electronic processes by intense light fields. Nature 421(6923), 611 (2003)
O. Vais, S. Bochkarev et al., Nonlinear Thomson scattering of a relativistically strong tightly focused ultrashort laser pulse. Laser Plasma 42, 796 (2016)
Y.Q. Wang, C.L. Wang, K. Li et al., Spatial radiation features of Thomson scattering from electron in circularly polarized tightly focused laser beams. Laser Phys. Lett. 18(1), 015303 (2021)
A. Yariv, Quantum Electron, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1975)
F. He et al., Ponderomotive acceleration of electrons by a tightly focused intense laser beam. Phys. Rev. E 68, 046407 (2003)
Z. Yan, Y.K. Ho, P.X. Wang, J.F. Hua, Z. Chen, L. Wu, Accurate description of ultra-short tightly focused Gaussian laser pulses and vacuum laser acceleration. Appl. Phys. B 81, 813 (2005)
P.F. Lan, P.X. Lu, W. Cao, X.L. Wang, Attosecond and zeptosecond X-ray pulses via nonlinear Thomson backscattering. Phys. Rev. E 72, 066501 (2005)
J.D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1975)
P. Gibbon, High-order harmonic generation in plasmas. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 33(11), 1915 (1997)
J.W. Zhuang, Y.L. Yan, X. Zhou, Z.J. Chen, S.L. Ren, Y.W. Tian, Quasi-monochromatic spectral emission characteristics from electron collision with tightly focused laser pulses. Laser Phys. 31, 035401 (2021)
J.W. Zhuang, Y.Q. Wang, C.L. Wang, Y.F. Cai, Y.W. Tian, Spectral shape of quasi-monochromatic radiation from electron colliding with tightly focused laser pulses. Laser Phys. 31, 065403 (2021)
J.W. Zhuang, X. Zhou, Y.L. Yan, S.L. Ren, H. Liu, Y.W. Tian, Numerical simulation of quasi-monoenergetic X-ray produced by laser pulse colliding with electrons. Laser J. 42(7) (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 10947170/A05 and 11104291, Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant No. 10KJB140006, Natural Sciences Foundation of Shanghai under Grant No. 11ZR1441300 and Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant No. NY221098 and sponsored by Jiangsu Qing Lan Project and STITP Project under Grant No. 202210293150Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, L., Yuan, Y., Zhu, S. et al. Nonlinear Thomson scattering radiation characteristics of strong focusing circular polarization laser pulses with different waist radius and initial phase. J Opt 53, 482–492 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01215-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01215-9