Abstract
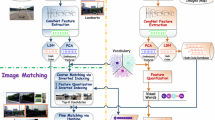
In the field of visual place recognition, a variety of methods using Visual Bag of Words has been suggested to cope with environmental change. This paper presents a sampling-based method which improves the speed and the accuracy of the existing Visual Bag of Words models. We first propose sampling of image features considering their density to speed up the quantization step. By using samples, a more accurate but rather slow ranking procedure is feasible. Thus, we also propose a ranking procedure which utilizes spatial information of samples. Lastly, a coarse and fine approach-based refinement method is proposed which increases the accuracy of the system by iteratively updating the similarity between images. The experimental results show that the proposed method improves the performance of the existing Visual Bag of Words models in terms of speed and accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Zhou, H. Li, and Q. Tian, “Recent advance in content-based image retrieval: a literature survey,” arXiv: 1706.06064, 2017.
S. Lawry, N. Sünderhau][, P. Newman, J. J. Leonard, D. Cox, P. Corke, and M. J. Milford, “Visual place recognition: a survey,” IEEE trans. Robotics, vol. 32, no. 1, pp.1–19, 2016.
D. Gálvez-López, and J. D. Tardós, “Bags of binary words for fast place recognition in image sequences,” IEEE Trans. Robot., vol. 28, no. 5, pp.1188–1197, 2012.
M. Cummins and P. Newman, “Appearance-only SLAM at large scale with FAB-MAP 2.0,” Int. J. Rob. Res., vol. 30, no. 9, pp. 1100–1123, 2011.
J. Philbin, O. Chum, M. Isard, J. Sivic, and A. Zisserman, “Object retrieval with large vocabularies and fast spatial matching,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2007.
D. Nistér and H. Stewénius, “Scalable recognition with a vocabulary tree,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, vol. 2, pp.2161–2168, 2006.
J. Sivic and A. Zisserman, “Video Google: a text retrieval approach to object matching in videos,” Towar. Categ. Object Recognit., pp. 1470, 2003.
J. L. Bentley, “K-d trees for semidynamic point sets,” Proc. Sixth Annu. Symp. Comput. Geom, pp. 187–197, 1990.
C. Silpa-Anan and R. Hartley, “Localisation using an image-map,” Australasian Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 162, 2004.
M. Muja and D.G. Lowe, “Scalable nearest neighbor algorithms for high dimensional data,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis andMachine Intelligence, vol. 36, no. 11, pp.2227–2240, 2014.
D. G. Lowe, “Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints,” Int. J. Comput. Vis., 2004.
A. Kelman, M. Sofka, and C. V Stewart, “Keypoint descriptors for matching across multiple image modalities and non-linear intensity variations,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1–7, 2007.
X. Zhang, L. Zhang, and H.Y. Shum, “QsRank: query-sensitive hash code ranking for efficient -neighbor search,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 2058–2065, 2012.
D. Mishkin, M. Perdoch, and J. Matas, “Place Recognition with WxBS Retrieval,” CVPR 2015 Work. Vis. Place Recognit. Chang. Environ, vol. 30, 2015.
H. Jégou, M. Douze, C. Schmid, and P. Pérez, “Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 3304–3311, 2010.
S. Lowry and H. Andreasson, “Lightweight, viewpoint-invariant visual place recognition in changing environments,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 3, no. 6, pp.957–964, 2018.
F. Perronnin, Y. Liu, J. Sánchez, and H. Poirier, “Large-scale image retrieval with compressed fisher vectors,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 3384–3391, 2010.
D. Mishkin, J. Matas, M. Perdoch, and K. Lenc, “WxBS: wide baseline stereo generalizations,” arXiv, 112, 2015.
D. Mishkin, J. Matas, and M. Perdoch, “MODS: Fast and robust method for two-view matching,” Compututer Vision and Image Understanding, vol. 141, pp.8193, 2015.
R. Baeza-Yates and B. Ribeiro-Neto, Modern Information Retrieval, vol. 463, ACM press, New York, 1999.
P. E. Forssén and D. G. Lowe, “Shape descriptors for maximally stable extremal regions,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 1–8, 2007.
K. Mikolajczyk and C. Schmid, “Scale affine invariant interest point detectors,” Ijcv., vol. 60, no. 1, pp.63–86, 2004.
H. Altwaijry, A. Veit, S. J. Belongie, and C. Tech, “Learning to detect and match keypoints with deep architectures.,” Bmvc., vol. 60, no. 2, pp.91–110, 2016.
Law of Large Numbers, https://www.dartmouth.edu/~chance/teaching_aids/books_articles/probability_book/Chapter8.pdf.
R. Mur-Artal, J. M. M. Montiel, and J. D. Tardos, “ORBSLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system,” IEEE Trans. Robot., vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 11471163, 2015.
C. Tang, O. Wang, and P. Tan, “GSLAM: initialization-robust monocular visual slam via global structure-from-motion,” Proc. - Int. Conf. 3D Vision, 3DV 2017, 2018.
J. Engel, T. Schöps, and D. Cremers, “LSD-SLAM: large-scale direct monocular SLAM,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., pp. 834–849, 2014.
E. Rublee, V. Rabau][, K. Konolige, and G. Bradski, “ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 2564–2571, 2011.
H. Bay, T. Tuytelaars, and L. Van Gool, “SURF: speeded up robust features,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., pp. 404–417, 2006.
N. Sünderhauf, The VPRiCE Challenge 2015-Visual Place Recognition in Changing Environments, https://roboticvision.atlassian.net/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=14188617.
M. A. Fischler and R. C. Bolles, “Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography,” Commun. ACM., vol. 24, no. 6, pp.381–395, 1981.
V. Lepetit and P. Fua, “Keypoint recognition using randomized trees,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 28, no. 9, pp.1465–1479, 2006.
J. Waksberg, “Sampling methods for random digit dialing,” J. Am. Stat. Assoc., vol. 73, no. 361, pp.40–46, 1978.
J. S. Simonoff, Smoothing Methods in Statistics, Science & Business Media, Berlin, Germany, 2012.
V. A. Epanechnikov, “Non-parametric estimation of a multivariate probability density,” Theory Probab. Its Appl., vol. 14, no. 1, pp.153–158, 1969.
L. Martino and J. Míguez, “Generalized rejection sampling schemes and applications in signal processing,” Signal Processing, vol. 90, no. 11, pp.2981–2995, 2010.
Geometric verification of matching, http://www.micc.unifi.it/delbimbo/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/slide_corso/A34%20Geometric%20verification.pdf, Accessed 15 November 2011.
R. Hartley and A. Zisserman, Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, Cambridge University Press, 2nd eds., Cambridge, England, 2003.
O. Chum, J. Matas, and J. Kittler, “Locally optimized RANSAC,” Joint Pattern Recognition Symposium, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 236243. 2003.
D. M. Chen, G. Baatz, K. Köser, S. S. Tsai, R. Vedantham, T. Pylvänäinen, K. Roimela, X. Chen, J. Bach, M. Pollefeys, B. Girod, and R. Grzeszczuk, “City-scale landmark identification on mobile devices,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 737–744, 2011.
R. Gomez-Ojeda, M. Lopez-Antequera, N. Petkov, and J. Gonzalez-Jimenez, “Training a convolutional neural network for appearance-invariant place recognition,” CVPR Work. Vis. Place Recognit. Chang. Environ., 2015.
O. Vysotska and C. Stachniss, “Lazy sequences matching under substantial appearance changes,” Proc. of ICRA 15 WS VPRiCE. (short paper), 2015.
M. Douze, A. Ramisa, and C. Schmid, “Combining attributes and Fisher vectors for efficient image retrieval,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 745–752, 2011.
S. Zhao, H. Yao, Y. Yang, and Y. Zhang, “Affective image retrieval via multi-graph learning,” Proc. ACM Int. Conf. Multimed., 2014.
R. Tao, A. W. M. Smeulders, and S. F. Chang, “Attributes and categories for generic instance search from one example,” Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1025–1028, 2015.
X. Chen and Y. Jia, “Indoor localization for mobile robots using lampshade corners as landmarks: visual system calibration, feature extraction and experiments,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 12, no. 6, pp.1313–1322, 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended by Associate Editor Kang-Hyun Jo under the direction of Editor Euntai Kim. This journal was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2016R1D1A3B03934808).
Sang Jun Lee received his B.S. degree in Computer science and Engineering from Handong Global University, Pohang-si, Korea, in 2017. He is currently pursuing an M.S. degree in the Dept. of Information Technology at the Handong Global University. His research interests include the SLAM system for the localization of self-driving cars, robotics, and AR with 3D reconstruction, and optimization.
Sung Soo Hwang received his B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from Handong Global Unveristy, Pohang, Korea in 2008, and his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea, in 2010 and 2015, respectively. His research interests include image-based 3D modeling, 3D data compression, augmented reality, and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping system.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Hwang, S.S. Bag of Sampled Words: A Sampling-based Strategy for Fast and Accurate Visual Place Recognition in Changing Environments. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 17, 2597–2609 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-018-0790-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-018-0790-6