Abstract
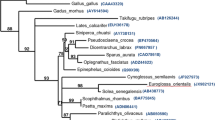
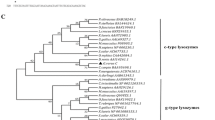
We identified two lysozyme cDNA isoforms from starry flounder Platichthys stellate. The c-type and g-type starry flounder lysozyme cDNAs encoded polypeptides of 143 and 188 amino acids, respectively. Based on bioinformatic sequence characterizations, both isoforms possessed catalytic and other conserved residues essential for their functionality. Tissue distribution analysis revealed that c-type and g-type lysozyme transcripts were ubiquitously found in all tissue types examined. In particular, the c-type lysozyme mRNA was highly predominant in the spleen. On the other hand, g-type lysozyme transcripts were markedly detectable in posterior intestine, followed by kidney and spleen. In response to Streptococcus parauberis challenge, the splenic c-type, but not g-type, lysozyme mRNA level was significantly induced, indicating that the spleen is a major lysozyme producer in response to bacterial infection-mediated stress condition. At protein levels, the enhanced lysozyme activities in the skin mucus and serum were observed as early as 4 h post injection, suggesting that the lysozyme could be involved in the acute phase responses against bacterial infection. Taken together, our data indicate that S. parauberis infection elicits a lysozyme-associated systemic immune response in starry flounder, possibly in a tissue-specific and/or isoform-specific manner.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239
Callewaert L, Michiels CW (2010) Lysozymes in the animal kingdom. J Biosci 35:127–160
Hikima J, Minagawa S, Hirono I, Aoki T (2001) Molecular cloning, expression and evolution of the Japanese flounder goose-type lysozyme gene, and the lytic activity of its recombinant protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:35–44
Yin ZX, He JG, Deng WX, Chan SM (2003) Molecular cloning, expression of orange-spotted grouper goose-type lysozyme cDNA, and lytic activity of its recombinant protein. Dis Aquat Organ 55:117–123
Jiménez-Cantizano RM, Infante C, Martin-Antonio B, Ponce M, Hachero I, Navas JI (2008) Molecular characterization, phylogeny, and expression of c-type and g-type lysozyme in brill (Scophthalmus rhombus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:57–65
Mohanty BR, Sahoo PK (2010) Immune responses and expression profiles of some immune-related genes in Indian major carp, Labeo rohita to Edwardsiella tarda infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:613–621
Whang I, Lee Y, Lee S, Oh MJ, Jung SJ, Choi CY, Lee WS, Kim HS, Kim SJ, Lee J (2011) Characterization and expression analysis of a goose-type lysozyme from the rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus, and antimicrobial activity of its recombinant protein. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:532–542
Fu GH, Bai ZY, Xia JH, Liu F, Liu P, Yue GH (2013) Analysis of two lysozyme genes and antimicrobial functions of their recombinant proteins in Asian seabass. PloS one. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079743
Hikima J, Hirono I, Aoki T (1997) Characterization and expression of c-type lysozyme cDNA from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 6:339–344
Fernández-Trujillo MA, Porta J, Manchado M, Borrego JJ, Alvarez MC, Béjar J (2008) c-Lysozyme from senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis): cDNA cloning and expression pattern. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:697–700
Ye X, Zhang L, Tian Y, Tan A, Bai J, Li S (2010) Identification and expression analysis of the g-type and c-type lysozymes in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Dev Comp Immunol 34:501–509
Demers NE, Bayne CJ (1997) The immediate effects of stress on hormones and plasma lysozyme in rainbow trout. Dev Comp Immunol 21:363–373
Lim HK, Byun SG, Lee JH, Park SU, Kim YC (2007) Sexual maturity and reproductive cycle of starry flounder Platichthys stellatus cultured in indoor tank. J Aquacu 20:212–218
Noh GE, Lim HK, Kim JM (2013) Characterization of genes encoding prolactin and prolactin receptors in starry flounder and their expression upon acclimation to freshwater. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:263–275
Cho MY, Lee JI, Kim MS, Choi HJ, Lee DC, Kim JW (2008) Isolation of Streptococcus parauberis from starry flounder, Platichthys stellate. Pallas J Fish Pathol 21:209–217 (in Korean with English abstract)
Kang CY, Kang BJ, Moon YG, Kim KY, Heo MS (2007) Characterization of Streptococcus parauberis isolated from cultured olive flounder, Paralichythys olivaceus in the Jeju island. J Fish Pathol 20:109–117 (in Korean with English abstract)
Magnadóttir B (2010) Immunological control of fish diseases. Mar Biotechnol 12:361–379
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 11:4673–4680
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Kim YK, Watanabe S, Park SI, Jeong JB, Kaneko T, Park MA, Yeo IK (2013) Molecular characterization and gene expression of Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter2 (NKCC2) in the gastrointestinal tract of olive flounder (Paralichythys olivaceus) during the four days after infection with Streptococcus parauberis. Mar Freshw Behav Phy 46:145–157
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonák J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjöback R, Sjögreen B, Strömbom L, Ståhlberg A, Zoric N (2006) The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol Aspects Med 27:95–125
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Taoka Y, Maeda H, Jo JY, Kim SM, Park SI, Yoshikawa T, Sakata T (2006) Use of live and dead probiotic cells in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Sci 72:755–766
Lange S, Gudmundsdottir BK, Magnadottir B (2001) Humoral immune parameters of cultured Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 11:523–535
Uribe C, Folch H, Enriquez R, Moran G (2011) Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: a review. Vet Med 56:486–503
Vocadlo DJ, Davies GJ, Laine R, Withers SG (2001) Catalysis by hen egg-white lysozyme proceeds via a covalent intermediate. Nature 412:835–838
Yu LP, Sun BG, Li J, Sun L (2013) Characterization of a c-type lysozyme of Scophthalmus maximus: expression, activity, and antibacterial effect. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:46–54
Kato S, Okamura M, Shimamoto N, Utiyama H (1981) Spectral evidence for a rapidly formed structural intermediate in the refolding kinetics of hen egg-white lysozyme. Biochemistry 20:1080–1085
Bachali S, Jager M, Hassanin A, Schoentgen F, Jolles P, Fiala-Medioni A, Deutsch JS (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of invertebrate lysozymes and the evolution of lysozyme function. J Mol Evol 54:652–664
Nitta K, Sugai S (1989) The evolution of lysozyme and α-lactalbumin. Eur J Biochem 182:111–118
Irwin DM, Biegel JM, Stewart CB (2011) Evolution of the mammalian lysozyme gene family. BMC Evol Biol 11:1–16
Mai W, Liu P, Chen H, Zhou Y (2014) Cloning and immune characterization of the c-type lysozyme gene in red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus akaara. Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:305–314
Buonocore F, Randelli E, Trisolino P, Facchiano A, de Pascale D, Scapigliati G (2014) Molecular characterization, gene structure and antibacterial activity of a g-type lysozyme from the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Mol Immunol 62:10–18
Zhao L, Sun JS, Sun L (2011) The g-type lysozyme of Scophthalmus maximus has a broad substrate spectrum and is involved in the immune response against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:630–637
Larsen AN, Solstad T, Svineng G, Seppola M, Lrgensen T, J (2009) Molecular characterisation of a goose-type lysozyme gene in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:122–132
Touch V, Hayakawa S, Saitoh K (2004) Relationships between conformational changes and antimicrobial activity of lysozyme upon reduction of its disulfide bonds. Food Chem 84:421–428
Pridgeon JW, Klesius PH, Dominowski PJ, Yancey RJ, Kievit MS (2013) Chicken-type lysozyme in channel catfish: expression analysis, lysozyme activity, and efficacy as immunostimulant against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:680–688
Gao FY, Qu L, Yu SG, Ye X, Tian YY, Zhang LL, Bai JJ, Lu M (2012) Identification and expression analysis of three c-type lysozymes in Oreochromis aureus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:779–788
Press CM, Evensen Ø (1999) The morphology of the immune system in teleost fishes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:309–318
Nakano T, Graf T (1991) Goose-type lysozyme gene of the chicken: sequence, genomic organization and expression reveals major differences to chicken-type lysozyme gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1090:273–276
Irwin DM, Gong ZM (2003) Molecular evolution of vertebrate goose-type lysozyme genes. J Mol Evol 56:234–242
Myrnes B, Seppola M, Johansen A, Øverbø K, Callewaert L, Vanderkelen L, Michiels CW, Nilsen IW (2013) Enzyme characterisation and gene expression profiling of Atlantic salmon chicken-and goose-type lysozymes. Dev Comp Immunol 40:11–19
Woo SH, Park SI (2013) Streptococcous parauberis infection in starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus: characterization of innate immune responses following experimental infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:413–420
Paulsen SM, Lunde H, Engstad RE, Robertsen B (2003) In vivo effects of β-glucan and LPS on regulation of lysozyme activity and mRNA expression in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 14:39–54
Rotllant J, Tort L (1997) Cortisol and glucose responses after acute stress by net handling in the sparid red porgy previously subjected to crowding stress. J Fish Biol 51:21–28
Chen SC, Yoshida T, Adams A, Thompson KD, Richards RH (1998) Non-specific immune response of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis nilotica, to the extracellular products of Mycobacterium spp. and to various adjuvants. J Fish Dis 21:39–46
Dos Santos N, Taverne-Thiele JJ, Barnes AC, van Muiswinkel WB, Ellis AE, Rombout JH (2001) The gill is a major organ for antibody secreting cell production following direct immersion of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) in a Photobacterium damselae ssp. Piscicida bacterin: an ontogenetic study. Fish Shellfish Immunol 11:65–74
Tokushima Y, Ito Y, Shimizu M, Omoto N, Hara A (2004) Immunochemical comparison between sera from the primary and secondary circulations in a salmonid fish, Sakhalin taimen (Huchoperryi). Fish Physiol Biochem 30:179–188
Madetoja J, Lönnström LG, Björkblom C, Uluköy G, Bylund G, Syvertsen C, Gravningen K, Norderhus EA, Wiklund T (2006) Efficacy of injection vaccines against Flavobacterium psychrophilum in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 29:9–20
Easy RH, Ross NW (2009) Changes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) epidermal mucus protein composition profiles following infection with sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Comp Biochem Physiol D Genomics Prot 4:159–167
Ghafoori Z, Heidari B, Farzadfar F, Aghamaali M (2014) Variations of serum and mucus lysozyme activity and total protein content in the male and female caspian kutum (Rutilusfrisii kutum, Kamensky 1901) during reproductive period. Fish Shellfish Immunol 37:139–146
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Arizcun M, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2014) Comparative skin mucus and serum humoral defence mechanisms in the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:545–551
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Abellán E, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2014) Comparative analysis of the humoral immunity of skin mucus from several marine teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 40:24–31
Rakers S, Gebert M, Uppalapati S, Meyer W, Maderson P, Sell AF, Kruse C, Paus R (2010) ‘Fish matters’: the relevance of fish skin biology to investigative dermatology. Exp Dermatol 19:313–324
Wang R, Feng J, Li C, Liu S, Zhang Y, Liu Z (2013) Four lysozymes (one c-type and three g-type) in catfish are drastically but differentially induced after bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:136–145
Yamamoto T, Kawai K, Oshima S (2011) Distribution of mucous cells on the body surface of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. J Fish Biol 78:848–859
Sigh J, Lindenstrom T, Buchmann K (2004) The parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis induces expression of immune relevant genes in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 27:409–417
Alishahi M, Buchmann K (2006) Temperature-dependent protection against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis following immunization of rainbow trout using live theronts. Dis Aquat Org 72:269–273
Sarmasik A, Warr G, Chen TT (2002) Production of transgenic medaka with increased resistance to bacterial pathogens. Mar Biotechnol 4:310–322
Yazawa R, Hirono I, Aoki T (2006) Transgenic zebrafish expressing chicken lysozyme show resistance against bacterial diseases. Transgenic Res 15:385–391
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.K., Nam, Y.K. Molecular characterization and expression pattern of c-type and g-type lysozyme isoforms in starry flounder Platichthys stellate infected with Streptococcus parauberis . Fish Sci 81, 353–363 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-015-0852-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-015-0852-0