Abstract
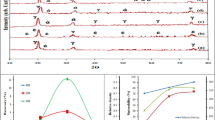
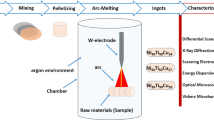
NITINOL is the most popular and economic shape memory alloy (SMA) used in various industries. For temperature associated applications, the shape memory effect (SME) is the major phenomenon for the shape and strain recovery of materials after deformation. The machinability and cold working ability of NiTi alloys are poor compared to conventional alloys. So to reduce the post-processing of the finished product with good homogenization of elements, the powder technology route is suitable for making these SMAs. Due to the simplicity and cost-effectiveness, the uniaxial press and sinter process was used for pellet making. In this paper, before sintering 450, 475, 500, 525, 550, 575 and 600 MPa compaction pressures were analysed by their green densities and 600 MPa compacted pellet yielded the better density. Sintering was done at 950, 1000, 1050, 1100 and 1150 °C with the variation of sintering time 0.5, 1, 1.5 and 2 h. The XRD and SEM studies showed that samples sintered at 950 °C have oxide phases with elemental Ni and Ni3Ti phases. For samples sintered at 1000, 1050 and 1100 °C, NiTi and Ti2Ni formed as major phases with minor phases of βTi and Ni4Ti3 precipitates formed inside the NiTi matrix. It was difficult to detect the minor phases for the sample sintered at 1150 °C. Needle shaped martensitic NiTi forms inside the austenitic NiTi matrix and was detected at a very high magnification of 5000× in SEM. From the Differential Scanning Calorimetry study, it was found that an increase in sintering time and sintering temperature results in a faster shape memory response.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Sharma, G. Srinivas, Flying smart: Smart materials used in aviation industry. Mater. Today Proc. 27, 244–250 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.10.115
NiTi Alloy Ball Bearings. https://technology.nasa.gov/patent/LEW-TOPS-129. Accessed 12 Mar 2020
B. Swain, S. Bajpai, A. Behera, Microstructural evolution of NITINOL and their species formed by atmospheric plasma spraying. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 7, 015006 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2051-672X/aaf30e
C. Chluba, K. Siemsen, C. Bechtold, C. Zamponi, C. Selhuber-Unkel, E. Quandt, R. Lima de Miranda, Microfabricated bioelectrodes on self-expandable NiTi thin film devices for implants and diagnostic instruments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 153, 112034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112034
C.R. Knick, G.L. Smith, C.J. Morris, H.A. Bruck, Rapid and low power laser actuation of sputter-deposited NiTi shape memory alloy (SMA) MEMS thermal bimorph actuators. Sensor. Actuat. A Phys. 291, 48–57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.03.016
S. Kim, E. Hawkes, K. Choy, M. Joldaz, J. Foleyz, R. Wood, Micro artificial muscle fiber using NiTi spring for soft robotics, in 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS 2009, St. Louis, 10-15 October 2009 (IEEE, New York, 2009), pp. 2228–2234
R. Neupane, Z. Farhat, Wear mechanisms of nitinol under reciprocating sliding contact. Wear 315, 25–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.02.018
W.J. Buehler, F.E. Wang, A summary of recent research on the nitinol alloys and their potential application in ocean engineering. Ocean Eng. 1, 105–120 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-8018(68)90019-x
R. Snodgrass, D. Erickson, A multistage elastocaloric refrigerator and heat pump with 28 K temperature span. Sci. Rep. 9, 18532 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54411-8
L. Zhang, Z.Y. He, J. Tan, Y.Q. Zhang, M. Stoica, K.G. Prashanth, M.J. Cordill, Y.H. Jiang, R. Zhou, J. Eckert, Rapid fabrication of function-structure-integrated NiTi alloys: Towards a combination of excellent superelasticity and favorable bioactivity. Intermetallics 82, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2016.11.004
S.K. Patel, B. Behera, B. Swain, R. Roshan, D. Sahoo, A. Behera, A review on NiTi alloys for biomedical applications and their biocompatibility. Mater. Today Proc. 33, 5548–5551 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.538
M.T. Andani, N.S. Moghaddam, C. Haberland, D. Dean, M.J. Miller, M. Elahinia, Metals for bone implants. Part 1. Powder metallurgy and implant rendering. Acta Biomater. 10, 4058–4070 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2014.06.025
G. Helbert, L. Dieng, S.A. Chirani, L. Saint-Sulpice, T. Lecompte, S. Calloch, Investigation of NiTi based damper effects in bridge cables vibration response: Damping capacity and stiffness changes. Eng. Struct. 165, 184–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.02.087
O. Ammar, N. Haddar, L. Dieng, Experimental investigation of the pseudoelastic behaviour of NiTi wires under strain- and stress-controlled cyclic tensile loadings. Intermetallics 81, 52–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2017.03.002
M. Xia, Q. Sun, Jump phenomena of rotational angle and temperature of NiTi wire in nonlinear torsional vibration. Int. J. Solids Struct. 56, 220–234 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2014.11.002
W. Tang, Thermodynamic study of the low-temperature phase B19′ and the martensitic transformation in near-equiatomic Ti–Ni shape memory alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28, 537–544 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0041-6
B. Swain, P. Mallick, S.K. Bhuyan, S.S. Mohapatra, S.C. Mishra, A. Behera, Mechanical properties of NiTi plasma spray coating. J. Therm. Spray Techn. 29, 741–755 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-01017-6
B.C. Hornbuckle, X.X. Yu, R.D. Noebe, R. Martens, M.L. Weaver, G.B. Thompson, Hardening behavior and phase decomposition in very Ni-rich Nitinol alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 639, 336–344 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.04.079
C. DellaCorte, F. Thomas, M.K. Stanford, Method for making small diameter nickel-titanium metal alloy balls, US Patent 11033963 (2021)
B. Bertheville, M. Neudenberger, J.-E. Bidaux, Powder sintering and shape-memory behaviour of NiTi compacts synthesized from Ni and TiH2. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 384, 143–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.06.025
M.H. Ismail, R. Goodall, H.A. Davies, I. Todd, Porous NiTi alloy by metal injection moulding/sintering of elemental powders: Effect of sintering temperature. Mater. Lett. 70, 142–145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.12.008
G. Chen, P. Cao, N. Edmonds, Porous NiTi alloys produced by press-and-sinter from Ni/Ti and Ni/TiH2 mixtures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 582, 117–125 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.05.082
K. Khanlari, M. Ramezani, P. Kelly, P. Cao, T. Neitzert, Mechanical and microstructural characteristics of as-sintered and solutionized porous 60NiTi. Intermetallics 100, 32–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2018.06.001
R. Singh, A.K. Sharma, A.K. Sharma, Physical and mechanical behavior of NiTi composite fabricated by newly developed uni-axial compaction die. Mater. Res. 24, e20200549 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2020-0549
T. Lai, J.-L. Xu, Q.-F. Xiao, Y.-X. Tong, J. Huang, J.-P. Zhang, J.-M. Luo, Y. Liu, Preparation and characterization of porous NiTi alloys synthesized by microwave sintering using Mg space holder. T. Nonferr Metal. Soc. China 31, 485–498 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65511-5
D.V.V. Satyanarayana, N. Eswara Prasad, Nickel-based superalloys, in Aerospace Materials and Material Technologies, vol. 1, ed. by N.E. Prasad, R.J.H. Wanhill (Springer, Singapore, 2017), pp. 199–228
B. Yin, G. Xie, L. Lou, J. Zhang, Abnormal increase of TCP phase during heat treatment in a Ni-based single crystal superalloy. Scripta Mater. 173, 1–4 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2019.07.027
L.M. Bortoluci Ormastroni, L. Mataveli Suave, A. Cervellon, P. Villechaise, J. Cormier, LCF, HCF and VHCF life sensitivity to solution heat treatment of a third-generation Ni-based single crystal superalloy. Int. J. Fatigue 130, 105247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105247
I. Lopez-Galilea, B. Ruttert, J. He, T. Hammerschmidt, R. Drautz, B. Gault, W. Theisen, Additive manufacturing of CMSX-4 Ni-base superalloy by selective laser melting: Influence of processing parameters and heat treatment. Addit. Manuf. 30, 100874 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100874
B. Swain, P. Mallick, S. Patel, R. Roshan, S.S. Mohapatra, S. Bhuyan, M. Priyadarshini, B. Behera, S. Samal, A. Behera, Failure analysis and materials development of gas turbine blades. Mater. Today Proc. 33, 5143–5146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.859
B. Swain, P. Mallick, Ram K. Gupta, S.S. Mohapatra, G. Yasin, T.A. Nguyen, Ajit Behera, Mechanical and tribological properties evaluation of plasma-sprayed shape memory alloy coating. J. Alloy. Compd. 863, 158599 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158599
C. Fu, Y. Chen, L. Li, S. Antonov, Q. Feng, Evaluation of service conditions of high pressure turbine blades made of DS Ni-base superalloy by artificial neural networks. Mater. Today Commun. 22, 100838 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100838
J. Belan, A. Vaško, E. Tillová, Microstructural analysis of DV - 2 Ni - base superalloy turbine blade after high temperature damage. Procedia Engineer. 177, 482–487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.02.249
N. Taheri, H. Naffakh-Moosavy, F.M. Ghaini, A new procedure for refurbishment of power plant superalloy 617 by pulsed Nd:YAG laser process. Opt. Laser Technol. 91, 71–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2016.12.013
P.M. Mignanelli, N.G. Jones, E.J. Pickering, O.M.D.M. Messé, C.M.F. Rae, M.C. Hardy, H.J. Stone, Gamma-gamma prime-gamma double prime dual-superlattice superalloys. Scripta Mater. 136, 136–140 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.04.029
S.K. Patel, B. Swain, A. Behera, Advanced processing of superalloys for aerospace industries, in Functional and Smart Materials, 1st edn., ed. by C. Prakash, S. Singh, J.P. Davim (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2020), pp. 109–122
B. Swain, P. Mallick, S.S. Mohapatra, A. Behera, D.K. Rajak, P.L. Menezes, Atmospheric plasma spray coating of NiTi on mild steel substrate: An microstructural investigation. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 7, 104 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-021-00541-4
K. Otsuka, X. Ren, Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 50, 511–678 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001
M. Farvizi, M.K. Javan, M.R. Akbarpour, H.S. Kim, Fabrication of NiTi and NiTi-nano Al2O3 composites by powder metallurgy methods: Comparison of hot isostatic pressing and spark plasma sintering techniques. Ceram. Int. 44, 15981–15988 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.025
X. Li, X. Chen, C. Zhang, J. Luo, Preparation of self-lubricating NiTi alloy and its self-adaptive behavior. Tribol. Int. 130, 43–51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.09.002
P. Bassani, S. Panseri, A. Ruffini, M. Montesi, M. Ghetti, C. Zanotti, A. Tampieri, A. Tuissi , Porous NiTi shape memory alloys produced by SHS: microstructure and biocompatibility in comparison with Ti2Ni and TiNi3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. M. 25, 2277–2285 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5253-x
C.Y. Tang, L.N. Zhang, C.T. Wong, K.C. Chan, T.M. Yue, Fabrication and characteristics of porous NiTi shape memory alloy synthesized by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 6006–6011 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.040
G. Wen, P. Cao, B. Gabbitas, D. Zhang, N. Edmonds, Development and design of binder systems for titanium metal injection molding: An overview. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 1530–1547 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1485-x
G. Tosun, M. Kilic, L. Ozler, N. Tosun, Characterization of a porous Nickel-Titanium alloy produced with self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Mater. Tehnol. 52, 435–442 (2018). https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2017.156
ASTM B962-13, Standard test methods for density of compacted or sintered powder metallurgy (PM) products using archimedes’ principle (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2013)
A.A. Atiyah, A.-R.K.A. Ali, N.M. Dawood, Characterization of NiTi and NiTiCu porous shape memory alloys prepared by powder metallurgy (part I). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 901–913 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1538-0
S. Ozan, K. Munir, A. Biesiekierski, R. Ipek, Y. Li, C. Wen, Titanium alloys, including Nitinol, in Biomaterials Science, 4th edn, ed.by W.R.Wagner et al. (Accadical Press, Cambridge, 2020), pp. 229–247
R.R. Boyer, Aerospace applications of beta titanium alloys. JOM 46, 20–23 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220743
W.-Y. Kai, K.-C. Chang, H.-F. Wu, S.-W. Chen, A.-C. Yeh, Formation mechanism of Ni2Ti4Ox in NITI shape memory alloy. Materialia 5, 100194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2018.100194
S.R. Soundararajan, J. Vishnu, G. Manivasagam, N.R. Muktinutalapati, Processing of beta titanium alloys for aerospace and biomedical applications, in Titanium Alloys—Novel Aspects of Their Manufacturing and Processing, ed. by M. Motyka, W. Ziaja, J. Sieniawsk (IntechOpen, London, 2018)
M. Abdel-Hady Gepreel, M. Niinomi, Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 20, 407–415 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.11.014
S. Conti, M. Lenz, N. Lüthen, M. Rumpf, B. Zwicknagl, Geometry of martensite needles in shape memory alloys. Comptes Rendus Math. 358, 1047–1057 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5802/CRMATH.120
S. Kumar Patel, B. Swain, R. Roshan, N.K. Sahu, A. Behera, A brief review of shape memory effects and fabrication processes of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 33, 5552–5556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.539
Y. Guo, A. Klink, C. Fu, J. Snyder, Machinability and surface integrity of Nitinol shape memory alloy. CIRP Ann. 62, 83–86 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2013.03.004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, S.K., Behera, A. Evolution of Phases and their Influence on Shape Memory Effect by Varying Sintering Parameters of NiTi Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 28, 2691–2705 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01166-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01166-5