Abstract
In this paper, we found that the first hydrogenation properties of TiFe alloy can be significantly improved by ball milling, cold rolling and doping. The samples by ball milling for 60 min and doped with (Zr + 2Cr) as additive showed a faster hydrogenation kinetics and the sample cold rolled for 5 passes showed the highest hydrogen capacity. Further study, it was clear that the first hydrogenation of TiFe ingot could be easily activated by using ball milling. The first hydrogenation kinetics of ball-milled TiFe was strongly dependent on ball milling time. Doping (Zr + 2Cr) made TiFe alloy show excellent first hydrogenation kinetics and better anti-poisoning property due to the presence of bright phase. In addition, the doped sample with prolonged air-exposed time about 30 h could not be activated at all, but cold rolling could effectively make the totally dead sample active again and leads to the faster first hydrogenation kinetics and higher hydrogen storage capacity.
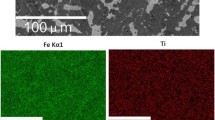
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 February 2020
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00629-5
References
A.P. Soldatov, Mechanism of hydrogen adsorption in graphene nanostructures synthesized in membrane pores and on zeolites. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 93, 494–500 (2019)
G. Deyu, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhu, L. Li, Purity of MgH2 improved by the process of pre-milling assisted hydriding of Mg powder under a hydrogen pressure of 0.5 MPa. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 93, 665–673 (2019)
N.A. Abdul Majid, N. Maeda, M. Notomi, Improved hydrogen desorption properties of magnesium hydride with TiFe0.8Mn0.2, graphite and iron addition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.190
K. Hirose, M. Hirscher, Handbook of Hydrogen Storage: New Materials for Future Energy Storage (Wiley, Hoboken, 2010)
R.A. Varin, T. Czujko, Z.S. Wronski, Nanomaterials for Solid State Hydrogen Storage (Springer, Berlin, 2009)
P. Chen, M. Zhu, Recent progress in hydrogen storage. Mater. Today 11, 36–43 (2008)
S.S. Srinivasan, D.E. Demirocak, Metal Hydrides used for Hydrogen Storage, in Nanostructured Materials for Next-Generation Energy Storage and Conversion: Hydrogen Production, Storage, and Utilization, ed. by Y.-P. Chen, S. Bashir, J.L. Liu (Springer, Berlin, 2017), pp. 225–255
G. Principi, F. Agresti, A. Maddalena, S.L. Russo, The problem of solid state hydrogen storage. Energy 34, 2087–2091 (2009)
V.Y. Zadorozhnyy, G.S. Milovzorov, S.N. Klyamkin, M.Y. Zadorozhnyy, D.V. Strugova, M.V. Gorshenkov, S.D. Kaloshkin, Preparation and hydrogen storage properties of nanocrystalline TiFe synthesized by mechanical alloying. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 27, 149–155 (2017)
P. Lv, J. Huot, Hydrogenation improvement of TiFe by adding ZrMn2. Energy 138, 375–382 (2017)
H. Leng, Z. Yu, J. Yin, Q. Li, Z. Wu, K.-C. Chou, Effects of Ce on the hydrogen storage properties of TiFe0.9Mn0.1 alloy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 23731–23736 (2017)
W. Ali, M. Li, P. Gao, C. Wu, Q. Li, X. Lu, C. Li, Hydrogenation properties of Ti–Fe–Mn alloy with Cu and Y as additives. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 2229–2238 (2017)
J. Yin, Q. Li, H. Leng, Advances in improvement of hydrogen storage properties of TiFe-based alloys. Mater. Rev. 24, 141–147 (2016)
P. Lv, J. Huot, Hydrogen storage properties of Ti0.95FeZr0.05, TiFe0.95Zr0.05 and TiFeZr0.05 alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 22128–22133 (2016)
C. Gosselin, J. Huot, Hydrogenation properties of TiFe doped with zirconium. Materials 8, 7864–7872 (2015)
H. Emami, K. Edalati, J. Matsuda, E. Akiba, Z. Horita, Hydrogen storage performance of TiFe after processing by ball milling. Acta Mater. 88, 190–195 (2015)
L.E.R. Vega, D.R. Leiva, R.M. Leal Neto, W.B. Silva, R.A. Silva, T.T. Ishikawa, C.S. Kiminami, W.J. Botta, Mechanical activation of TiFe for hydrogen storage by cold rolling under inert atmosphere. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 2913–2918 (2018)
J. Manna, B. Tougas, J. Huot, Mechanical activation of air exposed TiFe + 4 wt% Zr alloy for hydrogenation by cold rolling and ball milling. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 20795–20800 (2018)
K. Edalati, J. Matsuda, A. Yanagida, E. Akiba, Z. Horita, Activation of TiFe for hydrogen storage by plastic deformation using groove rolling and high-pressure torsion: similarities and differences. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 39, 15589–15594 (2014)
M.W. Davids, M. Lototskyy, A. Nechaev, Q. Naidoo, M. Williams, Y. Klochko, Surface modification of TiFe hydrogen storage alloy by metal-organic chemical vapour deposition of palladium. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 36, 9743–9750 (2011)
D. Khatamian, G. Weatherly, F. Manchester, Some effects of activation for hydrogen absorption in FeTi powder. Acta Metall. 31, 1771–1780 (1983)
T. Schober, D. Westlake, The activation of FeTi for hydrogen storage: a different view. Scr. Metall. 15, 913–918 (1981)
K. Edalati, J. Matsuda, M. Arita, T. Daio, E. Akiba, Z. Horita, Mechanism of activation of TiFe intermetallics for hydrogen storage by severe plastic deformation using high-pressure torsion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 143902 (2013)
S.K. Kulshreshtha, R. Sasikala, K.K. Pushpa, K.A. Rao, R.M. Iyer, On activation of FeTi: surface effects. Mater. Res. Bull. 24, 545–550 (1989)
T. Schober, On the activation of FeTi for hydrogen storage. J. Less-Common Metals 89, 63–70 (1982)
C.G. Figueroa, R. Schouwenaars, J. Cortés-Pérez, R. Petrov, L. Kestens, Ultrafine gradient microstructure induced by severe plastic deformation under sliding contact conditions in copper. Mater. Charact. 138, 263–273 (2018)
J. Huot, Nanocrystalline metal hydrides obtained by severe plastic deformations. Metals 2, 22–40 (2012)
Y.S. Kim, E. Choi, W.J. Kim, Characterization of the microstructures and the shape memory properties of the Fe–Mn–Si–Cr–Ni–C shape memory alloy after severe plastic deformation by differential speed rolling and subsequent annealing. Mater. Charact. 136, 12–19 (2018)
M. Němec, V. Gärtnerová, A. Jäger, Influence of severe plastic deformation on intermetallic particles in Mg-12wt.%Zn alloy investigated using transmission electron microscopy. Mater. Charact. 119, 129–136 (2016)
M. Němec, A. Jäger, K. Tesař, V. Gärtnerová, Influence of alloying element Zn on the microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of binary Mg–Zn alloys after severe plastic deformation. Mater. Charact. 134, 69–75 (2017)
L.S. Toth, C. Gu, Ultrafine-grain metals by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Charact. 92, 1–14 (2014)
S.-H. Hong, M.Y. Song, Preparation of Mg–MgH2 flakes by planetary ball milling with stearic acid and their hydrogen storage properties. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 544–549 (2016)
S.-H. Hong, M.Y. Song, Preparation of a sample with a single MgH2 phase by horizontal ball milling and the first hydriding reaction of 90 wt% Mg-10 wt% MgH2. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 422–428 (2015)
M.D.K. Dewa, S. Wiryolukito, H. Suwarno, Hydrogen absorption capacity of Fe–Ti–Al alloy prepared by high energy ball milling. Energy Proc. 68, 318–325 (2015)
S. Khajavi, M. Rajabi, J. Huot, Effect of cold rolling and ball milling on first hydrogenation of Ti0.5Zr0.5 (Mn1−xFex) Cr1, x = 0, 0.2, 0.4. J. Alloys Compd. 775, 912–920 (2019)
A.A.C. Asselli, D.R. Leiva, G.H. Cozentino, R. Floriano, J. Huot, T.T. Ishikawa, W.J. Botta, Hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 processed by cold forging. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S719–S724 (2014)
M.I. Abd El Aal, N. El Mahallawy, F.A. Shehata, M. Abd El Hameed, E.Y. Yoon, H.S. Kim, Wear properties of ECAP-processed ultrafine grained Al–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 3726–3732 (2010)
A.M. Jorge, E. Prokofiev, G.F. de Lima, E. Rauch, M. Veron, W.J. Botta, M. Kawasaki, T.G. Langdon, An investigation of hydrogen storage in a magnesium-based alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38, 8306–8312 (2013)
Á. Révész, M. Gajdics, L.K. Varga, G. Krállics, L. Péter, T. Spassov, Hydrogen storage of nanocrystalline Mg–Ni alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing and cold rolling. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 39, 9911–9917 (2014)
L. Wang, J. Jiang, A. Ma, Y. Li, D. Song, A critical review of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials processed by equal channel angular pressing. Metals 7, 324 (2017)
N. Endo, S. Suzuki, K. Goshome, T. Maeda, Operation of a bench-scale TiFe-based alloy tank under mild conditions for low-cost stationary hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 5246–5251 (2017)
K. Edalati, J. Matsuda, H. Iwaoka, S. Toh, E. Akiba, Z. Horita, High-pressure torsion of TiFe intermetallics for activation of hydrogen storage at room temperature with heterogeneous nanostructure. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 38, 4622–4627 (2013)
M. Abe, T. Kuji, Hydrogen absorption of TiFe alloy synthesized by ball milling and post-annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 446–447, 200–203 (2007)
V.Y. Zadorozhnyy, S.N. Klyamkin, M.Y. Zadorozhnyy, O.V. Bermesheva, S.D. Kaloshkin, Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped by aluminum and chromium. J. Alloys Compd. 586, S56–S60 (2014)
V.Y. Zadorozhnyy, S.N. Klyamkin, MYu. Zadorozhnyy, M.V. Gorshenkov, S.D. Kaloshkin, Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped with sulfur and magnesium. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S569–S572 (2014)
V. Zadorozhnyy, S. Klyamkin, M. Zadorozhnyy, O. Bermesheva, S. Kaloshkin, Hydrogen storage nanocrystalline TiFe intermetallic compound: synthesis by mechanical alloying and compacting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 17131–17136 (2012)
V.Y. Zadorozhnyy, S. Klyamkin, S. Kaloshkin, M.Y. Zadorozhnyy, O. Bermesheva, Mechanochemical synthesis and hydrogen sorption properties of nanocrystalline TiFe. Inorg. Mater. 47, 1081–1086 (2011)
V. Zadorozhnyy, E. Berdonosova, C. Gammer, J. Eckert, M. Zadorozhnyy, A. Bazlov, M. Zheleznyi, S. Kaloshkin, S. Klyamkin, Mechanochemical synthesis and hydrogenation behavior of (TiFe)100–xNix alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 796, 42–46 (2019)
Y. Li, H. Shang, Y. Zhang, P. Li, Y. Qi, D. Zhao, Investigations on gaseous hydrogen storage performances and reactivation ability of as-cast TiFe1–xNix (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4) alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44, 4240–4252 (2019)
H. Shang, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Qi, S. Guo, D. Zhao, Structure and hydrogenation performances of as-cast Ti1.1−xRExFe0.8Mn0.2 (RE = Pr, Sm and Nd; x = 0, 0.01) alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 19091–19101 (2018)
C. Gosselin, D. Santos, J. Huot, First hydrogenation enhancement in TiFe alloys for hydrogen storage. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 50, 375303 (2017)
P. Jain, C. Gosselin, J. Huot, Effect of Zr, Ni and Zr 7 Ni 10 alloy on hydrogen storage characteristics of TiFe alloy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40, 16921–16927 (2015)
S. Kumar, G. Tiwari, S. Sonak, U. Jain, N. Krishnamurthy, High performance FeTi–3.1 mass% V alloy for on board hydrogen storage solution. Energy. 75, 520–524 (2014)
S.-M. Lee, T.-P. Perng, Effect of the second phase on the initiation of hydrogenation of TiFe1−xMx (M = Cr, Mn) alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 19, 259–263 (1994)
R. NaotoYasuda, S. Wakabayashi, N. Sasaki, T. Okinaka, Akiyama, Self-ignition combustion synthesis of TiFe1−xMnx hydrogen storage alloy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 9122–9127 (2009)
H. Shang, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Qi, S. Guo, D. Zhao, Effects of adding over-stoichiometrical Ti and substituting Fe with Mn partly on structure and hydrogen storage performances of TiFe alloy. Renew. Energy 135, 1481–1498 (2019)
P. Jain, C. Gosselin, N. Skryabina, D. Fruchart, J. Huot, Hydrogenation properties of TiFe with Zr7Ni10 alloy as additive. J. Alloys Compd. 636, 375–380 (2015)
S.M. Lee, T.P. Perng, H.K. Juang, S.Y. Chen, W.Y. Chen, S.E. Hsu, Microstructures and hydrogenation properties of TiFel−xMχ alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 187, 49–57 (1992)
K. Edalati, M. Matsuo, H. Emami, S. Itano, A. Alhamidi, A. Staykov, D.J. Smith, S.-I. Orimo, E. Akiba, Z. Horita, Impact of severe plastic deformation on microstructure and hydrogen storage of titanium-iron-manganese intermetallics. Scripta Mater. 124, 108–111 (2016)
L. Lutterotti, S. Matthies, H. Wenk, MAUD: a friendly Java program for material analysis using diffraction, IUCr: Newsletter of the CPD, 21 (1999)
L. Lutterotti, S. Gialanella, X-ray diffraction characterization of heavily deformed metallic specimens. Acta Mater. 46, 101–110 (1998)
M.A. Rahmaninasab, S. Raygan, H. Abdizadeh, M. Pourabdoli, S.H. Mirghaderi, Properties of activated MgH2+ mischmetal nanostructured composite produced by ball-milling. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 7, 15 (2018)
A.K. Patel, P. Sharma, J. Huot, Effect of annealing on microstructure and hydrogenation properties of TiFe + X wt% Zr (X = 4, 8). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 6238–6243 (2018)
P. Lv, M.N. Guzik, S. Sartori, J. Huot, Effect of ball milling and cryomilling on the microstructure and first hydrogenation properties of TiFe + 4wt.% Zr alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 1828–1834 (2019)
G. Romero, P. Lv, J. Huot, Effect of ball milling on the first hydrogenation of TiFe alloy doped with 4 wt% (Zr + 2Mn) additive. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 13751–13757 (2018)
S.M. Lee, T.P. Perng, Effect of the second phase on the initiation of hydrogenation of TiFe1−xMx (M = Cr, Mn) alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 19, 259–263 (1994)
N. Hanada, T. Ichikawa, S.-I. Orimo, H. Fujii, Correlation between hydrogen storage properties and structural characteristics in mechanically milled magnesium hydride MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 366, 269–273 (2004)
M. Avrami, Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 9, 177–184 (1941)
M. Avrami, Kinetics of phase change. II transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 8, 212–224 (1940)
U. Bösenberg, J.W. Kim, D. Gosslar, N. Eigen, T.R. Jensen, J.B. Von Colbe, Y. Zhou, M. Dahms, D. Kim, R. Günther, Role of additives in LiBH4–MgH2 reactive hydride composites for sorption kinetics. Acta Mater. 58, 3381–3389 (2010)
N. Koga, J.M. Criado, Kinetic analyses of solid-state reactions with a particle-size distribution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 2901–2909 (1998)
N. Koga, J. Criado, Influence of the particle size distribution on the CRTA curves for the solid-state reactions of interface shrinkage type. J. Therm. Anal. 49, 1477–1484 (1997)
J. Carstensen, Stability of solids and solid dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 63, 1–14 (1974)
J. Crank, The Mathematics Of Diffusion (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1979)
A. Ginstling, B. Brounshtein, Concerning the diffusion kinetics of reactions in spherical particles. J. Appl. Chem. USSR 23, 1327–1338 (1950)
Y. Pang, Q. Li, A review on kinetic models and corresponding analysis methods for hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 18072–18087 (2016)
J. Lang, M. Eagles, M.S. Conradi, J. Huot, Hydrogenation rate limiting step, diffusion and thermal conductivity in cold rolled magnesium hydride. J. Alloys Compd. 583, 116–120 (2014)
O. Kircher, M. Fichtner, Hydrogen exchange kinetics in NaAlH 4 catalyzed in different decomposition states. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 7748–7753 (2004)
J. Huot, M. Tousignant, Hydrogen sorption enhancement in cold-rolled and ball-milled CaNi5. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 11911–11918 (2017)
M. Tousignant, J. Huot, Hydrogen sorption enhancement in cold rolled LaNi5. J. Alloys Compd. 595, 22–27 (2014)
S.M. Lee, T.P. Perng, Effects of boron and carbon on the hydrogenation properties of TiFe and Ti1.1Fe. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 25, 831–836 (2000)
S.M. Lee, T.P. Perng, Microstructural correlations with the hydrogenation kinetics of FeTi1 + ξ alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 177, 107–118 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by East China University of Technology (ECUT) for PhD research fund and experimental technology project (DHSY-201919114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The fifth author name Jacques Huot was missed in the original publication, and it has been included in this correction.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, P., Liu, Z., Patel, A.K. et al. Influence of Ball Milling, Cold Rolling and Doping (Zr + 2Cr) on Microstructure, First Hydrogenation Properties and Anti-poisoning Ability of TiFe Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 1346–1357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00501-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00501-1



