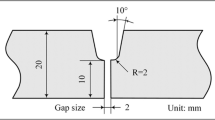
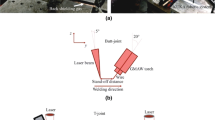
Abstract
The coaxial laser-plasma hybrid welding provides a novel method for the composition of two heat sources and achieves gently transitional butt joints with wider upper surfaces. The influence of hybrid welding parameters on the weld appearance and composite plasma behaviors had been proved with a significant composite heat source effect previously; the effect of microstructure on its mechanical properties has been investigated and explored in this paper. Finite element computation based on temperature field simulation is conducted to shed more light on the heat distribution characteristics of this novel hybrid welding method. The temperature in the hybrid-dominated region is much higher than that in the laser-dominated region. The tensile strength of the hybrid welded joints is higher than the standard requirement of base metal, and fractured at the base metal with an obvious necking, indicating as ductile fracture. The nanohardness results show the hardness rank order of the weld zone, heat-affected zone and base metal. It is revealed that the grain refinement of acicular α' martensite and fine αg particles, the increase of distribution of the geometric necessary dislocations and the large angle grain boundary proportion in the weld zone contribute to an increase in hardness, tensile strength of the hybrid welded joint of Ti–6Al–4V. It also discloses the reason why the tensile fracture location is on the base metal. This work provides a theoretical and practical basis for the application of thin titanium alloy welding, especially at high welding speed.
Graphical Abstract




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Shen, Z.H. Zhang, J.X. Xie, Simultaneously enhancing the hot workability and room-temperature strength of Ti–6Al–4V alloy via adding Mo and Fe. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 180, 32–44 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.04.054
J.C. Williams, R.R. Boyer, Opportunities and Issues in the application of titanium alloys for aerospace components. Metals 10, 70501–70522 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060705
R. Li, Z. Li, Y. Zhu, L. Rong, A comparative study of laser beam welding and laser–MIG hybrid welding of Ti–Al–Zr–Fe titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 1138–1142 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.09.084
B. Kumar, S. Bag, C.P. Paul, C.R. Das, R. Ravikumar, K.S. Bindra, Influence of the mode of laser welding parameters on microstructural morphology in thin sheet Ti6Al4V alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 131, 106456 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106456
J.Q. Shen, B. Li, S.S. Hu, H. Zhang, X.Z. Bu, Comparison of single-beam and dual-beam laser welding of Ti–22Al–25Nb/TA15 dissimilar titanium alloys. Opt. Laser Technol. 93, 118–126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.02.013
J. Chen, Z. Ouyang, X. Du, Y. Wei, Weld pool dynamics and joining mechanism in pulse wave laser beam welding of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy sheets assembled in butt joint with an air gap. Opt. Laser Technol. 146, 107558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107558
A. Squillace, U. Prisco, S. Ciliberto, A. Astarita, Effect of welding parameters on morphology and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V laser beam welded butt joints. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 212, 427–436 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.10.005
X. Cao, M. Jahazi, Effect of welding speed on butt joint quality of Ti–6Al–4V alloy welded using a high-power Nd:YAG laser. Opt. Lasers Eng. 47, 1231–1241 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.05.010
H. Bu, Q. Gao, Y. Li, F. Wang, X. Zhan, Comparative study on microstructure and aluminum distribution between laser beam welding and electron beam welding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy plates. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 3449–3461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00683-z
A. Chamanfar, M.F. Huang, T. Pasang, M. Tsukamoto, W.Z. Misiolek, Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al (Ti1023) titanium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 7721–7731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.028
S. Liu, S. Chen, Q. Wang, Y. Li, H. Zhang, H. Ding, Analysis of plasma characteristics and conductive mechanism of laser assisted pulsed arc welding. Opt. Lasers Eng. 92, 39–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.12.016
C. Bagger, F.O. Olsen, Review of laser hybrid welding. J. Laser Appl. 17, 2–14 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.1848532
H. Huang, P. Zhang, H. Yan, Z. L, Z. Yu, D. Wu, H. Shi, Y. Tian, Research on weld formation mechanism of laser-MIG arc hybrid welding with butt gap. Opt. Laser Technol. 133, 106530 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106530
D.T. Cai, Z.Y. Luo, S.G. Han, Y.F. Xue, C. Chen, Y. Zhang, Plasma characteristics of a novel coaxial laser-plasma hybrid welding of Ti alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 167, 107599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107599
X. Zhan, Y. Liu, W. Ou, C. Gu, Y. Wei, The numerical and experimental investigation of the multi-layer laser-MIG hybrid welding for Fe36Ni invar alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24(12), 4948–4957 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.04.015
J. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, X. Zhan, Microstructure, thermal behavior and tensile properties of laser welded bottom-locking joint for TA15 titanium alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 1441–1453 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01311-8
X. Ren, Z. Wang, X. Fang, H. Song, J. Duan, The plastic flow model in the healing process of internal microcracks in pre-deformed TC4 sheet by pulse current. Mater. Design 188, 108428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108428
Y. Zhao, X. Zhan, Q. Gao, S. Chen, Y. Kang, Research on the microstructure characteristic and tensile property of laser-MIG Hybrid welded joint for 5A06 aluminum alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 26, 346–359 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00340-0
M.Y. Krasnoperov, R.R.G.M. Pieters, I.M. Richardson, Weld pool geometry during keyhole laser welding of thin steel sheets. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joi. 9(6), 501–506 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1179/136217104225021733
G. Casalino, M. Mortello, S.L. Campanelli, Ytterbium fiber laser welding of Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 20, 250–256 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2015.07.003
C. Fu, Y. Wang, S. He, C. Zhang, X. Jing, Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of TIG weld joint made by forged Ti–4Al–2V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 821, 141604 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141604
H. Chen, L. Guo, C. Cao, Hot Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of TC11 alloy with lamellar structure. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 28, 18–22 (2008). (In Chinese)
Y.X. An, Y.C. Deng, X.Y. Zhang, B.F. Wang, Deformation mechanism diagram of a Ti–2.5Zr–2Al titanium alloy forged in the α+β region and grain refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 854, 143776 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.143776
C. Kumar, M. Das, C.P. Paul, K.S. Bindra, Characteristics of fiber laser weldments of two phases (α+β) titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 35, 351–359 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.08.023
H. Beladi, Q. Chao, G.S. Rohrer, Variant selection and intervariant crystallographic planes distribution in martensite in a Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Acta Mater. 80, 478–489 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.06.064
X.L. Gao, L.J. Zhang, J. Liu, J.X. Zhang, A comparative study of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding and TIG welding of thin Ti6Al4V titanium alloy plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 14–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.06.016
R.K. Maurya, D. Singh, Nano-mechanical behavior of MnTiO3 ceramics. Mater. Lett. 246, 49–51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.03.026
H. Gu, L. Jiao, P. Yan, Y. Song, Z. Guo, T. Qiu, X. Wang, Dual-crack failure behaviors of milled Ti–6Al–4V alloy in conformal contact fretting fatigue. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 832, 142465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142465
R.Z. Wang, L.Y. Cheng, S.P. Zhu, P.C. Zhao, H. Miura, X.C. Zhang, S.T. Tu, Semi-quantitative creep-fatigue damage analysis based on diffraction-based misorientation mapping and the correlation to macroscopic damage evolutions. Int. J. Fatigue 149, 106227 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106227
T. Yan, Y. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Zheng, X. Zhan, Bridging microstructure and crystallography with the crack propagation behavior in Ti–6Al–4V alloy fabricated via dual laser beam bilateral synchronous welding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 174, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.05.058
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the following grant: GDAS' Project of Science and Technology Development (2020GDASYL–20200301001), Foundation Project of Guangdong Province (2022A1515011118, 2019B1515120081), GDAS' Project of Science and Technology Development (2021GDASYL-20210103085, 2022GDASZH–2022010203, 2023GDASZH–2023010105), The S&T Project of Yangjiang (SDZX2022011, RCZX2023010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Luo, Z., Liu, W. et al. Microstructure, Texture, and Mechanical Properties of Thin Titanium Plates Jointed by Coaxial Laser-Plasma Hybrid Welding. Met. Mater. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-024-01659-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-024-01659-z