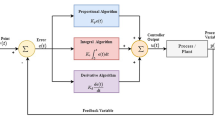
Abstract
One of the most important problems in the field of the iterative learning control (ILC) is to design algorithms, in order to achieve a desired convergence rate. In this paper a new type of the ILC algorithm is introduced, which is called N-parametric type ILC with optimal gains. The convergence of the proposed algorithm is analyzed and an optimal design method is presented to determine its gains. The effect of the number of the parameters on the convergence rate of the presented ILC is investigated. It is shown that N parametric type of this ILC has a better performance than the N-1 one. Illustrative simulation examples are given to verify the theoretical analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Arimoto, S. Kawamura, and F. Miyazaki, “Bettering operation of robots by learning,” Journal of Robotic Systems, vol. 1, no. (2), pp. 123–140, 1984.
H. S. Ahn, Y. Q. Chen, and K. L. Moore, “Iterative learning control: brief survey and categorization,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics–Part C: Applications and Reviews, vol. 37, no. (6), pp. 1099–1121, 2007.
Q. Zhu, J.-X. Xu, D. Huang, and G.-D. Hu, “Iterative learning control design for linear discrete–time systems with multiple high–order internal models,” Automatica, vol. 62, pp. 65–76, 2015.
M. Kim, T.-Y. Kuc, H. Kim, and J. S. Lee, “Adaptive iterative learning controller with input learning technique for a class of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 15, no. (1), pp. 315–328, 2017.
W. Messner, R. Horowitz, W.- W. Kao, and M. Boals, “A new adaptive learning rule,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 36, no. (2), pp. 245–251, 1991.
S. Garimella and K. Srinivasan, “Application of iterative learning control to coil–to–coil control in rolling,” IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 6, no. (2), pp. 281–293, 1998.
M. Pandit and K.-H. Buchheit, “Optimizing iterative learning control of cyclic production process with application to extruders,” IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 7, no. (3), pp. 382–390, 1999.
S. A. Saab, “A stochastic iterative learning control algorithm with application to an induction motor,” International Journal of Control, vol. 77, no. (2), pp. 144–163, 2004.
C. Freeman, E. Rogers, A.-M. Hughes, J. Burridge, and K. Meadmore, “Iterative learning control in health care: Electrical stimulation and robotic–assisted upper–limb stroke rehabilitation,” IEEE Control Systems, vol. 32, no. (1), pp. 18–43, 2012.
T. Liu, F. Gao, and Y. Wang, “IMC–based iterative learning control for batch processes with uncertain time delay,” Journal of Process Control, vol. 20, no. (2), pp. 173–180, 2010.
J. Li, Y. Wang, and H. Xiao, “Consensus seeking of multiagent systems from an iterative learning perspective,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 14, no. (5), pp. 1173–1182, 2016.
J. C. Cahuana, P. N. Landin, C. Fager, and T. Eriksson, “Iterative learning control for RF power amplifier linearization,” IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, vol. 64, no. (9), pp. 2778–2789, 2016.
B. Ko, J.-W. Park, and D. W. Kim, “A study on iterative learning control for vibration of Stewart platform,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 15, no. (1), pp. 258–266, 2017.
Z. Bien and J.-X. Xu, Iterative Learning Control: Analysis, Design, Integration and Applications, Kluwer Academic Prees, Boston, 1998.
Y. Q. Chen and C. Wen, Iterative Learning Control: Convergence, Robustness and Applications, vol. LNCIS–248 of Lecture Notes series on Control and Information Science, Springer–Verlag, London, 1999.
J.-X. Xu and Y. Tan, Linear and Nonlinear Iterative Learning Control, Springer–Verlag, New York, 2003.
D. H. Owens, Iterative Learning Control: An Optimization Paradigm, Springer–Verlag, London, 2016.
W. Chen, L. Jiao, R. Li, and J. Li, “Adaptive back–stepping fuzzy control for nonlinearly parameterized systems with periodic disturbances,” IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 18, no. (4), pp. 674–685, 2010.
W. Chen, J. M. Li, and J. Li, “Practical adaptive iterative learning control framework based on robust adaptive approach,” Asian Journal of Control, vol. 13, no. (1), pp. 85–93, 2011.
W. Chen and Z. Zhang, “Nonlinear adaptive learning control for unknown time–varying parameters and unknown time–varying delays,” Asian Journal of Control, vol. 13, no. (6), pp. 903–913, 2011.
A. Madady and H.-R. Reza–Alikhani, “A guaranteed monotonically convergent iterative learning control,” Asian Journal of Control, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 1299–1316, 2012.
P. Janssens, G. Pipeleers, and J. Swevers, “A data–driven constrained norm–optimal iterative learning control framework for LTI systems,” IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 21, no. (2), pp. 546–551, 2013.
T.-Y. Doh, J. R. Ryoo, and D. E. Chang, “Robust iterative learning controller design using the performance weighting function of feedback control systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 12, no. (1), pp. 63–70, 2014.
P. Axelsson, R. Karlsson, and M. Norrlf, “Estimationbased norm–optimal iterative learning control,” Systems & Control Letters, vol. 73, pp. 76–80, 2014.
D. H. Owens, C. T. Freeman, and B. Chu, “An inversemodel approach to multivariable norm optimal iterative learning control with auxiliary optimisation,” International Journal of Control, vol. 87, no. (8), pp. 1646–1671, 2014.
T.-F. Xiao, X.-D. Li, and J. K. L. Ho, “An adaptive discretetime ILC strategy using fuzzy systems for iteration–varying reference trajectory tracking,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 13, no. (1), pp. 222–230, 2015.
B. Xuhui, W. Taihua, H. Zhongsheng, and C. Ronghu, “Iterative learning control for discrete–time systems with quantised measurements,” IET Control Theory & Applications, vol. 9, no. (9), pp. 1455–1460, 2015.
C. Hua, L. Zhang, and X. Guan, “Decentralized output feedback adaptive NN tracking control for timedelay stochastic nonlinear systems with prescribed performance,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol.26, no.11, pp. 2749–2759, 2015.
Q.-Y. Xu, X.-D. Li, and M.-M. Lv, “Adaptive ILC for tracking non–repetitive reference trajectory of 2–D FMM under random boundary condition,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 14, no. (2), pp. 478–485, 2016.
Y.-S. Wei and X.-D. Li, “Iterative learning control for linear discrete–time systems with high relative degree under initial state vibration,” IET Control Theory & Applications, vol. 10, no. (10), pp. 1115–1126, 2016.
W. Paszke, E. Rogers, and K. Gałkowski, “Experimentally verified generalized KYP Lemma based iterative learning control design,” Control Engineering Practice, vol. 53, pp. 57–67, 2016.
Q. Fu, W.- G. Gu, P.-P. Gu, and J.-R. Wu, “Iterative learning control for a class of mixed hyperbolic–parabolic distributed parameter systems,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 14, no. (6), pp. 1455–1463, 2016.
D. Shen and Y. Xu, “Iterative learning control for discrete–time stochastic systems with quantized information,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 3, no. (1), pp. 59–67, 2016.
S. Z. Khong, D. Nešić, and M. Krstić, “Iterative learning control based on extremum seeking,” Automatica, vol. 66, pp. 238–245, 2016.
X. Ma and X. Bu, “A novel iterative learning control design for linear discrete time systems based on a 2D Roesser system,” Information Technology and Control, vol. 45, no. (4), pp. 384–392, 2016.
W. Gao and Z.-P. Jiang, “Adaptive dynamic programming and adaptive optimal output regulation of linear systems,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 61, no. (12), pp. 4164–4169, 2016.
W. Gao, Y. Jiang, Z.-P. Jiang, and T Chai, “Outputfeedback adaptive optimal control of interconnected systems based on robust adaptive dynamic programming,” Automatica, vol. 72, pp. 37–45, 2016.
T. D. Son, G. Pipeleers, and J. Swevers, “Multi–objective iterative learning control using convex optimization,” European Journal of Control, vol. 33, pp. 35–42, 2017.
Z. Shao and Z. Xiang, “Iterative learning control for nonlinear switched discrete–time systems,” IET Control Theory & Applications, vol. 11, no. (6), pp. 883–889, 2017.
L. A. Tuan, Y. H. Joo, L. Q. Tien, and P. X. Duong, “Adaptive neural network second–order sliding mode control of dual arm robots,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 2883–2891, 2017.
C. Hua, L. Zhang, and X. Guan, “Distributed adaptive neural network output tracking of leader–following highorder stochastic nonlinear multi–agent systems with unknown dead–zone input,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 47, no. (1), pp. 177–185, 2017.
W. Gao and Z.-P. Jiang, “Learning–based adaptive optimal tracking control of strict–feedback nonlinear systems,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 29, no. (6), pp. 2614–2624, 2017.
A. Madady, “PID type iterative learning control with optimal gains,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 6, no. (2), pp. 194–203, 2008.
A. Madady, “An extended PID type iterative learning control,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 11, no. (3), pp. 470–481, 2013.
S. Boyd, L. E. Ghaoui, E. Feron, and V. Balakrishnan, Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory, SIAM, Philadelphia, Pa, USA, 1994.
D. S. Bernstein, Matrix Mathematics: Theory, Facts, and Formulas, 2nd edition, Princeton University Press, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Changchun Hua under the direction of Editor Yoshito Ohta.
Ali Madady was born in Aqdash, Saveh, Iran in 1966. He received his B.Sc., M.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical and electronic engineering from Amir-Kabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic), Iran, in 1989, 1993, and 2001, respectively. From 1991 to 1996, he was a part-time research member of Iranian Research Organization for Science and Technology (IROST). Also from 1994 to 2001, he was a part-time lecturer of Shamsipour Institute of Technology (SIT), Tehran, Iran. In 2001, he joined Tafresh University, Tafresh, Iran, where he is currently an Associate Professor and originator and head of Control Engineering Group. His research interests include iterative learning, adaptive control, robust control and nonlinear systems.
Hamid-Reza Reza-Alikhani was born in Tehran, Iran in 1952. He received his B.Sc. degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Nottingham University, UK, in 1979, an M.Sc. degree in Power Electronics, and a Ph.D. in Digital Communication from Loughborough University, UK, in 1982 and 2000, respectively. He worked as an Electronics design Engineer in England. He is currently lecturing as an Assistant Professor in Tafresh University, Tafresh, Iran, as well as working as a design Engineer. His research interests include robotics control, iterative learning, neural networks, medical (physiotherapy) system design, power electronics, and image processing.
Sara Zamiri was born in Boroujerd, Iran in 1986. She received her B.Sc degree in electronic engineering and her M.Sc degree in control engineering from Islamic Azad University, in 2010 and 2013, respectively. Her research interests include iterative learning, adaptive and optimal control.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madady, A., Reza-Alikhani, HR. & Zamiri, S. Optimal N-Parametric Type Iterative Learning Control. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 16, 2187–2202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-017-0259-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-017-0259-z