Abstract
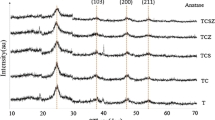
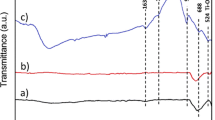
The present study reports the sol–gel synthesis and characterization of pure titania and metal-ion (Manganese) modified photocatalysts. The XRD results of pure titania confirmed the tetragonal structure having anatase as the predominant crystalline phase with no conspicuous presence of any secondary phase. In the modified photocatalysts, the shift in the peak position toward lower 2θ value reflects that manganese is occupying Ti position in TiO2 matrix. The position and width of the Raman peaks of the modified photocatalysts varies with oxygen vacancy and Mn doping level. Ti3+ and oxygen vacancies increased in the modified photocatalysts indicating a remarkable redshift of the absorption edge. Photoluminescence studies confirmed the formation of oxygen vacancy in TiO2 lattice and a decrease in intensity was observed after doping of Mn ions in TiO2. The maximum electrical conductivity of 2.85 × 10–2 S/cm was delivered by Mn2+@TiO2- D photocatalyst, which is more than fourfold of the pure TiO2 photocatalyst. Photocatalytic activity performances were evaluated by irradiating the sample degradation of methylene blue dye under visible light exposure. Mn2+@TiO2-C photocatalyst exhibits great improvement of photocatalytic activity (96%) within 120 min. It is found that Mn2+ doped TiOp2 hotocatalyst bleaches MB much faster than pure TiO2 since the transition metal ions can enhance photocatalytic activity. Mn2+@TiO2-C exhibited two times higher degradation activity toward MB compared to pure TiO2 suggesting that doping Mn2+ into TiO2 could very much enhance the photocatalytic performance and thus aid in environmental application.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Gratzel, Photoelectrochemical cell. Nature 414, 338–344 (2001)
E.G. Judith, J. Wijnhoven, W.L. Vos, Preparation of photonic crystals made of air spheres in Titania. Science 281, 802–804 (1998)
D Maycock C Watts 2011 J Nriagu Eds Encyclopedia of Environmental Health Elsevier Burlington 472 484
L. Linsebigler, G. Lu, J.T. Yates Jr., Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 95, 735–758 (1995)
H. Yu, H. Irie, K. Hashimoto, Conduction band energy level control of titanium dioxide: toward an efficient visible-light-sensitive photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 6898–6899 (2010)
X. Chen, A. Selloni, Introduction: titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 114, 9281–9282 (2014)
Gautam Kumar Naika, PravatManjari Mishra, KulamaniParida, Green synthesis of Au/TiO2 for effective dye degradation in aqueous system. Chem. Eng. J. 229, 492–497 (2013)
P. Pathak, M.J. Meziani, Y. Li, L.T. Cureton, Y.P. Sun, Improving photoreduction of CO2with homogeneously dispersed nanoscale TiO2 catalysts. Chem. Com. 10, 1234–1235 (2004)
Yu. Tao, Xin Tan, Lin Zhao, Yuxin Yin, Peng Chen, Jing Wei, Cerium and nitrogen co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 157, 86–92 (2010)
K.M. Soumyashree Pany, Parida, A facile in situ approach to fabricate N, S-TiO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposite with excellent activity for visible light induced water splitting for hydrogen evolution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 8070–8077 (2015)
Sriram Mansingh, Kundan Kumar Das, Arjun Behera, Satyabrata Subudhi, Sabiha Sultana, Kulamani Parida. (2020). Bandgap engineering via boron and sulphur doped carbon modified anatase TiO2: a visible light stimulated photocatalyst for photo-fixation of N2 and TCH degradation, Nano. Adv.2. 2004–2017
Xuewen Ning, Xixin Wang, Xiaofei Yu, Jianling Zhao, Mingli Wang, Haoran Li, YangYang. 2016. Outstanding supercapacitive properties of Mn-doped TiO2 micro/ nanostructure porous film prepared by anodization method, Sci. Rep. 1-8
K. Sivaranjani, C.S. Gopinath, Porosity driven photocatalytic activity of wormhole mesoporous TiO2-xNx in direct sunlight. J. Mat. Chem. 21, 2639–2647 (2011)
P. Periyat, D.E. McCormack, S.J. Hinder, S.C. Pillai, One-Pot, Synthesis of Anionic (Nitrogen) and Cationic (Sulfur) Codoped high-temperature stable, visible light active. Anatase photocatalysts. J. Phy. Chem. C. 113, 3246–3253 (2009)
S. Pany, B. Naik, S. Martha, K. Parida, Plasmon induced nano au particle decorated over S, N-modified TiO2 for exceptional photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 6, 839–846 (2014)
L.G. Devi, N. Kottam, B.N. Murthy, S.G. Kumar, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of transition metal ions Mn2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ doped polycrystalline titania for the degradation of Aniline Blue under UV/solar light. J. Mol. Cat. A. Chem. 328, 44–52 (2010)
Hanggara Sudrajat, Sandhya Babel, Anh Tuan Ta, Truong Khang Nguyen, Mn-doped TiO2photocatalysts: Role, chemical identity, and local structure of dopant. J. Phy. Chem. Sol. 144, 109517 (2020)
M. Lesnik, D. Verhovsek, N. Veronovski, M. Gracner, G. Drazic, Kristina Zagar Soderznik, Mihael Drofenik, hydrothermal synthesis of mn-doped tio2 with a strongly suppressed photocatalytic activity. Mat. Tech. 52, 411–416 (2018)
Z. Chen, Y. Li, M. Guo, Xu. Fengyun, YuDu. Peng Wang, P. Na, One-pot synthesis of Mn-doped TiO2 grown on graphene and themechanism for removal of Cr (VI) and Cr (III). J. Haz. Mat. 310, 188–198 (2016)
Q.R. Deng, X.H. Xia, M.L. Guo, Y. Gao, G. Shao, Mn-doped TiO2anopowders with remarkable visible light photocatalytic activity. Mat. Lett. 65, 2051–2054 (2011)
R. Chauhan, A. Kumar, Ram Pal Chaudhary, Structural and photocatalytic studies of Mn doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Spec. Act. Part A: Mol. Bio. Spect. 98, 256–264 (2012)
B.H. Shalendra Kumar, ChanGyu Lee. Koo, K.H. Sanjeev Gautam, S.K. Chae, M. Knobel. Sharma, Room temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Cu doped ZnO fun. Mat. Lett. 4(17), 20 (2011)
N.T.Q. Hoa, D.N. Huyen, Comparative Study of Room Temperature ferromagnetism in undoped and Ni doped TiO2 nanowires synthesized by solvothermal method. J. Mat. Sci. Mat Elect. 24, 793–798 (2013)
H. Shi, Y. Duan, First principles study of magnetic properties of 3d transition metals doped in ZnO nanowires. Nano. Res. Lett. 4, 480–484 (2009)
S. Zhou, H. Yuan, L. Liu, X. Chen, S. Lou, Y. Hao, R. Yuan, N. Li, Room temperature ferromagnetism of diamagnetically- doped ZnO aligned nanorods fabricated by vapor reaction. App. Phy. A. 102, 367–371 (2011)
Peter Szirmai, Endre Horvath, Balint Nafradi, Zlatko Mickovic, Rita Smajda, Dejan M. Djokic, Kurt Schenk, Laszlo Forro, Arnaudagrez. , Synthesis of homogeneous manganese doped titanium oxide nanotubes from titanate precursors. J. Phy. Chem. C. 117, 697–702 (2013)
S.A. Ahmed, Annealing effects on structure and magnetic properties of Mn-doped TiO2. J. Mag. Magnetic Mat. 402, 178–183 (2016)
G. Yang, Z. Yan, T. Xiao, B. Yang, Low-temperature synthesis of alkalis doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their photocatalytic performance for degradation of methyl orange. J. All. Com. 580, 15–22 (2013)
N. De la Cruz, R.F. Dantas, J. Gimenez, S. Esplugas, Photolysis and TiO2 photocatalysis of the pharmaceutical propranolol: Solar and artificial light. App. Cat. B: Env. 130–131, 249–256 (2013)
K Song X Han G Shao 2013 Electronic properties of rutile TiO2 doped with d transition metals: first-principles study J. All. Com. 551 118 124
E. Sanchez, T. Lopez, R. Gomez, X. Bokhimi, A. Morales, O. Novaro, Synthesis and characterization of Sol-Gel Pt/TiO2catalyst. J. Sol. Stat. Chem. 122, 309–314 (1996)
Y. Zhao, J. Liu, L. Shi, S. Yuan, J. Fang, Z. Wang, M. Zhang, Surfactant-free synthesis uniform Ti1−xSnxO2 nanocrystal colloids and their photocatalytic performance. App. Cat. B: Env. 100, 68–76 (2010)
K. Ocakoglu, C. Zafer, C. Varlikil, S. Icli, Preparation of dye sensitized titania oxide nanoparticlesfor solar cell applications. Mat. Sci. Semi. Process. 16, 1688–1694 (2013)
R. Mueller, L. Madler, S.E. Pratsinis, Nanoparticle synthesis at high production rates by flame spray pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 58, 1969–1976 (2003)
Y. Tanako, H. Sakai, T.T. Tsuke, Y. Uesugi, Y. Sasai, K. Nakamura, Influence of coil current modulation on TiO2 nanoparticle synthesis using pulse-modulated induction thermal plasmas. Thin sol. Film. 519, 7100–7105 (2011)
A.V. Vinogradov, V.V. Vinogradov, Low – temperature sol – gel synthesis of crystalline materials. RSC Adv. 4, 45903–45919 (2014)
S. Paul, B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Magnetic property study of Gd doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. All. Com. 601, 201–206 (2014)
Anand Kumar Tripathi, Mohan Chandra Mathpal, Promod Kumar, Manish Kumar Singh, M.A.G. Soler, Arvind Agarwal, Structural, optical and photoconductivity of Sn and Mn doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. All. Com. 622, 37–47 (2015)
S. Shalendra Kumar, G.W. Gautam, Faheem Ahmed Kim, M.S. Anwar, K.H. Chae, H.K. Choi, H. Chung, B.H. Koo, Structural, magnetic and electronic structure studies of Mn doped TiO2 thin films. App. Surf. Sci. 257, 10557–10561 (2011)
S.K. MominaKhannam Dolui, Cerium doped TiO2 photoanode for an efficient quasi-solid state dye sensitized solar cells based on polyethylene oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube/polyaniline gel electrolyte. Sol. Energy. 150, 55–65 (2017)
Y. Chen, Y. Li, A. Zhu, Y. Huang, Z. Liu, K. Yan, Degradation of aqueous Rhodamine B by plasma generated along the water surface and its enhancement using nanocrystalline Fe-, Mn-, and Ce-doped TiO2 films. Env. Sci. Poll. Res. 21, 9948–9958 (2014)
Alejandro Perez- Larios, Agileo Hernandez- Gordillo, Getsemani Morales- Mendoza, Luis Lartundo- Rojas, Angeles Mantilla, Ricardo Gomez, Enhancing the H2 evolution from water–methanol solution using Mn2+–Mn+3–Mn4+ redox species of Mn-doped TiO2 sol–gel photocatalysts. Cat. Today. 266(9), 16 (2016)
L. Kernazhitsky, V. Shymanovska, T. Gavrilko, G. Puchkovska, V. Naumova, T. Khalyavk, V. Kshnyakin, V. Chernyak, J. Baran, Optical and photocatalytic properties of titanium–manganese mixed oxides. Mat. Sci. Eng. B. 175, 48–55 (2010)
Y.-M. Hao, S.-Y. Lou, S.-M. Zhou, R.-J. Yuan, G.-Y. Zhu, N. Li, Structural, optical, and magnetic studies of manganese-doped zinc oxide hierarchical microspheres by self-assembly of nanoparticles. Nano. Res. Lett. 7, 100–109 (2012)
S. Mushtaq, B. Ismail, MisbahAurang Zeb, S. Kissinger, A. Zeb, Low-temperature synthesis and characterization of Sn-doped Sb2 S3 thin film for solar cell applications. J. All. Com. 632, 723–728 (2015)
S. Wang, L.N. Bai, H.M. Sun, Q. Jiang, J.S. Lian, Structure and photocatalytic property of Mo-doped TiO2nanoparticles. Pow. Tech. 244, 9–15 (2013)
L.V. Saraf, S.I. Patil, S.B. Ogalae, S.R. Sainkar, S.T. Kshirsager, Synthesis of nanophase Tio2 by ion beam sputtering and cold condensation technique. Int. J. Mod. Phy. B. 12, 2635–2647 (1998)
H. Tang, H. Berger, P.E. Schmid, F. Levy, Photoluminescence in TiO2 anatase single crystals. Sol. State Com. 87, 847–850 (1993)
L. Fross, M. L Schubnell, Temperature dependence of the luminescence of TiO2 powder. Appl. Phys. B 56, 363–366 (1996)
L. Qian, Z.S. Jin, S.Y. Yang, Z.L. Du, X.R. Xu, Bright visible photoluminescence from nanotube titania grown by soft chemical process. Chem. Mat. 17, 5334–5338 (2005)
C.R. Shyniya, K. Amarsingh Bhabu, T.R. Rajasekaran, Enhanced electrochemical behavior of novel acceptor doped titanium dioxide catalysts for photocatalytic applications. J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Elect. 28, 6959–6970 (2017)
T. Jayaraman, Senthil Arumugam Raja, Annadurai Priya, Madhavan Jagannathan, Muthupandian Ashokkumar, Synthesis of a visible-light active V2O5–g-C3N4 heterojunction as an efficient photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical material. RSC New J. Chem. 38, 3220–3226 (2014)
K. Siddhapara, D. Shah, Study of photocatalytic activity and magnetic properties of Co, Mn metal ions doped nanocrystalline TiO2 prepared by Sol-Gel method. J. Cry. Grow. 452, 158–161 (2016)
Maria F. Casula, Erika Conca, Ioanna Bakaimi, Ayyappan Sathya, Maria Elena Materia, Alberto Casu, Andrea Falqui, Elisa Sogne, Teresa Pellegrino, Antonios G. Kanaras, Manganese doped-iron oxide nanoparticle clusters and their potential as agents for magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 16848–16855 (2016)
M. Venkatesan, C. Fitzgerald, J. Lunney, J. Coey, Anisotropic ferromagnetism in substituted Zinc Oxide. Phy. Rev. Lett. 93, 177206–177209 (2004)
Y. Qiu, W. Chen, S. Yang, B. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Zhong, K. Wong, Hierarchical hollow spheres of ZnO and Zn1−xCoxO: directed assembly and room-temperature ferromagnetism. Cry. Grow. Des. 10, 177–183 (2010)
X. Ning, X. Wang, Yu. Xiaofei, J. Li, J. Zhao, Preparation and capacitance properties of Mn-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays by anodisation of Ti–Mn alloy. J. Alloy. Com. 658, 177–182 (2016)
R. Poonguzhali, N. Shanmugam, R. Gobi, A. Senthilkumar, G. Viruthagiri, N. Kannadasan, Effect of Fe doping on the electrochemical capacitor behavior of MnO2 nanocrystals. J. Pow. Source. 293, 790–798 (2015)
Z Chen, Y Li, MengGuo, Fengyun Xu, Peng Wang, Yu Du, Ping Na. One-pot synthesis of Mn-doped TiO2 grown on graphene and themechanism for removal of Cr (VI) and Cr (III). J. Haz. Mat. 310 188 198
He. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Enhanced electrochemical performance of manganese dioxide spheres deposited on a titanium dioxide nanotube arrays substrate. Pow. Source. 272, 866–879 (2014)
R. Mohammadpour, A. Irajizad, N. Taghavinia, M. Rahman, M.M. Ahadian, Electrochemically assisted photocatalytic oxidation of methanol on TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Mat. Sci. Tech. 26, 535–541 (2010)
S.T. Nishanthi, S. Iyyapushpam, B. Sundarakannan, E. Subramanian, D. Pathinettam Padiyan, Significance of crystallinity on the photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotube arrays. App. Surf. Sci. 313, 449–454 (2014)
S. Iyyapushpam, S.T. Nishanthi, D. PathinettamPadiyan, Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by gamma Bi2O3 and its kinetics. J. All. Com. 601, 85–87 (2014)
T. Jeyaraman, Senthil, Annadurai, Madhavan, Muthupandian Ashok Kumar, synthesis of visible-light active V2O5/g-C3N4 heterojunction as an efficient photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance. New J. Chem. 39, 1367–1374 (2015)
Y. Chen, S. Zhang, Y. Yu, H. Wu, S. Wang, B. Zhu, Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of N-Doped TiO2 nanotubes. J. Disp. Sci. Tech. 29, 245 (2008)
C. Zhu, I. Wang, L. Kong, X. Xang, S. Zheng, F. Chen, F. Maizhi, H. Zong, Photocatalytic degradation of AZO dyes by supported TiO2 + UV in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 41, 303–309 (2000)
M.N. Rashed, A.A. El-Amin, Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 under different solar irradiation sources. Int. J. Phy. Sci. 2, 73–81 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shyniya, C.R., Rajasekaran, T.R. Investigation on influence of manganese nanoparticles loading in electrochemical activity of anatase titania catalysts and its role in photocatalytic performance. J Opt 51, 246–259 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00775-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00775-y