Abstract
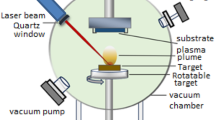
The purpose of this study is to explore if nanostructured WO3 particles can replace traditional, bulkier materials in gas sensing applications. Then, use a Nd-YAG laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm, number of shot 300, 440, 640 mJ, and 840 mJ laser ablated energy, the pulsed laser deposition technique has been widely used to prepare and characterize Tungsten Trioxide nanoparticles on Porous Silicon substrate produced on n-type Silicon wafer. The crystal structure and morphological characteristics of the WO3NPs are studied using X-ray diffraction and field emission-scanning electron microscopy. J–V and Jph–V characteristic in the dark and photocurrent densities, responsivity, quantum efficiency and sensing properties also be investigated. With increasing pulse laser energy, the peaks of the WO3 thin film become sharper, implying enhanced crystallinity. The size of the surface grains grew larger and energy gab as the energy pulse was increased, increasing homogeneity. A detector measurement is based on spectrum responsiveness and quantum efficiency curves, which are divided into three parts, the first of which causes WO3NPs absorption. The second section is in sync with the PS layer’s visible light absorption and due to the silicon surface’s absorption of light; the third area's responsivity emerges in the near infrared range. Changes in operation temperature had an effect on the sensitivity, recovery time, and reaction time of H2S and NO2 gas sensors made from prepared samples. For each of the gases tested, the highest sensitivity was 329% at 640 mJ for H2S gas 444 ppm and 114% at 840 mJ for NO2 gas 226 ppm at 300 °C.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Gullapalli, R. Vemuri, C. Venkata-Ramana, Structural transformation induced changes in the optical properties of nanocrystalline tungsten oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. 96(17), 171903 (2010)
K. Soon Ahn, S. Hee Lee, A. Dillon, C. Edwin Tracy, R. Pitts, “The effect of thermal annealing on photoelectrochemical responses of WO3 thin films. Appl. Phys. 101(9), 093524 (2007)
F. Amano, M. Tian, B. Ohtani, A. Chen, Facile preparation of platelike tungsten oxide thin film electrodes with high photoelectrode activity”. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf 3(10), 4047–4052 (2011)
H. Kim, S. Karuppanan, K. Yong, Photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic properties of tungsten oxide nanorods grown by thermal evaporation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120(2–3), 452 (2010)
F. Amano, D. Li, B. Ohtani, Fabrication and photoelectrochemical property of tungsten (VI) oxide films with a flake-wall structure. Chem Commun. 46(16), 2769 (2010)
K.J. Patel, C.J. Panchal, M.S. Desai, P.K. Mehta, An investigation of the insertion of the cations H+, Na+, K+ on the electrochromic properties of the thermally evaporated wo3 thin films grown at different substrate temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 124(1), 884–890 (2010)
C. Klinke, J. Hannon, L. Gignac, K. Reuter, P. Avouris, Tungsten oxide nanowire growth by chemically induced strain. J. Phys. Chem. B. 109(38), 17787–17790 (2005)
A. Harvin Mahan, P.A. Parilla, K. Jones, A.C. Dillon, Hot-wire chemical vapor deposition of crystalline tungsten oxide nanoparticles at high density. Chem Phys Lett 413(1–3), 88–94 (2005)
X. Chun Song, Y. Fan Zheng, E. Yang Eunmi, Y. Yun Wang, Large-scale hydrothermal synthesis Of WO3 nanowires in the presence of K2SO4. Mater Lett. 61(18), 3904–3908 (2007)
N. Shankar, M. Feng Yu, S.P. Vanka, N.G. Glumac, Synthesis of tungsten oxide (WO3) nanorods using carbon nanotubes as templates by hot filament chemical vapor deposition. Mater Lett. 60(6), 771–774 (2006)
N. Asim, Sh. Radiman, M. Ambar Yarmo, Synthesis of WO3 in nanoscale with the usage of sucrose ester microemulsion and CTAB micelle solution. Mater Lett. 61(13), 2652–2657 (2007)
X. Lu, X. Liu, W. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Wei, Large-scale synthesis of tungsten oxide nanofibers by electrospinning. J Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 2 (2006)
J. Dai, Y. Li, H. Ruan, Z. Ye, N. Chai, X.W. Shuchang Qiu, W. Bai, M. Yang, Fiber optical hydrogen sensor based on WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt nanocomposite films. Nanomaterials 11(1), 128 (2021)
H. Lin, X. Long, Y. An, Sh. Yang, In situ growth of Fe2WO6 on WO3 nanosheets to fabricate heterojunction arrays for boosting solar water splitting. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 21 (2020)
R. Vijayalakshmi, M. Jayachandran, S. Chinnappanadar, Structural, electrochromic and FT-IR studies on electrodeposited tungsten trioxide films. Curr Appl Phys 3(2–3), 171–175 (2003)
D. Susanti, A. Seras Perdana, H.Purwaningsih, and L. Noerochim “Preparation of CO gas sensor from WO3 nanomaterial synthesized via sol-gel method followed by hydrothermal process”, AIP Conference Proceedings. 1586, 14 (2014)
Y. Tsung Hsieh, L. Weichang, Synthesis of WO3 nanorods by thermal CVD at various gas flow rates and substrate temperatures. Electrochem Solid St Lett 14(7), K40 (2011)
T. Song Kima, Y. Bum Kim, K. Soo Yooc, G. Suk Sung, H. Yung Jin Junga, Sensing characteristics of dc reactive sputtered WO3 thin films as an NOx gas sensor. Sens. Actuators, B 62(2), 102 (2000)
L.G. Teoh, Y.M. Hon, J. Shieh, M.H. Hon, Sensitivity properties of a novel NO2 gas sensor based on mesoporous WO3 thin film. Sens. Actuators B Chem 96(1–2), 219 (2003)
R. Sivakumar, A.M.E. Raj, B. Subramanian, M. Jayachandran, D.C. Trivendi, C. Sanjeeviraja, Preparation and characterization of spray deposited n-type WO3 thin films for electrochromic. Mater Res Bull 39(10), 1479 (2004)
G. Kolbasov, Kinetics of coloration of electrochromic tungsten oxide films produced by cathodic electrodeposition. Russ J Appl Chem 79(2), 250–255 (2006)
T. Pauporte, M.C. Bernard, Y. Soldo-Olivier, R. Faure, Structural changes in electrochromic WO3 thin films induced by the first electrochemical cycles. Electrochem. Soc. 151, 5 (2004)
R. Eason, Pulsed laser deposition of thin films: applications-led growth of functional materials (Wiley, New Jersey, 2007)
C.R. Phipps Jr., T.P. Turner, R.F. Harrison, G.W. York, W.Z. Osborne, G.K. Anderson, X.F. Corlis, L.C. Haynes, H.S. Steele, K.C. Spicochi, Impulse coupling to targets in vacuum by KrF, HF, and Co2 single –pulse laser. J. Appl. Phys. 64, 3 (1988)
F. Mutlak, R. Jamal, A. Ahmed, “Pulsed laser deposition of TiO2 nanostructures for verify the linear and non-linear optical characteristics. Iraqi J Science (2021). https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.202162218
M. Abed, F. Mutlak, A. Ahmed, U. Nayef, S. Abdulridha, M. Jabir, Synthesis of Ag/Au (core/shell) nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid and study of their toxicity on blood human components. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1795(1), 012013 (2021)
F. Mutlak, A. Taha, U. Muhsin Nayef, Synthesis and characterization of SnO2 on porous silicon for photoconversion. Silicon-Neth 10(3), 967–974 (2017)
N. Harb, F. Mutlak, Production and characterization of porous silicon via laser-assisted etching: effect of gamma irradiation. Optik 246, 167800 (2021)
D. Jwied, U. Nayef, F. Mutlak, Improvement of responsivity of C: Se nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon". Optik 241, 167222 (2021)
H. Abid, U. Nayef, F. Mutlak, Preparation and characterization Co3O4 nanoparticles on porous silicon for humidity sensor by photoluminescence. Optik 178, 379–383 (2019)
N. Harb, The structure and optical properties of Ag doped CdO thin film prepared by pulse laser deposition (PLD). Baghdad Sci. J. 15, 3 (2018)
J. Christine, G. Nazri, O. Bergström, Raman scattering studies of microcrystalline V6O13. Phys. Status Solidi B Basic Res. 201(1), 319–326 (2017)
S.M. Sze, K.K. Ng, Physics of semiconductor devices, 3rd edn. (Wiley, New Jersey, 2006)
A. Ahmed, W. Yaseen, Q. Abbas, F. Mutlak, Plasma treatment effect on SnO2–GO nano-heterojunction: fabrication, characterization and optoelectronic applications. Appl Phys A 127, 746 (2021)
D. Jwied, U. Nayef, F. Mutlak, Preparation and characterization of C: Se nano-rods ablated on porous silicon. Optik 239, 166811 (2021)
L.A. Patil, A.R. Bari, M.D. Shinde, V.V. Deo, D.P. Amalnerkar, Synthesis of ZnO nanocrystalline powder from ultrasonic atomization technique, characterization, and its application in gas sensing. IEEE Sens J 11, 939–946 (2011)
U. Nayef, R. Kamel, Bi2O3 nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon for sensing NO2 gas. Optik 208, 164146 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harb, N.H., Mutlak, F.AH. Gas sensing characteristics of WO3NPs sensors fabricated by pulsed laser deposition on PS n-type. J Opt 52, 323–331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00877-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00877-1