Abstract
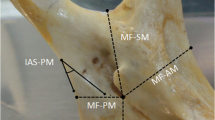
Error in localization of mandibular foramen is attributed to a high failure rate of inferior alveolar nerve block in clinical dentistry. We hypothesized that a remodelled approach towards exploring the morphology of mandibular foramen would be useful. In the present study, the location of the mandibular foramen was analysed with respect to the anatomical planes across the ramus of the mandible and also with respect to the quadrants on the medial surface of ramus of mandible. The study was conducted on 50 dry human mandibles of unknown age and sex. The anatomical planes were defined and drawn on the mandibles. Measurements were made with digital Vernier callipers and findings were noted. It was observed that the most consistent position of the mandibular foramen was along the vertical plane, however, the foramen was most likely to be localized along the oblique plane. Morphological analysis of the foramen with respect to the anatomical planes as well as the quadrants on the medial surface of ramus led to the analysis that occlusion plane should be the preferred plane of approach. Moreover, a rectangular area on the medial surface of the ramus was identified posterior to the mid-point of occlusion plane (8 mm above mid-point, 6 mm below mid-point and 6 mm behind mid-point) where the incidence of location of the foramen was significantly high. The findings of this study may potentially reduce the failure rate of inferior alveolar nerve block and clinical complications thereof.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardakani FE, Bahrololoumi Z, Booshehri MZ, Azam AN, Ayatollahi F (2010) The position of lingula as an index for inferior alveolar nerve block injection in 7 to 11-year-old children. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects 4:47
Berkovitz BKB (2016) Oral cavity. In: Standring S (ed) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier Limited, Philadelphia, pp 507–533
Ennes JP, Medeiros RM (2009) Localization of mandibular foramen and clinical implications. Int J Morphol 27:1305–1311
Epars JF, Mavropoulos A, Kiliaridis S (2015) Changes in the location of the human mandibular foramen as a function of growth and vertical facial type. Acta Odontol Scand 73:375–379
Feuerstein D, Costa-Mendes L, Esclassan R, Marty M, Vaysse F, Noirrit E (2019) The mandibular plane: a stable reference to localize the mandibular foramen, even during growth. Oral Radiol 3:1–1
Hwang TJ, Hsu SC, Huang QF, Guo MK (1990) Age changes in location of mandibular foramen. Zhonghua Ya Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 9:98–103
Khalil H (2014) A basic review on the inferior alveolar nerve block techniques. Anesth Essays Res 8:3
LavanyaVarma C, ImtiazulHaq RT (2011) Position of mandibular foramen in South Indian mandibles. Anatomica Karnataka 5:53–56
Mbajiorgu EF (2000) A study of the position of the mandibular foramen in adult black Zimbabwean mandibles. Central Afr J Med 46:184–190
Padmavathi G, Tiwari S, Varalakshmi KL, Roopashree R (2014) An anatomical study of mandibular and accessory mandibular foramen in dry adult human mandibles of south Indian origin. IOSR J Dent Med Sci 13:83–88
Pal A, Mandal T, Ghosal AK (2018) Mandibular accessory mandibular foramen—an anatomical study in dry adult human mandibles of eastern India. Indian J Basic Appl Med Res 8:7–12
Park HS, Lee JH (2015) A comparative study on the location of the mandibular foramen in CBCT of normal occlusion and skeletal class II and III malocclusion. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 37:25
Potočnik I, Bajrović F (1999) Failure of inferior alveolar nerve block in endodontics. Dent Traumatol 15:247–251
Prado FB, Groppo FC, Volpato MC, Caria PH (2010) Morphological changes in the position of the mandibular foramen in dentate and edentate Brazilian subjects. Clin Anat 23:394–398
Samanta PP, Kharb P (2013) Morphometric analysis of mandibular foramen and incidence of accessory mandibular foramina in adult human mandibles of an Indian population. Rev Arg Anat Clin 5:60–66
Sandhya K, Singh B, Lugun N, Prasad R (2015) Localization of mandibular foramen relative to landmarks in East Indian mandibles. Indian J Dent Res 26:571
Shalini R, RaviVarman C, Manoranjitham R, Veeramuthu M (2016) Morphometric study on mandibular foramen and incidence of accessory mandibular foramen in mandibles of south Indian population and its clinical implications in inferior alveolar nerve block. Anat Cell Biol 49:241–248
Shenoy V, Vijayalakshmi S, Saraswathi P (2012) Osteometric analysis of the mandibular foramen in dry human mandibles. J Clin Diagn Res 6:557–560
Thangavelu K, Kannan R, Kumar NS, Rethish E, Sabitha S, Sayeeganesh N (2012) Significance of localization of mandibular foramen in an inferior alveolar nerve block. J Nat Sci Biol Med 3:156
Wong MK, Jacobsen PL (1992) Reasons for local anesthesia failures. J Am Dent Assoc 123:69–73
Acknowledgements
The authors express heartfelt gratitude to all the residents and faculty members of the Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Phulwarisharif, Patna, India for their unconditional support throughout the study. We are grateful to the authorities of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Phulwarisharif, Patna, India for their kind cooperation during the course of this study.
Funding
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RKN: Project designing and development, data collection and analysis, manuscript writing and editing. SKG: Project designing and development, data collection and analysis, manuscript writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical clearance
The authors hereby declare that the study was conducted only after approval had been obtained from the Ethical Committee of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna whose guidelines are in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and all subsequent revisions.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayan, R.K., Ghosh, S.K. Morphological analysis of mandibular foramen through anatomical planes: implications for inferior alveolar nerve block. Anat Sci Int 95, 209–218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-019-00511-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-019-00511-4