Abstract
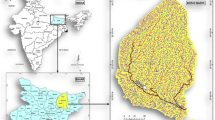
Demand for irrigation water increases day by day along with meteorological vagaries and extension of irrigated area in the drought-prone Barind area of Bangladesh. This increasing stress on water resource is gradually making the area water scare. The study is aimed at studying the morphometric parameters of the Atrai-Sib river basin in the Barind area and on their relevance in water resource management based on satellite images and SRTM DEM. Computation and delineation of linear and areal aspects of the river basin and its morphometric components reveals that stream order ranges from first to eighth order showing dendritic drainage pattern. The basin represents homogeneity of soil texture; possibility of flash flood after heavy rainfall with low discharge of runoff; and is not largely affected by structural disturbance. Moderate drainage density of the river basin area indicates semipermeable soil lithology with moderate vegetation. Mean bifurcation ratio of the basin is calculated as 3.92 and elongation ratio 0.75, which indicate elongated shape of the river basin with low to moderate relief bounded in the east and west by ‘moderate to steep’ sloping land area. It reveals a flatter peak of runoff flow for longer duration and gravity flow of water. The gentle but undulating slope of the basin represents ‘excellent’ category for groundwater management as the site is favorable for infiltration due to maximum time of runoff water percolation. The east facing slopes of the basin show higher moisture content and higher vegetation than the west-facing slope. The land use pattern of the area shows that major part (95.29%) comes under the cultivated land which will support future river basin development and management. Results obtained from the study would be useful in categorization of river basins for future water resource development and management, and selection of suitable sites for water conservation structures such as check dam, percolation tank, artificial recharge of groundwater through MAR technique etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, M.S. (1998) Paleoclimatic impact on the flood basin accretion and paleosol development in northwestern Bangladesh. Jour. Nepal Geol. Soc., v.18, pp.227–238.
Alexander, D. (1995) Changing perspectives on natural hazards in Bangladesh. Natural Hazards Observation, v.10(1), pp.1–2.
Berhanu, B., Melesse, A.M., Seleshi, Y. (2013) GIS-based hydrological zones and soil geo-database of Ethiopia. Catena, v.104, pp.21–31.
BMDA (Barind Multipurpose Development Authority) (2001) Project Proforma (rebound) for the Barind Integrated Area Development Project, Phase-II (4th revision), Barind Multipurpose Development Authority, Rajshahi.
Brammer, H. (1987) Drought in Bangladesh: lessons for planners and administrators. Disasters, v.1(1), pp.21–29.
Brammer, H. (1996) The Geography of the Soils of Bangladesh, 1st Ed, The University Press Limited, p.287.
Burrough, P.A., McDonnell, R.A. (1998) Principles of GIS. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, p.333.
Chitra, C., Alaguraja, P., Ganeshkunari, K., Yuvaraj, D., Manivel, M. (2011) Watershed characteristics of Kundah subbasin using remote sensing and GIS technique. Internat. Jour. Geomatics Geosci., v.2(1), pp.311–335.
Ellis, J.B., Revitt, D.M. (2010) The management of urban surface water drainage in England and Wales. Water and Environ. Jour., v.24, pp.1–8.
Eyquem, J. (2007) Using fluvial geomorphology to inform integrated river basin management. Water and Environ. Jour., v.21, pp.54–60.
Grohmann, C.H. (2004) Morphometric analysis in geographic information systems: applications of free software. Computer Geoscience, v.30, pp.1055–1067.
Hlaing, T.K., Haruyama, S., Aye, M.M. (2008) Using GIS-based distributed soil loss modeling and morphometric analysis to prioritize watershed for soil conservation in Bago river basin of lower Myanmar. Frontierd Earth Sci., China, v.2, pp.465–478.
Horton, R.E. (1932) Drainage basin characteristics. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v.13, pp.350–361.
Horton, R.E. (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.56, pp.275–370.
IRRI (International Rice Research Institute) (2010) World rice statistics (WRS), Manila, Philippines.
Jahan, C.S. and Ahmed, M. (1997) Flow of groundwater in the Barind area, Bangladesh: implication of structural framework. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.50, pp.743–752.
Jahan, C.S., Mazumder, Q.H., Islam, A.M.M. and Adham, M.I. (2010) Impact of Irrigation in Barind Area, NW Bangladesh -An Evaluation Based on the Meteorological Parameters and Fluctuation Trend in Groundwater Table. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.76, pp.134–142.
Jahan, C.S., Mazumder, Q.H. and Islam, T.M.M. (2008) Impact Evaluation of an Irrigation Project Based on Meteorological Data and Groundwater Hydrograph: A Case Study of BIADP, NW Bangladesh. Published in the Proceedings of the XXXIX IAH Congress (IAH 2008), Toyama, Japan. Held on 26 October to 1 November 2008.
Jahan, C.S., Rahman, A.T.M.S., Mazumder, Q.H., Kamruzzaman, M. (2015) Adaptation for Climate Change Effect on Groundwater Resource through MAR Technique in Drought Prone Barind Area, Rural Bangladesh. In S.M. Ali (Ed.), Bangladesh: Combating Land Degradation and Drought (pp.61-83). Dhaka: Series-II, Department of Environment (DoE), Ministry of Environment (MoEF), Government of Bangladesh.
Javed, A., Khanday, M.Y. and Ahmed, R. (2009) Prioritization of sub-watershed based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.37, pp.261–274.
Jha, M.K., Chowdhury, A., Chowdary, V.M. and Peiffer, S. (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated RS and GIS: Prospects and constraints. Water Resource Management, v.21, pp.427–467.
Khandoker, R.A. (1987) Origin of elevated Barind Madhupur areas, Bengal BasIn: Results of neotectonic activities, Bangladesh Jour. Geol., v.6, pp.1–9.
Korkalainen, T.H.J., Lauren, A.M. and Kokkonen, T.S. (2007) A GIS based analysis of catchment properties within a drumlin field. Boreal Environ. Res., v.12, pp.489–500.
Maathuis, B.H.P. (2006) Digital elevation model based on hydro-processing. Geocarto Internat., v.21(1), pp.21–26.
Mark, D.M. (1984) Automatic detection of drainage networks from digital elevation models. Cartographica, v.21, pp.168–178.
Miller, V.C. (1953) A Quantitative Geomorphologic Study of Drainage Basin Characteristics in the Clinch Mountain Area, Virginia and Tennessee, Project NR 389042, Tech Rept 3. Columbia University Department of Geology, ONR Geography Branch, New York.
Morgan, J.P. and McIntire, W.G. (1959) Quaternary geology of the Bengal Basin, East Pakistan and India. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.70, pp.319–342.
Nian, Y., Li, X., Zhou, J. and Hu, X. (2014) Impact of land use change on water resource allocation in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin in northwestern China. Jour. Arid Land, v.6(3), pp.273–286.
Pankaj, A. and Kumar, P. (2009) GIS based morphometric analysis of five major sub-watershed of Song River, Dehradun district, Uttarakhand with special reference to landslide incidences. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.37, pp.157–166.
Rahman, A.T.M.S., Jahan, C.S., Mazumder, Q.H., Kamruzzaman, M. and Hossain, A. (2016a) Evaluation of spatio-temporal dynamics of water table in NW Bangladesh -an integrated approach of GIS and statistics. Sustainable Water Resource Managmt., doi:10.1007/s40899-016-0057-4.
Rahman, A.T.M.S., Kamruzzaman, M., Jahan, C.S. and Mazumder, Q.H. (2016b) Long-term trend analysis of water table using ‘MAKESENS’ model and sustainability of groundwater resources in drought prone Barind Area, NW Bangladesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.87, pp.179–193.
Rao, N.S. (2008) A numerical scheme for groundwater development in a watershed basin of basement terraIn: a case study from India. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.17, pp.379–396.
Rawat, J.S., Biswas, V., Kumar, M. (2013) Changes in land use cover using geospatial techniques: A case study of Ramnagar town area, district Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. Egyptian Jour. Remote Sensing and Space Sci., v.16, pp.111–117.
Schumm SA (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., 67:597–646.
Schumm, S.A. (1963) Sinuosity of alluvial rivers in the Great Plains. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.74, pp.89–1100.
Scott, C.A., Sharma, B. (2009) Energy supply and the expansion of groundwater irrigation in the Indus-Ganges Basin; Internat. Jour. River Basin Management, v.7(2), pp.119–124.
Singh, P., Thakur J.K., Kumar, S., Singh, U.C. (2012) Assessment of land use/land cover using Geospatial Techniques in a semi-arid region of Madhya Pradesh, India. In: Hakur, Singh, Prasad, Gossel (Eds.), Geospatial Techniques for Managing Environmental Resources, Springer and Capital Publication, Heidelberg, Germany, pp.152–163.
Singh, P., Thakur, J.K., Singh, U.C. (2013) Morphometric analysis of Morar River Basin, Madhya Pradesh, India, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Environ. Earth Sci., v.68, pp.1967–1977.
Smith, K.G. (1950) Standards for grading texture of erosional topography. Amer. Jour. Sci., v.248, pp.65–668.
Sreedevi, P.D., Sreekanth, P.D., Khan, H.H., Ahmed, S. (2013) Drainage morphometry and its influence on hydrology in a semi-arid region: using SRTM data and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci., v.70(2), pp.839–848.
Strahler, A.N. (1957) Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v.38, pp.913–920.
Strahler, A.N. (1964) Quantative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks. In: Te Chow, Ven. (Ed.), Hand Book of Applied Hydrology, McGraw Hill Book Company, New York.
Sylla, L., Xiong, D., Zhang, H.Y., Bangoura, S.T. (2012) A GIS technology and method to assess environmental problems from land use/cover changes: Conakry, Coyah and Dubreka region case study. Egyptian Jour. Remote Sensing and Space Sci., v.15, pp.31–38.
Tarboton, D.G. (1997) A new method for the determination of flow directions and contributing areas in grid digital elevation models. Water Resources Res., v.33, pp.309–319.
Wagner, P.D., Kumar, S. and Schneider, K. (2013) An assessment of land use change impacts on the water resources of the Mula and Mutha rivers catchment upstream of Pune, India. Hydrology and Earth System Science, v.17(6), pp.2233–2246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahan, C.S., Rahaman, M.F., Arefin, R. et al. Morphometric Analysis and Hydrological Inference for Water Resource Management in Atrai-Sib River Basin, NW Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and GIS Technique. J Geol Soc India 91, 613–620 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0912-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0912-z