Abstract
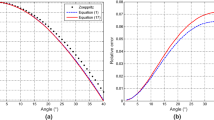
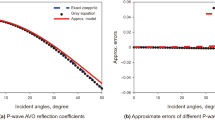
Elastic impedance (EI) inversion has been widely used in industry to estimate kinds of elastic parameters to distinguish lithology or even fluid. However, it is found that conventional three-term elastic impedance formula is unstable even with slight random noise in seismic data, due to the ill-conditioned coefficient matrix of elastic parameters. We presented two-term Fatti elastic impedance inversion method, which is more robust and accurate than conventional three-term elastic impedance inversion. In our method, density is ignored to increase the robustness of inversion matrix. Besides, P-impedance and S-impedance, which are less sensitive to random noise, are inverted instead of V P and V S in conventional three-term elastic impedance. To make the inversion more stable, we defined the range of K value as a constraint. Synthetic tests claim that this method can obtain promising results with low SNR (signal noise ratio) seismic data. With the application of the method in a 2D line data, we achieved λρ, μρ and V P/V S sections, which matched the drilled well perfectly, indicating the potential of the method in reservoir prediction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki, K., Richards, P. G., 1980. Quantitative Seismology, 2nd Ed.. W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco. 557
Bruce, V., VerWest, B., Masters, R., et al., 2000. Elastic Impedance Inversion. Expanded Abstracts of 70th SEG Mtg., Calgary. 1580–1582
Cambois, G., 2000. AVO Inversion and Elastic Impedance. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2000, 142–145. doi:10.1190/1.1815671
Castagna, J. P., Batzle, M. L., Eastwood, R. L., 1985. Relationships between Compressional-Wave and Shear-Wave Velocities in Clastic Silicate Rocks. Geophysics, 50(4): 571–581. doi:10.1190/1.1441933
Connolly, P., 1999. Elastic Impedance. The Leading Edge, 18(4): 438–452. doi:10.1190/1.1438307
Downton, J. E., 2005. Seismic Parameter Estimation from AVO Inversion: [Dissertation]. University of Calgary, Calgary
Fatti, J. L., Smith, G. C., Vail, P. J., et al., 1994. Detection of Gas in Sandstone Reservoirs Using AVO Analysis: A 3-D Seismic Case History Using the Geostack Technique. Geophysics, 59(9): 1362–1376. doi:10.1190/1.1443695
Gardner, G. H. F., Gardner, L. W., Gregory, A. R., 1974. Formation Velocity and Density—The Diagnostic Basics for Stratigraphic Traps. Geophysics, 39(6): 770–780. doi:10.1190/1.1440465
Greenberg, M. L., Castagna, J. P., 1992. Shear-Wave Velocity Estimation in Porous Rocks: Theoretical Formulation, Preliminary Verification and Applications. Geophysical Prospecting, 40(2): 195–209. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1992.tb00371.x
Han, D., Nur, A., Morgan, D., 1986. Effects of Porosity and Clay Content on Wave Velocities in Sandstones. Geophysics, 51(11): 2093–2107. doi:10.1190/1.1442062
Lu, S. M., McMechan, G. A., 2004. Elastic Impedance Inversion of Multichannel Seismic Data from Unconsolidated Sediments Containing Gas Hydrate and Free Gas. Geophysics, 69(1): 164–179. doi:10.1190/1.1649385
Mallick, S., 2001. AVO and Elastic Impedance. The Leading Edge, 20(10): 1094–1104. doi:10.1190/1.1487239
Mallick, S., 2007. Amplitude-Variation-With-Offset, Elastic-Impedence, and Wave-Equation Synthetics—A Modeling Study. Geophysics, 72(1): C1–C7. doi:10.1190/1.2387108
Mallick, S., Huang, X. R., Lauve, J., et al., 2000. Hybrid Seismic Inversion: A Reconnaissance Tool for Deepwater Exploration. The Leading Edge, 19(11): 1230–1237. doi:10.1190/1.1438512
Ostrander, W. J., 1984. Plane-Wave Reflection Coefficients for Gas Sands at Nonnormal Angles of Incidence. Geophysics, 49(10): 1637–1648. doi:10.1190/1.1441571
Santos, L. T., Tygel, M., Ramos, A. C. B., 2002, Reflection Impedance. 64th Conference European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, Expanded Abstracts, Florence. 182
Tsuneyama, F., Mavko, G., 2007. Elastic-Impedance Analysis Constrained by Rock-Physics Bounds. Geophysical Prospecting, 55(3): 289–306. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.2007.00616.x
Wang, B., Yin, X., Zhang, F., et al., 2008. Elastic Impedance Equation Based on Fatti Approximation and Inversion. Progress in Geophysics, 23: 192–197 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Whitcombe, D. N., 2002. Elastic Impedance Normalization. Geophysics, 67(1): 60–62. doi:10.1190/1.1451331
Whitcombe, D. N., Connolly, P. A., Reagan, R. L., et al., 2002. Extended Elastic Impedance for Fluid and Lithology Prediction. Geophysics, 67(1): 63–67. doi:10.1190/1.1451337
Xu, S. Y., White, R. E., 1996. A Physical Model for Shear-Wave Velocity Prediction. Geophysical Prospecting, 44(4): 687–717. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00170.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liu, H., Tong, S. et al. Estimation of elastic parameters using two-term fatti elastic impedance inversion. J. Earth Sci. 26, 556–566 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0564-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0564-5