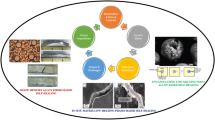
Abstract
Zn is considered one of the most attractive bioresorbable candidates for metal implants, because it does not exhibit the inherent limitations of Fe and Mg. To explore the coordination of the toughness and strength of Zn alloys via grain size, secondary phase, and texture modification, we designed a micro-alloyed binary Zn–0.5 Mg (wt%) alloy. The sample was processed through hot extrusion at 220 °C with an extrusion ratio of 25:1 and subjected to rapid heat treatment at varying temperatures. Interestingly, the ductility of the low-temperature annealed alloys increased without exhibiting strength loss, in contrast to the known behavior of most other metallic alloys. The mechanical properties were optimized in the sample by thermal deformation and 30 min annealing at 150 °C, exhibiting the following results: yield strength of 240.3 ± 4.3 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 293.6 ± 3.8 MPa, and elongation to failure of 36.3 ± 4.5%. During the low-temperature annealing of extruded Zn–0.5 Mg rods, the fine Mg2Zn11 phase particles pinning effect and the recrystallization behavior inhibited grain coarsening. The prismatic <a> and pyramidal <c + a> slip systems were activated by a non-basal texture, which contributed to the enhanced toughness. The balance between strength and ductility was mainly attributed to a synergistic effect of grain refinement, unique texture modification, and secondary phases.
Graphical Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Li, H. Yang, Y. Zheng, X.-H. Chen, J.-A. Yang, D. Zhu, L. Ruan, K. Takashima, Challenges in the use of zinc and its alloys as biodegradable metals: perspective from biomechanical compatibility. Acta Biomater. 97, 23–45 (2019)
H. Guo, Hu. Jili, Z. Shen, Du. Dexiao, Y. Zheng, J. Peng, In vitro and in vivo studies of biodegradable Zn-Li-Mn alloy staples designed for gastrointestinal anastomosis. Acta Biomater. 121, 713–723 (2021)
E. Mostaed, M. Sikora-Jasinska, A. Mostaed, S. Loffredo, A.G. Demir, B. Previtali, D. Mantovani, R. Beanland, M. Vedani, Novel Zn-based alloys for biodegradable stent applications: Design, development and in vitro degradation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 60, 581–602 (2016)
C. Iglesias, O.G. Bodelón, R. Montoya et al., Fracture bone healing and biodegradation of AZ31 implant in rats. Biomed. Mater. 10(2), 025008 (2015)
K. Pieła, M. Wróbel, K. Sztwiertnia, M. Jaskowski, J. Kawałko, M. Bieda, M. Kiper, A. Jarzębsk, Zinc subjected to plastic deformation by complex loading and conventional extrusion: comparison of the microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 117, 111–120 (2017)
S. Liu, D. Kent, N. Doan, M. Dargusch, G. Wang, Effects of deformation twinning on the mechanical properties of biodegradable Zn-Mg alloys. Bioactive Mater. 4, 8–16 (2019)
L. Ye, He. Huang, C. Sun, X. Zhuo, Q. Dong, H. Liu, Ju. Jia, F. Xue, J. Bai, J. Jiang, Effect of grain size and volume fraction of eutectic structure on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of as-cast Zn–Mg binary alloys. J. Market. Res. 16, 1673–1685 (2022)
Yu. Yilong Dai, H.L. Zhang, H. Fang, D. Li, Xu. Xuemei, Y. Yan, L. Chen, Lu. Yujiao, Yu. Kun, Mechanical strengthening mechanism of Zn-Li alloy and its mini tube as potential absorbable stent material. Mater. Lett. 235, 220–223 (2019)
H.F. Li, X.H. Xie, Y.F. Zheng et al., Development of biodegradable Zn-1X binary alloys with nutrient alloying elements Mg, Ca and Sr. Sci. Rep. 5, 10719 (2015)
Bo. Jia, Yu. Hongtao Yang, Z.Z. Han, Qu. Xinhua, Y. Zhuang, Wu. Qiang, Y. Zheng, K. Dai, In vitro and in vivo studies of Zn-Mn biodegradable metals designed for orthopedic applications. Acta Biomater. 108, 358–372 (2020)
X. Tong, D. Zhang, J. Lin, Y. Dai, Y. Luan, Q. Sun, Z. Shi, K. Wang, Y. Gao, J. Lin, Y. Li, M. Dargusch, C. Wen, Development of biodegradable Zn–1Mg–0.1RE (RE = Er, Dy, and Ho) alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 117, 384–399 (2020)
S. Huang, L. Wang, Y. Zheng, L. Qiao, Y. Yan, In vitro degradation behavior of novel Zn–Cu–Li alloys: roles of alloy composition and rolling processing. Mater Des 212, 110288 (2021)
X. Wang, Y. Ma, B. Meng, M. Wan, Effect of equal-channel angular pressing on microstructural evolution, mechanical property and biodegradability of an ultrafine-grained zinc alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 824, 141857 (2021)
H. Zhang, Y. Ding, R. Li, Y. Shen, J. Lei, Achieving exceptional improvement of yield strength in Mg–Zn–Ca alloy wire by nanoparticles induced by extreme plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 853, 143733 (2022)
J. Venezuela, M.S. Dargusch, The influence of alloying and fabrication techniques on the mechanical properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility of zinc: a comprehensive review. Acta Biomater. 87, 1–40 (2019)
L. Ye, C. Sun, X. Zhuo, H. Liu, J. Jia, F. Xue, J. Bai, J. Jiang, Y. Xin, Evolution of grain size and texture of Zn-0.5Cu ECAP alloy during annealing at 200 °C and its impact on mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 919, 165871 (2022)
J.N. Li, P. Cao, X.N. Zhang et al., In vitro degradation and cell attachment of a PLGA coated biodegradable Mg–6Zn based alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 6038–6045 (2010)
H. Zhou, B. Liang, H. Jiang, Z. Deng, Yu. Kexiao, Magnesium-based biomaterials as emerging agents for bone repair and regeneration: from mechanism to application. J. Magn. Alloys 9(3), 779–804 (2021)
Su. Yingchao, I. Cockerill, Y. Wang, Y.-X. Qin, L. Chang, Y. Zheng, D. Zhu, Zinc-based biomaterials for regeneration and therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 37(4), 428–441 (2019)
H. Yang, Bo. Jia, Z. Zhang, Qu. Xinhua, G. Li, W. Lin, D. Zhu, K. Dai, Y. Zheng, Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 1–16 (2020)
N. Yang, J. Venezuela, S. Almathami, M. Dargusch, Zinc-nutrient element based alloys for absorbable wound closure devices fabrication: current status, challenges, and future prospects. Biomaterials 280, 121301 (2022)
J. Kubásek, I. Pospíšilová, D. Vojtěch, E. Jablonska, T. Ruml, Structural, mechanical and cytotoxicity characterization of as-cast biodegradable Zn-xMg (x = 0.8–8.3%) alloys. Mater. Tehnol. 48(5), 623–629 (2014)
C. García-Mintegui, L.C. Córdoba, J. Buxadera-Palomero, A. Marquina, E. Jiménez-Piqué, M.-P. Ginebra, J.L. Cortina, M. Pegueroles, Zn-Mg and Zn-Cu alloys for stenting applications: from nanoscale mechanical characterization to in vitro degradation and biocompatibility. Bioactive Mater. 6(12), 4430–4446 (2021)
J. Kubásek, D. Vojtěch, I. Pospíšilová et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of the micrograined hypoeutectic Zn–Mg alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 23(10), 1167–1176 (2016)
S. Lin, X. Ran, X. Yan et al., Systematical evolution on a Zn–Mg alloy potentially developed for biodegradable cardiovascular stents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 30(11), 1–12 (2019)
J. Čapek, J. Kubásek, J. Pinc, J. Maňák, O. Molnárová, J. Drahokoupil, M. Čavojský, ZnMg0.8Ca0.2 (wt%) biodegradable alloy—the influence of thermal treatment and extrusion on microstructural and mechanical characteristics. Mater Charact 162, 110230 (2020)
M.S. Ardakani, E. Mostaed, M. Sikora-Jasinska, S.L. Kampe, J.W. Drelich, The effects of alloying with Cu and Mn and thermal treatments on the mechanical instability of Zn-0.05Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 770, 138529 (2020)
H. Yan, X.H. Shao, H.P. Li, R.S. Chen, H.Z. Cui, En-Hou Han, Synergization of ductility and yield strength in a dilute quaternary Mg-Zn-Gd-Ca alloy through texture modification and Guinier-Preston zone. Scr. Mater. 207, 114257 (2022)
R. Zhao, Q. Ma, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, Xu. Chunxiang, Wu. Yuan, J. Zhang, Revealing the influence of Zr micro-alloying and hot extrusion on a novel high ductility Zn–1Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 801, 140395 (2021)
R. Li, Y. Ding, H. Zhang, J. Lei, Y. Shen, Effective strengthening and toughening in Zn–1Mg alloy with bimodal grain structure achieved by conventional extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 854, 143850 (2022)
H. Okamoto, Supplemental literature review of binary phase diagrams: Cs-In, Cs-K, Cs-Rb, Eu-In, Ho-Mn, K-Rb, Li-Mg, Mg-Nd, Mg-Zn, Mn-Sm, O-Sb, and Si-Sr. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 34(3), 251–263 (2013)
J. Jiang, H. Huang, J. Niu et al., Fabrication and characterization of biodegradable Zn-Cu-Mn alloy micro-tubes and vascular stents: Microstructure, texture, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior. Acta Biomater. 151, 647–660 (2022)
J.D. Robson, D.T. Henry, B. Davis, Particle effects on recrystallization in magnesium–manganese alloys: Particle-stimulated nucleation. Acta Mater. 57(9), 2739–2747 (2009)
Z. Yan, Z. Zhang, X. Li, Xu. Jian, Q. Wang, G. Zhang, J. Zheng, H. Fan, Xu. Kaihua, J. Zhu, Y. Xue, A novel severe plastic deformation method and its effect on microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 153698 (2020)
D. Lou, L. Wang, Y. Ren, H. Li, G. Qin, Textural evolution and improved ductility in Zn-0.2Mg-0.8Mn (wt%) alloys at different extrusion temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 860, 158530 (2021)
L. Wang, Y. He, H. Zhao, H. Xie, S. Li, Y. Ren, G. Qin, Effect of cumulative strain on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Zn-002 wt%Mg alloy wires during room-temperature drawing process. J. Alloys Compd. 740(9), 949–957 (2018)
Y.N. Wang, J.C. Huang, Texture analysis in hexagonal materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 81(1), 11–26 (2003)
L.B. Tong, J.H. Chu, W.T. Sun, Z.H. Jiang, D.N. Zou et al., Development of a high-strength Mg alloy with superior ductility through a unique texture modification from equal channel angular pressing. J. Magn. Alloys 9, 1007–1018 (2021)
C. Xiao, L. Wang, Y. Ren, S. Sun, E. Zhang, C. Yan et al., Indirectly extruded biodegradable Zn-0.05wt%Mg alloy with improved strength and ductility: in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(9), 1618–1627 (2018)
L.Q. Wang, Y.P. Ren, S.N. Sun et al., Microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture behavior of as-extruded Zn–Mg binary alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 30, 931–940 (2017)
H. Gong, K. Wang, R. Strich, J.G. Zhou, In vitro biodegradation behavior, mechanical properties, and cytotoxicity of biodegradable Zn-Mg alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 103(8), 1632–1640 (2015)
S. Sun, Y. Ren, L. Wang, Bo. Yang, H. Li, G. Qin, Abnormal effect of Mn addition on the mechanical properties of as-extruded Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 701, 129–133 (2017)
Z.-Z. Shi, Yu. Jing, X.-F. Liu, Microalloyed Zn-Mn alloys: From extremely brittle to extraordinarily ductile at room temperature. Mater. Des. 144, 343–352 (2018)
W. Bednarczyk, M. Wątroba, J. Kawałko, P. Bała, Can zinc alloys be strengthened by grain refinement? A critical evaluation of the processing of low-alloyed binary zinc alloys using ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 748, 357–366 (2019)
Z. Tang, J. Niu, H. Huang, H. Zhang, J. Pei, Ou. Jingmin, G. Yuan, Potential biodegradable Zn-Cu binary alloys developed for cardiovascular implant applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 72, 182–191 (2017)
W. Zhang, P. Li, G. Shen, X. Mo, C. Zhou, D. Alexander, F. Rupp, J. Geis-Gerstorfer, H. Zhang, G. Wan, Appropriately adapted properties of hot-extruded Zn–05Cu–xFe alloys aimed for biodegradable guided bone regeneration membrane application. Bioactive Mater. 6(4), 975–989 (2021)
M. Sikora-Jasinska, E. Mostaed, A. Mostaed, R. Beanland, D. Mantovani, M. Vedani, Fabrication, mechanical properties and in vitro degradation behavior of newly developed ZnAg alloys for degradable implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 77, 1170–1181 (2017)
D. Zhu, I. Cockerill, Su. Yingchao et al., Mechanical strength, biodegradation, and in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of Zn biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(7), 6809–6819 (2019)
C. Liu, Y. Chen, C. Zhang, D. Chen, G. Cui, Enhanced strength and plasticity in a novel 55Si2MnMoV spring steel via austempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 825, 141887 (2021)
E. Mostaed, M. Sikora-Jasinska, J.W. Drelich, M. Vedani, Zinc-based alloys for degradable vascular stent applications. Acta Biomater. 71, 1–23 (2018)
A. Bahrami, A.J. den Bakker, A. Miroux, J. Sietsma, in Light Metals 2013, ed. by B.A. Sadler (Springer, Cham, 2013), pp. 347–350
M. Wątroba, W. Bednarczyk, J. Kawałko, P. Bała, Fine-tuning of mechanical properties in a Zn–Ag–Mg alloy via cold plastic deformation process and post-deformation annealing. Bioactive Mater. 6(10), 3424–3436 (2021)
J. Hirsch, T. Al-Samman, Superior light metals by texture engineering: optimized aluminum and magnesium alloys for automotive applications. Acta Mater. 61(3), 818–843 (2013)
J. Koike, T. Kobayashi, T. Mukai, H. Watanabe, M. Suzuki, K. Maruyama, K. Higashi, The activity of non-basal slip systems and dynamic recovery at room temperature in fine-grained AZ31B magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 51(7), 2055–2065 (2003)
X. Nie, J. Ni, S. Dong et al., Preferential grain growth and textural evolution of AZ31B Mg alloy during annealing after isothermal compression at 400 °C. Mater. Charact. 169, 110566 (2020)
Z. Liu, R. Li, R. Jiang, X. Li, M. Zhang, Effects of Al addition on the structure and mechanical properties of Zn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 687(5), 885–892 (2016)
X. Zhuo, Wu. Yuna, Ju. Jia, H. Liu, J. Jiang, Hu. Zhichao, J. Bai, F. Xue, Recent progress of novel biodegradable zinc alloys: from the perspective of strengthening and toughening. J. Market. Res. 17, 244–269 (2022)
Z. Liu, D. Qiu et al., Effect of grain refinement on tensile properties of cast Zinc alloys. Metall. and Mater. Trans. A 47(2), 830–841 (2016)
Z.C. Cordero, B.E. Knight, C.A. Schuh, Six decades of the Hall-Petch effect-a survey of grain-size strengthening studies on pure metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 61, 495–512 (2016)
S. Luo, N. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Chen, H. Qin, S. Kong, T. Bai, L. Wenjie, L. Xiao, X. Ma, X. Yang, J. Zhang, Texture, microstructure and mechanical properties of an extruded Mg-10Gd-1Zn-0.4Zr alloy: Role of microstructure prior to extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 849, 143476 (2022)
R.G. Li, H.R. Li, D.Y. Zhao et al., High strength commercial AZ91D alloy with a uniformly fine-grained structure processed by conventional extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 780, 139193 (2020)
Di. Liu, Z. Liu, E. Wang, Effect of rolling reduction on microstructure, texture, mechanical properties and mechanical anisotropy of AZ31 magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 612, 208–213 (2014)
D. Zhao, X. Ma, A. Srivastava, G. Turner, I. Karaman, K.Y. Xie, Significant disparity of non-basal dislocation activities in hot-rolled highly-textured Mg and Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy under tension. Acta Mater. 207, 116691 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to the financial support from Hongliu first-class discipline construction plan of Lanzhou University of Technology. This study was also supported by Outstanding Postgraduate Innovation Star Project of Gansu Provincial Department of Education (Project No. 2022CXZX-389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Ding, Y. & Zhang, H. Toughness and Strength Coordination in a Low-Alloy Zn–0.5 Mg Alloy via Extrusion and Post-Deformation Annealing. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 2807–2825 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01420-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01420-y