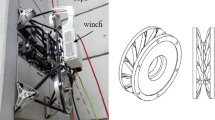
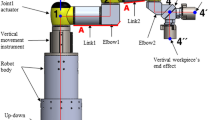
Abstract
In this study, an optimized traction pulley is designed to achieve high repeatability of rope winches of surface-cleaning robots that estimate positions using the lengths of the ascender and flexible rope. When a slip occurs, measuring the length of the rope becomes difficult, which further complicates position estimation and control. However, if the slip is constant and repeatable, the error can be corrected by estimating the position. Herein, traction pulley’s design parameters(Pulley diameter, Number of groove,Pressure roller force) was experimentally evaluated using Taguchi method and Full Factorial Design. Based on two experiments, the optimal design parameters of the pulley were determined to be a diameter of 205 mm, 45 grooves, and a pressure roller force of 47 N. The optimized pulley demonstrated improved performance by reducing the standard deviation in the position error by 70.1\(\%\) compared with that of the optimized pulley reported in a previous study. Thus, applying the optimized traction pulley in future studies is expected to improve the accuracy of position estimation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mills, F. (2022). What makes a building a skyscraper? the answer is more complicated than you might imagine. THEB1Mhttps://www.theb1m.com/article/what-makes-a-building-a-skyscraper-2020.
Seo, T., Jeon, Y., Park, C., & Kim, J. (2019). Survey on glass and façade-cleaning robots: Climbing mechanisms, cleaning methods, and applications. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6, 367–376.
Moon, S.-M., Huh, J., Lee, S., Kang, S., Han, C.-S., & Hong, D. (2013). A survey on robot systems for high-rise building wall maintenance. Journal of the Korean Society for precision Engineering, 30, 359–367.
Seo, M., Yoo, S., Kim, J., Kim, H. S., & Seo, T. (2020). Dual ascender robot with position estimation using angle and length sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(13), 7422–7432.
Yoo, S., Kim, T., Seo, M., Oh, J., Kim, J., Kim, H. S., & Seo, T. (2021). Modeling and verification of multi-winding rope winch for facade operation. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 155, 104105.
Yoo, S., Kim, T., Seo, M., Oh, J., Kim, H. S., & Seo, T. (2021). Position-tracking control of dual-rope winch robot with rope slip compensation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 26(4), 1754–1762.
Bechtel, S., Vohra, S., Jacob, K., & Carlson, C. (2000). The stretching and slipping of belts and fibers on pulleys. J. Appl. Mech., 67(1), 197–206.
Eytelwein, J. (1793). Ausgaben großtentheils aus der angewandten mathematik. Freidrich Manrer, Berlin, Germany.
Euler, L. (1769). Remarques sur l’effet du frottement dans l’equilibre. Memoires de l’academie des sciences de Berlin, pp. 265–278.
Leech, C. (2002). The modelling of friction in polymer fibre ropes. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 44(3), 621–643.
Yoo, S., Joo, I., Hong, J., Kim, J., Kim, H. S., & Seo, T. (2020). Mechanical and empirical parameter design on a multi-wound differential pulley winch for a wall-climbing robot. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 21(5), 857–867.
Kyong, H., Choi, M., Moon, Y., Lee, K., Kim, J., Kim, T., & Seo, T. (2021). Position error compensation of façade-cleaning robot by optimal rope winch design. IEEE Access, 9, 143392–143405.
Choi, M., Chae, H., Kim, K., & Seo, T. (2021). Robust design of a rope ascender based on geometric parameters of traction sheave. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 22(5), 965–974.
Kechagias, J. D., Aslani, K.-E., Fountas, N. A., Vaxevanidis, N. M., & Manolakos, D. E. (2020). A comparative investigation of taguchi and full factorial design for machinability prediction in turning of a titanium alloy. Measurement, 151, 107213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107213.
Yoo, S., Kim, T., Seo, M., Oh, J., Kim, J., Kim, H. S., & Seo, T. (2020). Highly repeatable rope winch design with multiple windings and differential gear mechanism. IEEE Access, 8, 87291–87308.
Baser, O., & Konukseven, E. I. (2010). Theoretical and experimental determination of capstan drive slip error. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 45(6), 815–827.
Leamy, M. J., & Wasfy, T. M. (2002). Analysis of belt-driven mechanics using a creep-rate-dependent friction law. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 69(6), 763–771.
Kong, L., & Parker, R. G. (2005). Microslip friction in flat belt drives. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 219(10), 1097–1106.
Jun, M., Ge, S.-R., & Zhang, D.-K. (2008). Distribution of wire deformation within strands of wire ropes. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 18(3), 475–478.
ISO, I. (2014). Test code for machine toolspart 2: Determination of accuracy and repeatability of positioning of numerically controlled axes. ISO Standard 4, Geneva.
Ghani, J. A., Choudhury, I., & Hassan, H. (2004). Application of taguchi method in the optimization of end milling parameters. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 145(1), 84–92.
Rosa, J. L., Robin, A., Silva, M., Baldan, C. A., & Peres, M. P. (2009). Electrodeposition of copper on titanium wires: Taguchi experimental design approach. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209(3), 1181–1188.
Tanabe, I. (2017). Development of a tool for the easy determination of control factor interaction in the design of experiments and the taguchi methods. 2017 International Conference on Control, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics & Optimization (ICCAIRO). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAIRO.2017.62.
Shang, J. S., Li, S., & Tadikamalla, P. (2004). Operational design of a supply chain system using the taguchi method, response surface methodology, simulation, and optimization. International Journal of Production Research, 42(18), 3823–3849.
Yum, B.-J., Kim, S.-J., Seo, S.-K., Byun, J.-H., & Lee, S.-H. (2013). The taguchi robust design method: Current status and future directions. Journal of Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers, 39(5), 325–341.
Aita, C. A. G., Góss, I. C., Rosendo, T. D. S., Tier, M., Wiedenhöft, A., & Reguly, A. (2020). Shear strength optimization for fssw aa6060-t5 joints by taguchi and full factorial design. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 9(6), 16072–16079.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT for Bridge Convergence R &D Program (NRF-2021M3C1C3096807, NRF-2021M3C1C3096808). (Corresponding author: TaeWon Seo)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hyun, D., Park, S., Yang, J. et al. Robust Parameter Design of an Ascender Affecting Rope Deformation for High Repeatability. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 24, 755–766 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00767-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00767-x