Abstract
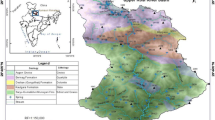
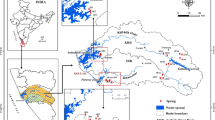
Spring water is a reliable source of potable water in many parts of the world. Uplifted coasts of the Southern Kerala host many high yielding cold water springs which emerge from the sand - clay interface of the Neogene outcrops. Lack of adequate studies on the hydrological and water quality aspects of these springs is challenging the wise use and management of these springs. Therefore, an attempt has been made to map the locations and study the water quality of the free-falling type of springs emerging from the Neogene outcrops exposed on the cliffed coasts of Southern Kerala, especially falling within the jurisdiction of Kollam and Thiruvananthapuram districts. A total of 31 springs from four distinct geomorphic settings has been located in our survey conducted in 2008–2009 period. But, our recent survey carried out in March 2017 revealed that about 10 % of the springs were dried out due to various reasons. The total spring water discharge during 2017 was about 450 liters/minute against the total discharge of 800 liters/minute in 2007–08 period. In general, the hydrochemistry of spring waters is dominated by alkali and strong acids, i.e. alkali-chloride type. Most of the hydrochemical parameters exhibit a great degree of seasonal and spatial variations and are well within the permissible limits (with the exception of pH) for all four groups of springs. The low mineral contents may be attributed to minimal weathering from silicate-rich rocks and insignificant leaching from soil due to infiltration from anthropogenic activities. The spring water quality in all the four groups of the study area is bacteriologically contaminated and therefore proper disinfection is required before human consumption. Most of the spring water samples are classified to be “excellent to good” for irrigation and is not expected to cause any salinity hazard.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA.
Bhargava, D.S. and Killender, D.J. (1988) The technology of water resources in industries. A rational approach. Jour. Indian Water Works Assoc., v.20, pp.107–112.
BIS (2012) Indian standard drinking water specifications, IS 10500:2012.
CGWB (2009) Ground water information booklet of Kollam district. Central Ground Water Board, Thiruvananthapuram: Kerala state.
CPCB (2008) Guidelines for water quality management. New Delhi: Central Pollution Control Board.
Eaton, F.M. (1954) Formulas for estimating leaching and gypsum requirements of irrigation waters. Texas Agricultural Experiment Station.
Grimmeisen, F., Lehmann, M.F., Liesch, T., Goeppert, N., Klinger, J., Zopfi, J. and Goldscheider, N. (2017) Isotopic constraints on water source mixing, network leakage and contamination in an urban groundwater system. Science of the Total Environment, v.583, pp.202–213.
Joshi, D.M., Kumar, A. and Agrawal, N. (2009). Assessment of the irrigation water quality of river Ganga in Haridwar district. Rasayan Jour. Chem., v.2(2), pp.285–292.
Kelepertsis, A., Tziritis, E., Kelepertzis, E., Leontakianakos, G. and Pallas, K. (2009). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic implications of Edipsos thermal springs, north Euboea, Greece. Central European Jour. Geosciences, v.1(3), pp.241–250.
Nagaraju, A., Suresh, S., Killham, K. and Hudson-Edwards, K. (2006) Hydrogeochemistry of waters of mangampeta barite mining area, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India. Turkish Jour. Engg. Environ. Sci., v.30(4), pp.203–219.
Padmalal, D., Maya, K., Babu, K.N. and Sreebha, S. (2007) Environmental effects of mining and processing of China clay a case from Velichikkala, Kollam dist., Kerala. Report submitted to the Department of Environment, Government of Kerala.
Pichamuthu, C.S. (1967) Physical Geography of India. Delhi: National Book Trust (India). 244p.
Piper, A.M. (1953) A graphic procedure for the geo-chemical interpretation of water analysis. USGS Groundwater (No. 12). note.
Prasad, N.B.N. (1984) Hydrogeological studies in the Bhadra River Basin. Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. thesis, University of Mysore, Karnataka, India, p.323.
Reuter, M., Piller, W. E., Harzhauser, M., Kroh, A., Roegl, F. and Coric, S. (2011) The Quilon Limestone, Kerala Basin, India: an archive for Miocene Indo Pacific seagrass beds. Lethaia, v.44(1), pp.76–86.
Richards, L.A. (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Science, v.78(2), pp.154.
Saleh, A., Al-Ruwaih, F. and Shehata, M. (1999) Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. Jour. Arid Environ., v.42(3), pp.195–209.
Schoeller, H. (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development. UNESCO, pp.54–83.
Schoeller, H. (1977) Geochemistry of Groundwater. Groundwater Studies-An International Guide for Research and Practice. UNESCO, Paris, Ch. 15, pp.1–18.
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, recommendations (3rd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wilcox, L. (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. USDA Circular No. 969, Washington, DC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maya, K., Das, P., Sreelash, K. et al. The Coastal Springs of Southern Kerala, SW India – Hydrology and Water Quality Assessment. J Geol Soc India 92, 616–625 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1075-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1075-7