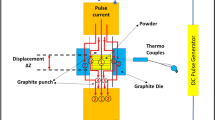
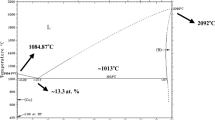
Abstract
The relentless effort for the innovation of improved materials for application in high-temperature environment, structural and functional application has paved the way for the synthesis of ceramics based materials—with current research activities being channeled towards the application of metallic and non-metallic based nano-powders as a sintering additive or as a reinforcement for ceramic-based materials. Metallic and non-metallic based nanopowders additive possesses excellent thermal, physical, and mechanical properties and hence, serves as a good additive for ceramic-based materials in achieving good sinterability, full densification, and excellent mechanical properties. One of the critical factors that have affected the densification and properties of the ceramic-based material is the type of consolidation applied. Powder metallurgy (PM) is the most prominent technique to date for the syntheses of ceramic-based materials. Although previous reviews have stated diverse PM techniques viz., hot press, hot-isostatic press, pressureless sintering, spark plasma sintering (SPS). More also, various reinforcement such as Metallic and non-metallic based nano-powders additive has been used in achieving the desired properties. SPS amidst diverse PM techniques has been given high attention to the routes of manufacturing ceramic materials because good microstructures and excellent mechanical properties can be achieved. This review focuses on past, present, and future works of ZrB2, and TiB2, reinforced with sintering additive with more attention on silicides, carbides, or nitrides based material as sintering additive.
Graphic Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mukhopadhyay, G.B. Raju, B. Basu, Ultra-high temperature ceramics: processing, properties, and applications, in MAX Phases and Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments, ed. by I.M. Low (IGI Global, Hershey, 2013), pp. 49–99
B.R. Golla, A. Mukhopadhyay, B. Basu, S.K. Thimmappa, Review on ultra-high temperature boride ceramics. Prog. Mater Sci. 111, 100651 (2020)
R. Mukherjee, B. Basu, Opportunities and challenges in processing and fabrication of ultra-high temperature ceramics for hypersonic space vehicles: a case study with ZrB2–SiC. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 117, s2–s8 (2018)
M. Fattahi, A. Babapoor, S.A. Delbari, Z. Ahmadi, A. S. Namini, M.S. Asl, Strengthening of TiC ceramics sintered by spark plasma via nano-graphite addition. Ceram. Int. 46, 12400–12408 (2020)
R. Orrù, G. Cao, Comparison of reactive and non-reactive spark plasma sintering routes for the fabrication of monolithic and composite ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTC) materials. Materials 6, 1566–1583 (2013)
D. Segal, Chemical Synthesis of Advanced Ceramic Materials, vol. 1 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991)
M. Alsawat, T. Altalhi, N.F. Alotaibi, Z.I. Zaki, Titanium carbide–titanium boride composites by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis approach: influence of zirconia additives on the mechanical properties. Results Phys. 13, 102292 (2019)
J.T. Black, R.A. Kohser, DeGarmo’s Materials and Processes in Manufacturing (Wiley, Hoboken, 2017)
J. Binner, M. Porter, B. Baker, J. Zou, V. Venkatachalam, V.R. Diaz et al., Selection, processing, properties and applications of ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites, UHTCMCs—a review. Int. Mater. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2019.1652006
J.-X. Xue, J.-X. Liu, G.-J. Zhang, H.-B. Zhang, T. Liu, X.-S. Zhou et al., Improvement in mechanical/physical properties of TiC-based ceramics sintered at 1500 C for inert matrix fuels. Scr. Mater. 114, 5–8 (2016)
Z. Feng, J. Qi, X. Guo, Y. Wang, X. Cao, Y. Yu et al., A new and highly active sintering additive: SiO2 for highly-transparent AlON ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 787, 254–259 (2019)
G.B. Raju, B. Basu, Densification, sintering reactions, and properties of titanium diboride with titanium disilicide as a sintering aid. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 3415–3423 (2007)
G.B. Raju, A. Mukhopadhyay, K. Biswas, B. Basu, Densification and high-temperature mechanical properties of hot-pressed TiB2–(0–10 wt%) MoSi2 composites. Scr. Mater. 61, 674–677 (2009)
T.S.R.C. Murthy, J.K. Sonber, C. Subramanian, R.K. Fotedar, M.R. Gonal, A.K. Suri, Effect of CrB2 addition on densification, properties and oxidation resistance of TiB2. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 976–984 (2009)
S.H. Kang, D.J. Kim, E.S. Kang, S.S. Baek, Pressureless sintering and properties of titanium diboride ceramics containing chromium and iron. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 893–895 (2001)
A.L. Chamberlain, W.G. Fahrenholtz, G.E. Hilmas, D.T. Ellerby, High-strength zirconium diboride-based ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87, 1170–1172 (2004)
F. Monteverde, A. Bellosi, Efficacy of HfN as a sintering aid in the manufacture of ultrahigh-temperature metal diborides-matrix ceramics. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3576–3585 (2004)
F. Monteverde, A. Bellosi, Development and characterization of metal-diboride-based composites toughened with ultra-fine SiC particulates. Solid State Sci. 7, 622–630 (2005)
M. Oghbaei, O. Mirzaee, Microwave versus conventional sintering: a review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 494, 175–189 (2010)
R.K. Bordia, S.J.L. Kang, E.A. Olevsky, Current understanding and future research directions at the onset of the next century of sintering science and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 2314–2352 (2017)
R. Prasad, Spark plasma sintering of cerium dioxide and its composites (Doctoral dissertation, University of British Columbia) (2017)
A. Prasad, L. Malakkal, L. Bichler, J. Szpunar, Effect of spark plasma sintering process parameters on density and microstructure of cerium(IV) oxide. Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress (2016)
N. Gupta, A. Mukhopadhyay, K. Pavani, B. Basu, Spark plasma sintering of novel ZrB2–SiC–TiSi2 composites with better mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534, 111–118 (2012)
Ö. Balcı, U. Burkhardt, M. Schmidt, J. Hennicke, M.B. Yağcı, M. Somer, Densification, microstructure and properties of TiB2 ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Charact. 145, 435–443 (2018)
R.-G. Duan, G.-D. Zhan, J.D. Kuntz, B.H. Kear, A.K. Mukherjee, Spark plasma sintering (SPS) consolidated ceramic composites from plasma-sprayed metastable Al2TiO5 powder and nano-Al2O3, TiO2, and MgO powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 373, 180–186 (2004)
J. Laszkiewicz-Łukasik, L. Jaworska, P. Putyra, P. Klimczyk, G. Garzeł, The influence of SPS heating rates on the synthesis reaction of tantalum diboride. Bol. Soc. Esp. Cerám. Vidr. 55, 159–168 (2016)
Z.A. Munir, U. Anselmi-Tamburini, M. Ohyanagi, The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 763–777 (2006)
W.G. Fahrenholtz, G.E. Hilmas, I.G. Talmy, J.A. Zaykoski, Refractory diborides of zirconium and hafnium. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1347–1364 (2007)
S. Chakraborty, P.K. Das, D. Ghosh, Spark plasma sintering and structural properties of ZrB2 based ceramics: a review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 44, 182–193 (2016)
J.K. Sonber, A.K. Suri, Synthesis and consolidation of zirconium diboride. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 110, 321–334 (2011)
S.-Q. Guo, Densification of ZrB2-based composites and their mechanical and physical properties: a review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 995–1011 (2009)
M.S. Asl, B. Nayebi, Z. Ahmadi, M.J. Zamharir, M. Shokouhimehr, Effects of carbon additives on the properties of ZrB2-based composites: a review. Ceram. Int. 44, 7334–7348 (2018)
B. Basu, G.B. Raju, A.K. Suri, Processing and properties of monolithic TiB2 based materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 51, 352–374 (2006)
V. Mazánek, H. Nahdi, J. Luxa, Z. Sofer, M. Pumera, Electrochemistry of layered metal diborides. Nanoscale 10, 11544–11552 (2018)
M.S. Asl, S.A. Delbari, F. Shayesteh, Z. Ahmadi, A. Motallebzadeh, Reactive spark plasma sintering of TiB2–SiC–TiN novel composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 81, 119–126 (2019)
M.S. Asl, M.G. Kakroudi, M. Rezvani, F. Golestani-Fard, Significance of hot-pressing parameters on the microstructure and densification behavior of zirconium diboride. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 50, 140–145 (2015)
Z. Balak, M. Azizieh, H. Kafashan, M.S. Asl, Z. Ahmadi, Optimization of effective parameters on thermal shock resistance of ZrB2–SiC-based composites prepared by SPS: using Taguchi design. Mater. Chem. Phys. 196, 333–340 (2017)
N.P. Vafa, B. Nayebi, M.S. Asl, M.J. Zamharir, M.G. Kakroudi, Reactive hot pressing of ZrB2-based composites with changes in ZrO2/SiC ratio and sintering conditions. Part II: mechanical behavior. Ceram. Int. 42, 2724–2733 (2016)
M.S. Asl, M.G. Kakroudi, B. Nayebi, A fractographical approach to the sintering process in porous ZrB2–B4C binary composites. Ceram. Int. 41, 379–387 (2015)
B. Basu, K. Balani, Advanced Structural Ceramics (Wiley, Hoboken, 2011)
S.R. Mercurio, Effect of coprecipitation of sintering aids on the microstructure and grain boundary development of sintered silicon carbide. (Doctoral dissertation, Rutgers University-Graduate School-New Brunswick) (2011)
S. Chakraborty, A.R. Mallick, D. Debnath, P.K. Das, Densification, mechanical and tribological properties of ZrB2 by SPS: effect of pulsed current. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 48, 150–156 (2015)
T.S.R.C. Murthy, B. Basu, A. Srivastava, R. Balasubramaniam, A.K. Suri, Tribological properties of TiB2 and TiB2–MoSi2 ceramic composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 1293–1300 (2006)
Z.H. Zhang, X.B. Shen, F.C. Wang, S.K. Lee, L. Wang, Densification behavior and mechanical properties of the spark plasma sintered monolithic TiB2 ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 5947–5951 (2010)
F. Monteverde, A. Bellosi, Beneficial effects of AlN as sintering aid on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-pressed ZrB2. Adv. Eng. Mater. 5, 508–512 (2003)
H. Jin, S. Meng, W. Xie, C. Xu, J. Niu, ZrB2-CNTs nanocomposites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Materials 9, 967 (2016)
M. Ikegami, S. Guo, Y. Kagawa, Densification behavior and microstructure of spark plasma sintered ZrB2-based composites with SiC particles. Ceram. Int. 38, 769–774 (2012)
S.Q. Guo, T. Nishimura, Y. Kagawa, J.M. Yang, Spark plasma sintering of zirconium diborides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 2848–2855 (2008)
S. Grasso, T. Saunders, H. Porwal, O. Cedillos-Barraza, D.D. Jayaseelan, W.E. Lee et al., Flash spark plasma sintering (FSPS) of pure ZrB2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 2405–2408 (2014)
R. Inoue, Y. Arai, Y. Kubota, Y. Kogo, K. Goto, Initial oxidation behaviors of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC ternary composites above 2000 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 731, 310–317 (2018)
M. Quarto, G. Bissacco, G. D’Urso, Machinability and energy efficiency in micro-EDM milling of zirconium boride reinforced with silicon carbide fibers. Materials 12, 3920 (2019)
E.W. Neuman, G.E. Hilmas, W.G. Fahrenholtz, Mechanical behavior of zirconium diboride–silicon carbide ceramics at elevated temperature in air. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 2889–2899 (2013)
D. Sciti, L. Silvestroni, G. Celotti, C. Melandri, S. Guicciardi, Sintering and mechanical properties of ZrB2–TaSi2 and HfB2–TaSi2 ceramic composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 3285–3291 (2008)
A. Purwar, R. Mukherjee, K. Ravikumar, S. Ariharan, N.K. Gopinath, B. Basu, Development of ZrB2–SiC–Ti by multi-stage spark plasma sintering at 1600 °C. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 124, 393–402 (2016)
W.G. Fahrenholtz, G.E. Hilmas, A.L. Chamberlain, J.W. Zimmermann, Processing and characterization of ZrB2-based ultra-high temperature monolithic and fibrous monolithic ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 5951–5957 (2004)
W.C. Tripp, H.C. Graham, Thermogravi metric study of the oxidation of ZrB2 in the temperature range of 800 to 1500°C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 118, 1195 (1971)
X. Zhang, R. Liu, X. Xiong, Z. Chen, Mechanical properties and ablation behavior of ZrB2–SiC ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 48, 120–125 (2015)
R. Licheri, R. Orru, C. Musa, A.M. Locci, G. Cao, Spark plasma sintering of ZrB2-and HfB2-based ultra high temperature ceramics prepared by SHS. Int. J. Self Propag. High Temp. Synth. 18, 15–24 (2009)
I. Akin, M. Hotta, F.C. Sahin, O. Yucel, G. Goller, T. Goto, Microstructure and densification of ZrB2–SiC composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 2379–2385 (2009)
S.S. Hwang, A.L. Vasiliev, N.P. Padture, Improved processing and oxidation-resistance of ZrB2 ultra-high temperature ceramics containing SiC nanodispersoids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464, 216–224 (2007)
M.S. Asl, M.G. Kakroudi, A processing-microstructure correlation in ZrB2–SiC composites hot-pressed under a load of 10 MPa. Univers. J. Mater. Sci. 3, 14–21 (2015)
F. Monteverde, Beneficial effects of an ultra-fine α-SiC incorporation on the sinterability and mechanical properties of ZrB2. Appl. Phys. A 82, 329–337 (2006)
R. Stadelmann, M. Lugovy, N. Orlovskaya, P. McHaffey, M. Radovic, V.M. Sglavo et al., Mechanical properties and residual stresses in ZrB2–SiC spark plasma sintered ceramic composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 1527–1537 (2016)
Y. Kubota, H. Tanaka, Y. Arai, R. Inoue, Y. Kogo, K. Goto, Oxidation behavior of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC at 1700 °C. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 1187–1194 (2017)
J. Bull, M. J. White, L. Kaufman, Ablation resistant zirconium and hafnium ceramics. Google Patents (1998)
Z. Wang, C. Hong, X. Zhang, X. Sun, J. Han, Microstructure and thermal shock behavior of ZrB2–SiC–graphite composite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 338–341 (2009)
Z. Wu, Z. Wang, G. Shi, J. Sheng, Effect of surface oxidation on thermal shock resistance of the ZrB2–SiC–ZrC ceramic. Compos. Sci. Technol 71, 1501–1506 (2011)
A. Snyder, D. Quach, J.R. Groza, T. Fisher, S. Hodson, L.A. Stanciu, Spark Plasma Sintering of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC ultra-high temperature ceramics at 1800 C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 6079–6082 (2011)
H. Wang, C.A. Wang, X. Yao, D. Fang, Processing and mechanical properties of zirconium diboride-based ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1992–1997 (2007)
I. Akin, O. Kaya, Microstructures and properties of silicon carbide-and graphene nanoplatelet-reinforced titanium diboride composites. J. Alloys Compd. 729, 949–959 (2017)
Q. Guo, J. Li, Q. Shen, L. Zhang, Preparation, microstructure, and mechanical properties of ZrB2-based ceramics with layered Zr2Al4C5 inclusions. Ceram. Int. 39, 2215–2222 (2013)
F. Ghafuri, M. Ahmadian, R. Emadi, M. Zakeri, Effects of SPS parameters on the densification and mechanical properties of TiB2–SiC composite. Ceram. Int. 45, 10550–10557 (2019)
S. Guo, Y. Kagawa, T. Nishimura, H. Tanaka, Thermal and electric properties in hot-pressed ZrB2–MoSi2–SiC composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 2255–2258 (2007)
A. Bellosi, F. Monteverde, D. Sciti, Fast densification of ultra-high-temperature ceramics by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 3, 32–40 (2006)
D. Sciti, L. Silvestroni, M. Nygren, Spark plasma sintering of Zr-and Hf-borides with decreasing amounts of MoSi2 as a sintering aid. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 1287–1296 (2008)
A. Balbo, D. Sciti, Spark plasma sintering and hot pressing of ZrB2–MoSi2 ultra-high-temperature ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 475, 108–112 (2008)
D. Sciti, F. Monteverde, S. Guicciardi, G. Pezzotti, A. Bellosi, Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrB2–MoSi2 ceramic composites produced by different sintering techniques. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 434, 303–309 (2006)
J.J. Meléndez-Martınez, A. Domınguez-Rodrıguez, F. Monteverde, C. Melandri, G. De Portu, Characterisation and high-temperature mechanical properties of zirconium boride-based materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 2543–2549 (2002)
D. Jain, K.M. Reddy, A. Mukhopadhyay, B. Basu, Achieving uniform microstructure and superior mechanical properties in ultrafine-grained TiB2–TiSi2 composites using innovative multi-stage spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 200–207 (2010)
K.M. Reddy, N. Kumar, B. Basu, Inhibition of grain growth during the final stage of multi-stage spark plasma sintering of oxide ceramics. Scr. Mater. 63, 585–588 (2010)
K.M. Reddy, N. Kumar, B. Basu, Innovative multi-stage spark plasma sintering to obtain strong and tough ultrafine-grained ceramics. Scr. Mater. 62, 435–438 (2010)
S.K. Thimmappa, B.R. Golla, V.V.B. Prasad, B. Majumdar, B. Basu, Phase stability, hardness and oxidation behaviour of spark plasma sintered ZrB2–SiC–Si3N4 composites. Ceram. Int. 45, 9061–9073 (2019)
B.R. Golla, S.K. Thimmappa, Comparative study on microstructure and oxidation behaviour of ZrB2-20 vol% SiC ceramics reinforced with Si3N4/Ta additives. J. Alloys Compd. 797, 92–100 (2019)
M.S. Asl, Z. Ahmadi, S. Parvizi, Z. Balak, I. Farahbakhsh, Contribution of SiC particle size and spark plasma sintering conditions on grain growth and hardness of TiB2 composites. Ceram. Int. 43, 13924–13931 (2017)
A.S. Namini, S.N.S. Gogani, M.S. Asl, K. Farhadi, M.G. Kakroudi, A. Mohammadzadeh, Microstructural development and mechanical properties of hot-pressed SiC reinforced TiB2 based composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 51, 169–179 (2015)
Y. Wang, M. Yao, Z. Hu, H. Li, J.-H. Ouyang, L. Chen et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2-40 wt% TiC composites: effects of adding a low-temperature hold prior to sintering at high temperatures. Ceram. Int. 44, 23297–23300 (2018)
Z. Ahmadi, B. Nayebi, M.S. Asl, I. Farahbakhsh, Z. Balak, Densification improvement of spark plasma sintered TiB2-based composites with micron-, submicron-and nano-sized SiC particulates. Ceram. Int. 44, 11431–11437 (2018)
K. Farhadi, A.S. Namini, M.S. Asl, A. Mohammadzadeh, M.G. Kakroudi, Characterization of hot-pressed SiC whisker reinforced TiB2 based composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 61, 84–90 (2016)
M.S. Asl, A.S. Namini, M.G. Kakroudi, Influence of silicon carbide addition on the microstructural development of hot pressed zirconium and titanium diborides. Ceram. Int. 42, 5375–5381 (2016)
D. Demirskyi, Y. Sakka, High-temperature reaction consolidation of TaC–TiB2 ceramic composites by spark-plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 405–410 (2015)
L. Liu, L. Zhong, B. Zhang, Z. Lai, F. Ye, Z. Zhang et al., Densification of tantalum carbide ceramics with 5 mol.% Al, Cu, Ag and Au. Scr. Mater. 69, 574–577 (2013)
I. Bogomol, H. Borodianska, T. Zhao, T. Nishimura, Y. Sakka, P. Loboda et al., A dense and tough (B4C–TiB2)–B4C ‘composite within a composite’ produced by spark plasma sintering. Scr. Mater. 71, 17–20 (2014)
I. Bogomol, T. Nishimura, O. Vasylkiv, Y. Sakka, P. Loboda, Microstructure and high-temperature strength of B4C–TiB2 composite prepared by a crucibleless zone melting method. J. Alloy. Compd. 485, 677–681 (2009)
T.S.R.C. Murthy, C. Subramanian, R.K. Fotedar, M.R. Gonal, P. Sengupta, S. Kumar et al., Preparation and property evaluation of TiB2 + TiSi2 composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 629–636 (2009)
Z. Ahmadi, Z. Hamidzadeh Mahaseni, M. Dashti Germi, M. Shahedi Asl, Microstructure of spark plasma sintered TiB2 and TiB2–AlN ceramics. Adv. Ceram. Prog. 5, 36–40 (2019)
L.-H. Li, H.-E. Kim, E.S. Kang, Sintering and mechanical properties of titanium diboride with aluminum nitride as a sintering aid. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 973–977 (2002)
H.J. Kim, H.J. Choi, J.G. Lee, Mechanochemical synthesis and pressureless sintering of TiB2–AlN composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1022–1024 (2002)
X.M. Yue, G.J. Zhang, Y.M. Wang, Reaction synthesis and mechanical properties of TiB2–AlN–SiC composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 293–298 (1999)
Z.H. Mahaseni, M.D. Germi, Z. Ahmadi, M.S. Asl, Microstructural investigation of spark plasma sintered TiB2 ceramics with Si3N4 addition. Ceram. Int. 44, 13367–13372 (2018)
J.H. Park, Y.H. Koh, H.E. Kim, C.S. Hwang, E.S. Kang, Densification and mechanical properties of titanium diboride with silicon nitride as a sintering aid. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 3037–3042 (1999)
F. Shayesteh, S.A. Delbari, Z. Ahmadi, M. Shokouhimehr, M.S. Asl, Influence of TiN dopant on the microstructure of TiB2 ceramic sintered by spark plasma. Ceram. Int. 45, 5306–5311 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguntuyi, S.D., Johnson, O.T. & Shongwe, M.B. Spark Plasma Sintering of Ceramic Matrix Composite of ZrB2 and TiB2: Microstructure, Densification, and Mechanical Properties—A Review. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 2146–2159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00874-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00874-8