Abstract
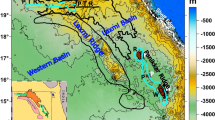
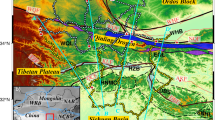
The Western Ghats (WG), a topographic scarp facing towards the west coast of India and extending over diverse geological terranes – Deccan Volcanic Province (DVP), Dharwar Craton (DC) and Southern Granulite Terrain (SGT), is an enigmatic geomorphic feature. WG is characterized by low gravity anomalies. In order to decipher the sources of gravity anomalies, we have decomposed the gravity anomalies using wavelength filter and have obtained estimates of the depth to crust-mantle boundary (CMB) under WG and surrounding regions from the inversion of gravity data, which is compared with seismically determined CMB estimates. Overall, the CMB depth varies from 33 to 50 km, which is consistent with seismically determined values, except in the region of shear zones between DC and SGT probably indicating a different density contrast at CMB. The major source of gravity low is found to be the deepening of CMB under the WG compared to adjacent regions regardless of surface lithology. The CMB depths under WG and surrounding region generally approximate the CMB depths estimated for low strength flexural isostatic models, which suggests that flexural compensation of uplifted topography, later modified by tectonic and denudation processes, is a likely development model for the Western Ghats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora, K., Tiwari, V.M., Singh, B., Mishra, D.C. and Gravimeter, I. (2012) Lithospheric Structure and Tectonic Evolution of the Western Continental Margin of India - evidence from 3D Modelling of Gravity and Geoid Data. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.190, pp.131–150; doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05506.x
Buck, W.R. (1986) Small scale convection induced by passing rifting: the cause of uplift of rift shoulders, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.77, pp.362–372.
Cochran, J.R. (1983) Effects of finite extension times on the development of sedimentary basins, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.66, pp.289–302.
Courtillot, V., Besse, J., Vandamme, D., Montigny, R., Jaeger, J.J. and Cappetta, H. (1986) Deccan flood basalts at the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.80, pp.361–374.
Cox, N.J. (1980) On the relationship between bedrock lowering and regolith thickness: Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, v.5, p. 271–274.
Corfield, R.I., Carmichael, S., Bennet, J., Akhter, S., Fatimi, M. and Carig, T., (2010) Variability in the crustal structure of the West Indian Continental Margin in the Northern Arabian Sea. Petroleum Geoscience, v.16, pp.257–265.
Devey, C.W. and Lightfoot, P.C. (1986) Volcanological and tectonic control of stratigraphy and structure in the western Deccan traps, Bull. Volcanol., v.48, pp.195–207.
Feng, M., Van der Lee, S., Assumpção, M. (2007) Upper mantle structure of South America from joint inversion of waveforms and fundamental-mode group velocities of Rayleigh waves. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.112, B04312. DOI: 10.1029/2006JB004449.
Fermor, L.L. (1936) An attempt at the correlation of the ancient schistose formations of Peninsular India. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.70, pp.1–52.
Fountain, D.M., Salisbury, M.H. (1981) Exposed cross-sections through the continental crust; implications for crustal structure, petrology and evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.56, pp.263–277.
Gilchrist, A.R. and Summerfield, M.A. (1994) Tectonics model of passive margin evolution and their implications for theories of long term landscape development, In Kirby, M.J. (Ed.), Process Models and Theoretical Geomorphology, John Wiley and Sons Ltd., pp.5–84.
Gunnell, Y. (2001) Dynamics and kinematics of rifting and uplift at the western continental margin of India, Insights from geophysics and numerical models. In: Gunnell, Y. and Radhakrishna, B.P. (Eds.), Sahyadri: the Great Escarpment of the Indian Subcontinent. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.47, pp.475–496.
Gunnell, Y., and Fleitout, L. (2000) Morphotectonic evolution of the Western Ghats, India. In: Summerfield, M. (Ed.), Geomorphology and Global Tectonics. John Wiley and Sons, pp.321–338.
Kaila, K.L., Chowdhury, R.K., Reddy, P.R., Krishna, V.G., Narain, Hari, Subbotin, S.I., Sollogub, V.B., Chekunov, A.V., Kharetchko, G.E., Lazarenko, M.A., Ilchenko, T.V. (1979) Crustal structure along KavalieUdipi profile in the Indian peninsular shield from deep seismic sounding. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.20, pp.307–333.
Kumar, N., Zeyen, H., Singh, A.P., Singh, B. (2013) Lithospheric structure of Southern Indian shield and adjoining oceans: integrated modelling of topography, gravity, geoid and heat flow data. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.194, pp.30–44. DOI:10.1093/gji/ggt080.
Kumar, N., Singh, A. P., and Singh, B. (2011) Insights into the crustal structure and geodynamic evolution of the Southern Granulite Terrain, India, from isostatic considerations. Pure Appld. Geophys., v.168, pp.1781–1798
Lloyd, S., van der Lee, S., França, G.S., Assumpção, M., Feng, M. (2010) Moho map of South America from receiver functions and surface waves. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.115, pp.B11315. DOI:10.1029/2009JB006829.
Matmon, A., Bierman, P., and Enzel, Y. (2002) Pattern and tempo of great escarpment erosion. Geology, v.30(12), pp.1135–1138. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613
Mishra, D.C. (1988) Geophysical evidence of thick crust south of Palghat–Tiruchi gap in the high grade terrain of south India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.31, pp.79–81.
Mishra, D.C., Tiwari, V.M., Gupta, S.B., Vyaghreswara Rao, M.B.S. (1998) Anomalous mass distribution in epicentral area of Latur earthquake. Curr. Sci., v.74, pp.469–471.
Moore, A., Blenkinsop, T. and Cotterill, F. (2009) Southern African topography and erosion history: plumes or plate tectonics? Terra Nova, v.21, pp.310–315.
Morgan, W.J. (1972) Deep mantle convection plumes and plate motions, Bull. Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol., v.56, pp.203–213.
Nair, M.M., Vidhyadharan, K.T., Pawar, S.D., Sukumaran, P.V., Murthy Y.G.K., (1976) The structural and stratigraphic relationship of the schistose rocks and associated igneous rocks of the Tellicherry–Manantoddy area, Cannanore district, Kerala. Indian Minerals, v.16, pp.89–100.
Nielsen, S.B., Clausen, O.R., Jacobsen, B.H., Thomsen, E., Huuse, M., Gallagher, K., Balling, N. and Egholm, D. (2010) The ICE hypothesis stands: How the dogma of late Cenozoic tectonic up-lift can no longer be sustained in the light of data and physical laws. Jour. Geodyn., v.50, pp.102–111.
Nielsen, S.B., Gallagher, K., Leightonc, C., Balling, N., Svenningsen, L., Jacobsen, B.H., Thomsen, E., Nielsen, O.B., Heilmann-Clausen, C., Egholm, D.L., Summerfield, M.A., Clausen, O.R., Piotrowski, J.A., Thorsen, M.R., Huuse, M., Abrahamsen, N., King, C. and Lykke-Andersen, H. (2009) The evolution of western Scandinavian topography: a review of Neogene uplift versus the ICE (isostasy–climate–erosion) hypothesis. Journal Geodyn., v.47, pp.72–95.
McKenzie, D. (1978) Some remarks on the development of sedimentary basins. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.40, pp.25–32.
Norton, I.O., and Sclater J.G. (1979) Model for the Evolution of the Indian-Ocean and the Breakup of Gondwanaland. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.84, pp.6803–6830.
Paul H., Ravi Kumar, M., Tiwari, V.M., Srinagesh D., Chadha, R.K. (2018) Density contrast across the Moho beneath the Indian shield: Implications for Isostasy. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.154, pp.67–81. DOI: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.12.009
Radhakrishna, B.P. and Vaidyanadhan, R. (1997) Geology of Karnataka. Geological Society India, Bangalore.
Rai, S.S., Borah, K., Das, R., Gupta S., Srivastava, S., Prakasam, K.S., Sivaram, K., Kumar, S., and Meena, R. (2013) The South India Precambrian crust and shallow lithospheric mantle: Initial results from the India Deep Earth Imaging Experiment (Index). Jour. Earth System Sci., v.122(6), pp.1435–1453.
Richards, M.A., Duncan, R.A., Courtillot, V. (1989) Flood basalts and hot spot tracks: plume heads and tails. Science, v.246, pp.103–107.
Singh, A.P., Mishra, D.C., Gupta, S.B. and Rao, M.R.K.P. (2004) Crustal structure and domain tectonics of the Dharwar craton (India): insight from new gravity data. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.23(1), pp.141–152.
Storey, M., Mahoney, J.J., Saunders, A.D., Duncan, R.A., Kelley, S.P., Coffin, M.F. (1995) Timing of hotspot-related volcanism and the breakup of Madagascar and India. Science, v.267, pp.852–855.
Subrahmanyam, C., and Verma, R.K. (1986) Gravity field, structure and tectonics of the Eastern Ghats. Tectonophysics, v.126, pp.195–212.
Subramanyam, K.S., and Muraleedharan, M.P. (1985) Origin of the Palghat Gap in South India–A Synthesis. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.26(1), pp.28–37.
Tiwari V.M., Rao, M.B.S.V. and Mishra D.C. (2001) Density inhomogeneities under Deccan Volcanic Province as derived from gravity data., Jour. Geodynamics, v.31, pp.1–17.
Tiwari, V.M., Mishra, D.C. (1999) Estimation of effective elastic thickness from gravity and topography data under the Deccan Volcanic Province, India. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.171(2), pp.289–299.
Weissel, J.K. and Karner, G.D. (1989) Flexural uplift of rift flanks due to mechanical unloading of the lithosphere during extension. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.94, pp.13,919–13,950.
Widdowson, M. and Cox, K.G. (1996) Uplift and erosional history of the Deccan traps, India: evidence from laterites and drainage patterns of the WG and Konkan coast, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.137, pp.57–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubey, C.P., Tiwari, V.M. Gravity Anomalies and Crustal Thickness Variations over the Western Ghats. J Geol Soc India 92, 517–522 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1059-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1059-7