Abstract
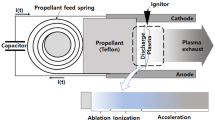
Parallel-plate pulsed plasma thrusters (PPTs) and quasi-steady MPD thrusters are largely distinguished by the discrete current sheet propagation (also referred as detonation acceleration mode) and stationary steady-phase current patterns (deflagration acceleration mode), respectively. Experimental and numerical research attempts in the past have focused on showing that the two modes of operations could be explained using the same continuum process. Present work proposes a simple unified analytical energy balance model to capture this mode transition in pulsed electromagnetic thrusters. The model is tested for a high-energy PPT developed at NASA-Glenn Research Center, which operates predominantly in the quasi-steady mode. The influence of thruster geometry and circuit parameters on the mode of operation and electrical energy efficiency is analyzed. Based on the analysis of the energy transfer efficiency, it is found that operating the thruster in the quasi-steady mode improves the transfer efficiency by approximately \(10\%\). It is concluded that the effective electrode length, pulse timing, circuit parameters, and electrode geometry could be optimized to operate the thruster in the quasi-steady/deflagration mode, hence improving the electrical energy transfer efficiency.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For further discussion regarding the calculations of the neutral mass velocity, kindly refer to Appendix C of [20]
References
Burton, R.L., Turchi, P.J.: Pulsed plasma thruster. J. Propul. Power 14, 716–735 (1996)
Jahn, R.G.: Physics of Electric Propulsion. Courier Corporation, Chelmsford (2006)
Laperriere, D., Gatsonis, N., Demetriou, M.: Electromechanical modeling of applied field micro pulsed plasma thrusters. In: 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit (2005)
Clark, K.E., Eckbreth, A.C., Jahn, R.G.: Current pattern stabilization in pulsed plasma accelerators. AIAA J. 6(11), 2125–2132 (1968)
Naso, V., Melli, R., Universitct degli Studi di Roma: Design of solid-propellant MPD thrusters. Electric propulsion and its applications to space missions (1981)
Guarducci, F., Paccani, G., Lehnert, J.: Quasi steady MPD performance analysis. Acta Astronaut. 68(7-8), 904–914 (2011)
Paccani, G.: Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Solid Propellant MPD Thruster with Segmented Anodes. IEPC Paper 93-159, 23rd IEPC, Seattle, Washinghton (USA) (1993)
Lau, M., et al.: Investigation of the plasma current density of a pulsed plasma thruster. J. Propul. Power 30(6), 1459–1470 (2014)
Misra, K.: Multiple Plasma Stream Electromechanical Model for Pulsed Plasma Thruster. arXiv:1804.08568 (arXiv preprint) (2018)
Poehlmann, F., Gascon, N., Cappelli, M.: The deflagration–detonation transition in gas-fed pulsed plasma accelerators. In: 43rd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit (2007)
Sitaraman, H., Raja, L.L.: Magneto-hydrodynamics simulation study of deflagration mode in co-axial plasma accelerators. Phys. Plasmas 21(1), 012104 (2014)
Polzin, K.A., Greve, C.M.: Acceleration modes and transitions in pulsed plasma accelerators. In: 2018 AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting (2018)
Polzin, K.A., Greve, C.M.: Modeling of initial detonation-mode acceleration in pulsed plasma and magnetoplasmadynamic thrusters.’ In: 2018 Joint Propulsion Conference, p. 4728 (2018)
Andrenucci, M., Lensi, R., Naso, V., Melli, R.: Designing solid propellant MPD thrusters. In: 14th International Electric Propulsion Conference, p. 2059
Yang, L., et al.: Analysis of teflon pulsed plasma thrusters using a modified slug parallel plate model. In: 47th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit (2011)
Turchi, P., Mikellides, I., Mikellides, P., Kamhawi, H.: Optimization of pulsed plasma thrusters for microsatellite propulsion. In: 35th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, p. 2301 (1999)
Henrikson, E., Mikellides, P.: Experimental assessment of a benchmark ablation-fed pulsed plasma thruster. In: 43rd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference Exhibit, p. 5221 (2007)
Henrikson, E., Mikellides, P.: Modeling of ablation-fed pulsed plasma thruster operation using a new approach to the ablation process. In: 44th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference Exhibit, p. 4645 (2008)
Cheng, X., Liu, X., Wu, Z., Xie, K., Wang, N., Zhang, X.: Two-stream model of the pulsed plasma thruster and simulation research. In: 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Georgia Institute of Technology, USA, IEPC, vol. 321, p. 2017 (2017)
Mikellides, Y.G.: Theoretical modeling and optimization of ablation-fed pulsed plasma thrusters. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA (1999)
Pencil, E., Kamhawi, H.: Alternate propellants evaluation for 100-Joule-class pulsed plasma thrusters. In: 39th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, p. 5171 (2003)
Yang, L., Liu, X., Guo, W., Wu, Z., Wang, N.: Simulation of parallel-plate pulsed plasma Teflon®thruster based on the electromechanical model. In: Advanced Computer Control (ICACC), 2010 2nd International Conference on Vol. 5, pp. 148–151. IEEE (2010)
Ashby, D.E.T.F., et al.: Quasi-steady-state pulsed plasma thrusters. AIAA J. 4(5), 831–835 (1966)
Ashby, D.E.T.F.: Energy loss in pulsed coaxial plasma guns. AIAA J. 3(6), 1045–1047 (1965)
Rezaeiha, A., Schönherr, T.: Analysis of effective parameters on ablative PPT performance. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 84(4), 231–243 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Dr. Kurt Polzin from NASA Marshall Space Flight Center for his feedbacks regarding the work presented in the present paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misra, K. Detonation–deflagration one-dimensional mode transition analysis for parallel-plate plasma accelerators. CEAS Space J 12, 203–212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-019-00290-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-019-00290-8