Abstract
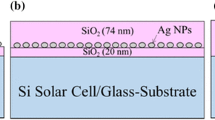
Plasmonics is a new promising approach to enhance the light absorption in the thin film solar cells. The plasmonic effects of the metal nanoparticle introduced in thin film solar cells could also be detrimental for the higher optical absorption and hence the higher efficiency of solar cells. The effects of the Ag nanospheres arrays on the absorption of amorphous silicon solar cells were investigated by a numerical simulation based on the finite element method. The light absorption under different radius and width of the grating has been calculated. The optimization results show that the absorption of the solar cell with Ag nanospheres is enhanced up to 64 % under AM1.5 illumination in the 500–730 nm wavelength range compared with the reference cell. The physical mechanisms of absorption enhancement in different wavelength range have been discussed. These results are promising for the design of amorphous silicon thin film solar cells with enhanced performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Bullock, D.Y. Yan, Y.F. Wan, A. Cuevas, Amorphous silicon passivated contacts for diffused junction silicon solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 163703 (2014)
V. Gusak, B. Kasemo, C. Hagglund, High aspect ratio plasmonic nanocones for enhanced light absorption in ultrathin amorphous silicon films. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 22840–22846 (2014)
B. Rech, T. Repmann, M. Berginski, Challenges in microcrystalline silicon based solar cell technology. Thin Solid Films 511, 548–555 (2006)
J. Mueller, B. Rech, J. Springer, M. Vanecek, TCO and light trapping in silicon thin film solar cells sol. Energy 77, 917–930 (2004)
D. Zhang, D. Deligiannis, G. Papakonstantinou, A.C.M.M. Rene, V. Swaaij, M. Zeman, Optical enhancement of silicon heterojunction solar cells Wi hydrogenated amorphous silicon carbide emitter. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4, 1326–1330 (2014)
S.A. Maier, Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications (Springer, New York, 2007)
S.L. He, Y.X. Cui, Y.Q. Ye, P. Zhang, Y. Jin, Optical nano-antennas and metamaterials. Mater. Today 12, 16–24 (2009)
J.A. Schuller, E.S. Barnard, W.S. Cai, Y.C. Jun, J.S. White, M.L. Brongersma, Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat. Mater. 9, 193–204 (2010)
H. Raether, Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings (Springer, Berlin, 1988)
U. Kreibig, M. Vollmer, Optical Properties of Metal Clusters (Springer, Berlin, 1995)
M.A. Sefunc, A.K. Okyay, H.V. Demir, Plasmonic backcontact grating for P3HT: PCBM organic solar cells enabling strong optical absorption increased in all polarizations. Opt. Express 19, 14200–14209 (2011)
H.H. Shen, P. Bienstman, B. Maes, Plasmonic absorption enhancement in organic solar cells with thin active layers. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 073109–073113 (2009)
K.Q. Le, A. Abass, B. Maes, P. Bienstman, A. Alu, Comparing plasmonic and dielectric gratings for absorption enhancement in thin-film organic solar cells. Opt. Express 20, A39–A50 (2012)
A. Abass, H.H. Shen, P. Bienstman, B. Maes, Angle insensitive enhancement of organic solar cells using metallic gratings. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 023111 (2011)
V.E. Ferry, M.A. Verschuuren, H.B. Li, R.E.I. Schropp, H.A. Atwater, A. Polman, Improved red-response in thin film a-Si: H solar cells with soft-imprinted plasmonic back reflectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 183503 (2009)
E.D. Palik, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (Academic, New York, 1998), pp. 350–369
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11204276) and the key project of scientific research in Colleges and universities in Henan Province (Nos. 15A140041, 15A140044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Yang, Se., Han, J. et al. Research of Ag nanospheres for absorption enhancement in amorphous silicon thin film solar cells. J Opt 46, 265–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-016-0370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-016-0370-1