Abstract
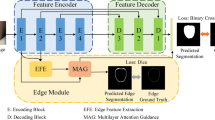
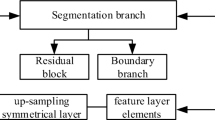
Existing deep learning–based medical image segmentation methods have achieved gratifying progress, but they still suffer from the coarse boundaries with similar pixels of target. Because the boundary of medical images becomes blurred and the gradient is inconsistent and not apparent, high-resolution images are needed for more accurate segmentation. To tackle these problems, we propose an efficient multi-layer edge perception U-shaped structure for medical image segmentation. In this paper, we present a multi-layer edge perception network for describing more precise edges of medical targets. The U-structure architecture of our network embeds a multi-layer edge perception module, which has the following advantages: (1) connecting different scales and channels to help the network better learn the feature of the medical image via the combination of a pyramid structure and several edge perception modules; (2) a new downsampling block is designed to improve the network’s sensibility to the target boundary. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model on the DRIVE datasets, and achieve a Dice gain of 0.841 over other models. In this paper, we propose an efficient multi-layer edge perception U-shaped structure for medical image segmentation. A large number of experiments show that the performance of our proposed multi-layer edge perception U-shaped network is significantly better than the traditional segmented network structure.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Minaee S, Boykov YY, Porikli F, Plaza AJ, Kehtarnavaz N, Terzopoulos D. Image segmentation using deep learning: a survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2021;1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3059968.
Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, Franke U, Roth S, Schiele B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2016.
Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite, in. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2012;2012:3354–61. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248074.
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2015.
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells WM, Frangi AF, editors. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2015. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015. p. 234–41.
del Mar Vila M, Remeseiro B, Grau M, Elosua R, Betriu À, Fernandez-Giraldez E, Igual L. Semantic segmentation with densenets for carotid artery ultrasound plaque segmentation and CIMT estimation. Artif Intell Med. 2020;103:101784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101784. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S093336571830770X
Zhou Z. M. M. Rahman Siddiquee, N. Tajbakhsh, J. Liang, Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov D, Taylor Z, Carneiro G, Syeda-Mahmood T, Martel A, Maier-Hein L, Tavares JMR, Bradley A, Papa JP, Belagiannis V, Nascimento JC, Lu Z, Conjeti S, Moradi M, Greenspan H, Madabhushi A, editors. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018. p. 3–11.
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2017;39(12):2481–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615.
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFS. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2018;40(4):834–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184.
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv:1804.03999 [Preprint]. 2017. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587.
Chen L-C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 2018.
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla NY, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D. Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv:1804.03999 [Preprint]. 2018. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999.
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2018.
Chen Y, Kalantidis Y, Li J, Yan S, Feng J. \(a^2\)-nets: Double attention networks. arXiv:1810.11579 [Preprint]. 2018. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.11579.
Huang H, Lin L, Tong R, Hu H, Zhang Q, Iwamoto Y, Han X, Chen Y-W, Wu J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected Unet for medical image segmentation. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). 2020. p. 1055–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053405.
Salehi SSM, Erdogmus D, Gholipour A. Tversky loss function for image segmentation using 3d fully convolutional deep networks. In: Wang Q, Shi Y, Suk H-I, Suzuki K, editors. Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2017. p. 379–87.
Crum W, Camara O, Hill D. Generalized overlap measures for evaluation and validation in medical image analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006;25(11):1451–61. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2006.880587.
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). 2016. p. 565–71. https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2016.79.
Lin G, Milan A, Shen C, Reid I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2016.
Cho K, van Merrienboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078 [Preprint]. 2014. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1078.
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le QV. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. arXiv:1409.3215 [Preprint]. 2014. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.3215.
Luo P, Wang G, Lin L, Wang X. Deep dual learning for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). 2017.
Zeiler MD, Taylor GW, Fergus R. Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 2011. 2011. p. 2018–25. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126474.
Pohlen T, Hermans A, Mathias M, Leibe B. Full-resolution residual networks for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
Peng C, Zhang X, Yu G, Luo G, Sun J. Large kernel matters – improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
Amirul Islam M, Rochan M, Bruce NDB, Wang Y. Gated feedback refinement network for dense image labeling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
Hoang TM, Zhou, Fan JY. Image compression with encoder-decoder matched semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops. 2020.
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Dehghan M, Zaiane OR, Jagersand M. U2-net: Going deeper with nested u-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recogn. 2020;106:107404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2019.
Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Zisserman A, Kavukcuoglu K. Spatial transformer networks. arXiv:1506.02025 [Preprint]. 2016. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025.
Wang F, Jiang M, Qian C, Yang S, Li C, Zhang H, Wang X, Tang X. Residual attention network for image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2015;37(9):1904–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824.
Lee Y, Park J. Centermask: Real-time anchor-free instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2020.
Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2017.
Orhan AE, Pitkow X. Skip connections eliminate singularities. arXiv:1701.09175 [Preprint]. 2018. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.09175.
Cortes C, Gonzalvo X, Kuznetsov V, Mohri M, Yang S. AdaNet: Adaptive structural learning of artificial neural networks. In: Precup D, Teh YW, editors. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 70 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. PMLR; 2017. p. 874–83. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/cortes17a.html.
Alom MZ, Hasan M, Yakopcic C, Taha TM, Asari VK. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv:1802.06955 [Preprint]. 2018. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.06955.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (CN) (Nos. 61876125, and 62076180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Li, P., Ren, J. et al. Attention Mechanism Enhanced Multi-layer Edge Perception Network for Deep Semantic Medical Segmentation. Cogn Comput 15, 348–358 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-022-10094-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-022-10094-4