Abstract
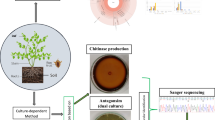
Application of atoxigenic strains to compete against toxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus strains has emerged as one of the practical strategies for reducing aflatoxin contamination in corn, peanut, and tree nuts. The actual mechanism that results in aflatoxin reduction is not fully understood. Real-time RT-PCR and relative quantification of gene expression protocol were applied to elucidate the molecular mechanism. Transcriptional analyses of aflatoxin biosynthetic gene cluster in dual culture of toxigenic and atoxigenic A. flavus strains were carried out. Six targeted genes, aflR, aflJ, omtA, ordA, pksA, and vbs, were downregulated to variable levels depending on paired strains of toxigenic and atoxigenic A. flavus. Consistent with the decreased gene expression levels, the aflatoxin concentrations in dual cultures were reduced significantly in comparison with toxigenic cultures. Fluorescent images showed fungal hyphae in dual culture displayed green fluorescent, and contacts of live hyphae were seen. A coconut agar plate assay was used to show that toxigenic A. flavus colony produced blue fluorescence under long UV exposure, suggesting that aflatoxin is exported outside fungal hyphae. Furthermore, the assay was applied to demonstrate the potential role of thigmo-regulation in fungal interaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas HK, Zablotowicz RM, Bruns HA, Abel CA (2006) Biocontrol of aflatoxin in corn by inoculation with non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates. Biocontrol Sci Tech 16:437–449
Adhikari BN, Bandyopadhyay R, Cotty PJ (2016) Degeneration of aflatoxin gene clusters in Aspergillus flavus from Africa and North America. AMB Express 6(1):62
Almeida MC, Brand AC (2017) Thigmo responses: the fungal sense of touch. Microbiol Spectrum 5(2):FUNK-0040-2016. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0040-2016
Atehnkeng J, Ojiambo PS, Cotty PJ, Bandyopadhyay R (2014) Field efficacy of a mixture of atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus link: FR vegetative compatibility groups in preventing aflatoxin contamination in maize (Zea mays L.). Biol Control 72:62–70
Bayman P, Cotty PJ (1993) Genetic diversity in Aspergillus flavus: association with aflatoxin production and morphology. Can J Bot 71:23–31
Cary JW, Ehrlich KC, Bland JM, Montalbano BG (2006) The aflatoxin biosynthesis cluster gene, aflX, encodes an oxidoreductase involved in conversion of versicolorin a to demethylsterigmatocystin. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1096–1101. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.2.1096-1101.2006
Chanda A, Roze LV, Kang S, Artymovich KA, Hicks GR, Raikhel NV, Calvo AM, Linz JE (2009) A key role for vesicles in fungal secondary metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:19533–19538. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907416106
Chanda A, Roze LV, Linz JE (2010) A possible role for exocytosis in aflatoxin export in Aspergillus parasiticus. Eukaryot Cell 9:1724–1727
Chang PK, Hua SS (2007) Nonaflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus TX9-8 competitively prevents aflatoxin accumulation by A. flavus isolates of large and small sclerotial morphotypes. Int J Food Microbiol 114:275–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.09.017
Chang PK, Horn BW, Dorner JW (2005) Sequence breakpoints in the aflatoxin biosynthesis gene cluster and flanking regions in nonaflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates. Fungal Genet Biol 42:914–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2005.07.004
Cotty PJ (1990) Effect of atoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus on aflatoxin contamination of developing cottonseed. Plant Dis 74(3):233–235
Cotty PJ (1997) Aflatoxin-producing potential of communities of Aspergillus section Flavi from cotton producing areas in the United States. Mycol Res 101:698–704. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756296003139
Cotty PJ, Bayman P (1993) Competitive exclusion of a toxigenic strain of Aspergillus flavus by an atoxigenic strain. Phytopathology 83:1283–1287
Damann KE Jr (2015) Atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus biological control of aflatoxin contamination: what is the mechanism? World Mycotoxin J 8:235–244
Dorner JW (2009a) Biological control of aflatoxin contamination in corn using a nontoxigenic strain of Aspergillus flavus. J Food Prot 72:801–804
Dorner JW (2009b) Development of biocontrol technology to manage aflatoxin contamination in peanuts. Peanut Sci 36:60–67
Dorner JW, Cole RJ, Wicklow DT (1999) Aflatoxin reduction in corn through field application of competitive fungi. J Food Prot 62(6):650–656
Ehrlich KC, Montalbano BG, Cary JW (1999) Binding of the C6-zinc cluster protein, AFLR, to the promoters of aflatoxin pathway biosynthesis genes in Aspergillus parasiticus. Gene 230:249–257
Ehrlich KC, Montalbano BG, Cotty PJ (2003) Sequence comparison of aflR from different Aspergillus species provides evidence for variability in regulation of aflatoxin production. Fungal Genet Biol 38(1):63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00509-1
Ehrlich KC, Montalbano BG, Cotty PJ (2005) Divergent regulation of aflatoxin production at acidic pH by two Aspergillus strains. Mycopathologia 159:579–581
FAO (2009) Declaration of the World Summit on Food Security. WFSFS 2009/2, Rome, 16–18 November 2009
Fernandes M, Keller NP, Adams TH (1998) Sequence-specific binding by Aspergillus nidulans AflR, a C6zinc cluster protein regulating mycotoxin biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol 28:1355–1365. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00907.x
Flaherty JE, Weaver ME, Payne GA, Woloshuk CP (1995) A beta-glucuronidase reporter gene construct for monitoring aflatoxin biosynthesis in A. flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2482–2486
Georgianna DR, Payne GA (2009) Genetic regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis: from gene to genome. Fungal Genet Biol 46(2):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.10.011
Hedayati MT, Pasqualotto AC, Warn PA, Bowyer P, Denning DW (2007) Aspergillus flavus: human pathogen, allergen and mycotoxin producer. Microbiology. 153(6):1677–1692. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2007/007641-0
Henry SH, Bosch FX, Bowers JC (2002) Aflatoxin, hepatitis and worldwide liver cancer risks. Adv Exp Med Biol 504:229–233
Hruska Z, Rajasekaran K, Yao H, Kincaid R, Darlington D, Brown RL, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE (2014) Co-inoculation of aflatoxigenic and non-aflatoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus to study fungal invasion, colonization, and competition in maize kernels. Front Microbiol 5(122). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00122
Hua SS, Brandl MT, Hernlem B, Eng JG, Sarreal SB (2011) Fluorescent viability stains to probe the metabolic status of aflatoxigenic fungus in dual culture of Aspergillus flavus and Pichia anomala. Mycopathologia 171:133–138
Hua SST, McAlpin CE, Chang PK, Sarreal SBL (2012) Characterization of aflatoxigenic and non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates from pistachio. Mycotoxin Res 28:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-011-0117-4
Hua SST, Chang PK, Palumbo JD (2017) Mycotoxins. In: Witczak ASZ (ed) Toxins and other harmful compounds in foods. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 153–168
Hua SST, Palumbo JD, Parfitt DE, Sarreal SBL, O’Keeffe T (2018) Development of a droplet digital PCR assay for population analysis of aflatoxigenic and atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus mixtures in soil. Mycotoxin Res 34:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-018-0313-6
Huang C, Jha A, Sweany R, DeRobertis C, Damann KE Jr (2011) Intraspecific aflatoxin inhibition in Aspergillus flavus is thigmoregulated, independent of vegetative compatibility group and is strain dependent. PLoS One 6:e23470
Klich MA (2007) Aspergillus flavus: the major producer of aflatoxin. Mol Plant Pathol 8:713–722
Linz JE, Chanda A, Hong SY, Whitten DA, Wilkerson C, Roze LV (2012) Proteomic and biochemical evidence support a role for transport vesicles and endosomes in stress response and secondary metabolism in Aspergillus parasiticus. J Proteome Res 11:767–775
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mehl HL, Cotty PJ (2010) Variation in competitive ability among isolates of Aspergillus flavus from different vegetative compatibility groups during maize infection. Phytopathology 100:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-100-2-0150
Meyers DM, O’Brian G, Du WL, Bhatnagar D, Payne GA (1998) Characterization of aflJ, a gene required for conversion of pathway intermediates to aflatoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3713–3717
Moore GG, Singh R, Horn BW, Carbone I (2009) Recombination and lineage-specific gene loss in the aflatoxin gene cluster of Aspergillus flavus. Mol Ecol 18:4870–4887
Moore GG, Elliott JL, Singh R, Horn BW, Dorner JW, Stone EA, Chulze SN, Barros GG, Naik MK, Wright GC, Hell K, Carbone I (2013) Sexuality generates diversity in the aflatoxin gene cluster: evidence on a global scale. PLoS Pathog 9(8):e1003574
Ohkura M, Cotty PJ, Orbach MJ (2018) Comparative genomics of Aspergillus flavus S and L morphotypes yield insights into niche adaptation. G3 (Bethesda) 8:3915–3930. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.118.200553
Ojiambo PS, Battilani P, Cary JW, Blum BH, Carbone I (2018) Culture and genetic approaches to manage aflatoxin contamination: recent insights provide opportunities for improved control. Phytopath 108:1024–1037
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pfaffl MW (2004) Quantification strategies in real-time PCR, in: A-Z of quantitative PCR. 87–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-011-0963-1
Pfaffl MW (2012) Quantification strategies in real-time polymerase chain reaction. https://www.gene.quantification.de/pfaffl-chapter-3-quan-strategies-appl-microbiol-2012.pdf
Van Egmond HP, Schothorst RC, Jonker MA (2007) Regulations relating to mycotoxins in food: perspectives in a global and European context. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:147–157
Wicklow DT, Bobell JR, Palmquist DE (2003) Effect of intraspecific competition by Aspergillus flavus on aflatoxin formation in suspended disc culture. Mycol Res 107:617–623
Woloshuk CP, Foutz KR, Brewer JF, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Payne GA (1994) Molecular characterization of aflR, a regulatory locus for aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2408–2414
Yu J (2012) Current understanding on aflatoxin biosynthesis and future perspective in reducing aflatoxin contamination. Toxins (Basel) 41:24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4111024
Yu JH, Butchko RAE, Fernandes M, Keller N, Leonard T (1996) Conservation of structure and function of the aflatoxin regulatory gene aflR from Aspergillus nidulans and A. flavus. Curr Genet 29:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02426959
Yu J, Chang PK, Ehrlich KC, Cary JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Payne GA, Linz JE, Woloshuk CP, Bennett JW (2004) Clustered pathway genes in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ 70(3):1253–1262
Funding
This work is supported by in-house research program funds from U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Services (Project Numbers: 5325-42000-039-00D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, S.S.T., Parfitt, D.E., Sarreal, S.B.L. et al. Dual culture of atoxigenic and toxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus to gain insight into repression of aflatoxin biosynthesis and fungal interaction. Mycotoxin Res 35, 381–389 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-019-00364-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-019-00364-w