Abstract
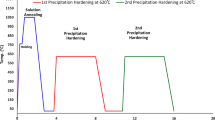
Conventional and two-step heating transient liquid phase bonding (TLP) experiments of martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel 17-4-PH were studied employing AMS 4777 braze filler at temperature of 1050 °C for different times (15 to 90 min) to accomplish the ideal brazing condition. The effect of TLP methods and bonding conditions on the microstructure and shear bond strength was investigated. The critical bonding time for isothermal solidification in conventional and two-step heating TLP was 60 min and 45 min, respectively. The microstructure of isothermal solidification zone consisted of Ni-rich solid solution phase. Eutectic constituents Cr-rich boride and Ni3Si were formed in the joint centerline in the athermally solidified zone. In the conventional method planar interface was formed, however in TLP bonding under temperature gradient non-planar interface was formed, high angel grain boundaries merged at the end of isothermal solidification and homogenous bond was produced. Due to the decrease of athermally solidified zone the shear strength increased by increasing the holding time and when using the two-step heating process because of better metal to metal contact, the shear strength was higher. The optimum condition was a temperature gradient TLP in 60 min bonding time, which led to shear strength of 435 MPa.
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bahrami-Balajaddeh, H. Naffakh-Moosavy, Pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of 17-4 PH stainless steel: microstructure, mechanical properties, and weldability investigation. Opt. Laser Technol. 119, 105651 (2019)
S. Vunnam, A. Saboo, C. Sudbrack, T.L. Starr, Effect of powder chemical composition on the as-built microstructure of 17-4 PH stainless steel processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 30, 100876 (2019)
W. Jun, Z. Hong, W. Xiao-yong, L. Cong, Q. Shao-yu, S. Bao-luo, The effect of long-term isothermal aging on dynamic fracture toughness of type 17-4 PH SS at 350 °C. Mater. Trans. 46, 846–851 (2005)
O.A. Idowu, N.L. Richards, M.C. Chaturvedi, Effect of bonding temperature on isothermal solidification rate during transient liquid phase bonding of Inconel 738LC superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 397, 98–112 (2005)
W. Li, X. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Wang, C. Liu, H. Li, Homogenization stage during TLP bonding of RAFM steel with a Fe–Si–B interlayer: microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 780, 139205 (2020)
M. Min, Y. Mao, Q. Deng, G. Wang, S. Wang, Vacuum brazing of Mo to 316L stainless steel using BNi-2 paste and Cu interlayer. Vacuum 175, 109282 (2020)
X. Yue, F. Liu, Q. Li, H. Qin, H. Gao, L. Li, Y. Yi, Effect of post-bond heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of the wide gap TLP bonded IC10 superalloy with a low boron Ni3Al-based interlayer. J. Manuf. Process. 54, 109–119 (2020)
D.M. Jacobson, G. Humpston, Brazing (ASM International, Materials Park, 2005)
T.I. Khan, M.J. Kabir, R. Bulpett, Effect of transient liquid-phase bonding variables on the properties of a micro-duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 372, 290–295 (2004)
S. Shakerin, V. Maleki, S.A. Ziaei, H. Omidvar, Microstructural and mechanical assessment of transient liquid phase bonded commercially pure titanium. Can. Metall. Q. 56, 1–8 (2017)
I. Hoyer, B. Wielage, in Advances in Brazing, ed. by D.P. Sekulic (Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, 2013), p. 545
D.L. Olson, T. Siewert, S. Liu, G. Edwards, Welding Brazing and Soldering (ASM International, Materials Park, 2008)
X. Wang, X. Li, C. Wang, Effect of two-step heating process on joint microstructure and properties during transient liquid phase bonding of dissimilar materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 711–716 (2013)
X.G. Wang, X.G. Li, Q. Yan, Effect of two step heating process on joint microstructure and properties during transient liquid phase bonding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joint 12, 455–459 (2007)
A. Amirkhani, B. Beidokhti, K. Shirvani, M.R. Rahimipour, Two-step heating transient liquid phase bonding of Inconel 738LC. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 266, 1–9 (2019)
J. Ma, M.M. Atabaki, W. Liu, R. Pillai, B. Kumar, U. Vasudevan, R. Kovacevic, Laser-based welding of 17-4 PH martensitic stainless steel in a tubular butt joint configuration with a built-in backing bar. Opt. Laser Technol. 82, 38–52 (2016)
D.W. Deng, C.P. Zhang, R. Chen, H.F. Xia, Microstructure and microhardness of 17-4PH deposited with cobased alloy hardfacing coating. Phys. Procedia 50, 177–184 (2013)
F.Z. Wang, Q.Z. Wang, B.H. Yu, B.L. Xiao, Z.Y. Ma, Interface structure and mechanical properties of Ti(C, N)-based cermet and 17-4PH stainless steel joint brazed with nickel-base filler metal BNi-2. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211, 1804–1809 (2011)
R.K. Shiue, S.K. Wu, J.Y. Shiue, Infrared brazing of Ti–6Al–4V and 17-4 PH stainless steel with (Ni)/Cr barrier layer(s). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 488, 186–194 (2008)
A.H.M.E. Rahman, M.N. Cavalli, Interface microstructure and strength of TLP bonded iron and steel. Exp. Appl. Mech. 4, 191–199 (2016)
H. Okamoto, T.B. Massalski, Thermodynamically improbable phase diagrams. J. Phase Equilib. 12, 148–168 (1991)
B. Rhee, S. Roh, D. Kim, Transient liquid phase bonding of nitrogen containing duplex stainless steel UNS S31803 using Ni-Cr-Fe-Si-B insert metal. Mater. Trans. 44, 1014–1023 (2003)
R. Abdolvand, M. Atapour, M. Shamanian, A. Allafchian, The effect of bonding time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of transient liquid phase bonding between SAF 2507 and AISI 304. J. Manuf. Process. 25, 172–180 (2017)
M. Jafari, M. Rafiei, H. Mostaan, Effect of solidification mode on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI420 steel to SAF2507 steel dissimilar joint produced by transient liquid phase. Met. Mater. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00406-z
X. Yuan, M.B. Kim, C.Y. Kang, Characterization of transient-liquid-phase-bonded joints in a duplex stainless steel with a Ni–Cr–B insert alloy. Mater. Charact. 60, 1289–1297 (2009)
E.A. Leone, A. Rabinkin, B. Sarna, Microstructure of thin-gauge austenitic and ferritic stainless steel joints brazed using Metglas amorphous foil. J. Adv. Mater. 38, 28–39 (2006)
C.L. Ou, R.K. Shiue, Microstructural evolution of brazing 422 stainless steel using the BNi-3 braze alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 2337–2346 (2003)
M. Sadeghian, A. Ekrami, R. Jamshidi, Transient liquid phase bonding of 304 stainless steel using a Co-based interlayer. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joint 1, 1–7 (2017)
M.A. Jabbareh, H. Assadi, Modelling of microstructure evolution in transient-liquid-phase diffusion bonding under temperature gradient. Scr. Mater. 60, 780–782 (2009)
A. Ghoneim, O.A. Ojo, Numerical modeling and simulation of a diffusion-controlled liquid-solid phase change in polycrystalline solids. Comput. Mater. Sci. 50, 1102–1113 (2011)
V. Jalilvand, H. Omidvar, M.R. Rahimipour, H.R. Shakeri, Influence of bonding variables on transient liquid phase bonding behavior of nickel based superalloy IN-738LC. Mater. Des. 52, 36–46 (2013)
X.G. Wang, X.G. Li, Transient liquid phase bonding of T91 steel using two-step heating process. Adv. Mater. Res. 712–715, 701–704 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moradi, M.J., Emadoddin, E. & Omidvar, H. Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of 17-4-PH Stainless Steel Using Conventional and Two-Step Heating Process. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 5268–5277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00792-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00792-9