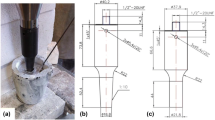
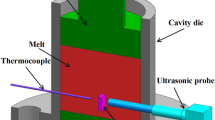
Abstract
In foundry practice, ultrasonic treatment has been used as an efficient technique to achieve grain refinement in aluminium and magnesium alloys. This article shows the strong effect of pouring temperature and ultrasonic treatment at various temperatures on the grain refinement of Al-1 wt% Mg-0.3 wt% Sc alloy. Without ultrasonic treatment, a fine grain structure was obtained at the pouring temperature of 700 °C. The average grain size sharply decreases from 487 ± 20 to 103 ± 2 μm when the pouring temperature decreases from 800 to 700 °C. Ultrasonic vibration proved to be a potential grain refinement technique with a wide range of pouring temperature. A microstructure with very fine and homogeneous grains was obtained by applying ultrasonic treatment to the melt at the temperature range between 700 and 740 °C, before pouring. Cavitation-enhanced heterogeneous nucleation is the mechanism proposed to explain grain refinement by ultrasound in this alloy. Moreover, ultrasonic treatment of the melt was found to lead to cast samples with hardness values similar to those obtained in samples submitted to precipitation hardening, suggesting that ultrasonic treatment can avoid carrying out heat treatment of cast parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Cantor and K. O’Reilly, Solidification and Casting, pp. 213–219, Institute of Physics Pub, Bristol, England (2003).
A. L. Greer, P. S. Cooper, M. W. Meredith, W. Schneider, P. Schumacher, J. A. Spittle, and A. Tronche, Adv. Eng. Mater. 5, 81 (2003).
A. L. Greer, A. M. Bunn, A. Tronche, P. V. Evans, and D. J. Bristow, Acta. Mater. 48, 2823 (2000).
P. S. Mohanty and J. E. Gruzleski, Acta. Metall. Mater. 43, 2001 (1995).
S. Nafisi, D. Emadi, M. T. Shehata, and R. Ghomashchi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 432, 71 (2006).
K. Xia and G. Tausig, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 246, 1 (1998).
R. Haghayeghi, E. J. Zoqui, D. G. Eskin, and H. Bahai, J. Alloy. Compd. 485, 807 (2009).
R. Haghayeghi and L. Nastac, Mater. Lett. 65, 3230 (2011).
W. Khalifa, Y. Tsunekawa, and M. Okumiya, Int. J. Cast. Metal. Res. 21, 129 (2008).
X. Jian, H. Xu, T. T. Meek, and Q. Han, Mater. Lett. 59, 190 (2005).
H. K. Feng, S. R. Yu, Y. L. Li, and L. Y. Gong, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 208, 330 (2008).
H. Xu, Q. Han, and T. T. Meek, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 473, 96 (2008).
G. I. Eskin, Ultrasonic Treatment of Light Alloy Melts, pp. 135–166, Gordon and Breach Science, Amsterdam, Netherlands (1998).
Y. L. Li, H. K. Feng, F. R. Cao, Y. B. Chen, and L. Y. Gong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 487, 518 (2008).
M. A. Easton and D. H. StJohn, Acta. Mater. 49, 1867 (2001).
J. D. Hunt and K. A. Jackson, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 37, 254 (1966).
X. Jian, T. T. Meek, and Q. Han, Scripta. Mater. 54, 893–896 (2006).
O. V. Abramov, Ultrasound in Liquid and Solid Metals, pp. 273–326, CRC Press, Florida, U.S.A (1994).
G. I. Eskin, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 1, S59 (1994).
M. Qian, A. Ramirez, and A. Das, Journal of Crystal Growth. 311, 3708 (2009).
X. Liu, Y. Osawa, S. Takamori, and T. Mukai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 487, 120 (2008).
D. Gao, Z. Li, Q. Han, and Q. Zhai, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. A 502, 2 (2009).
M. Qian, A. Ramirez, A. Das, and D. H. StJohn, Journal of Crystal Growth 312, 2267 (2010).
A. Ramirez, M. Qian, B. Davis, T. Wilks, and D. H. StJohn, Scripta. Mater. 59, 19 (2008).
M. Khosro Aghayani, and B. Niroumand, J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 114 (2011).
S. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X. Cheng, G. Chen, and Q. Dai, J. Alloy. Compd. 470, 168 (2009).
H. Puga, J. Barbosa, S. Costa, S. Ribeiro, A. M. P. Pinto, and M. Prokic, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 589 (2013).
H. Puga, S. Costa, J. Barbosa, S. Ribeiro, and M. Prokic, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 211, 1729 (2011).
S. R. Yu, H. K. Feng, Y. L. Li, and L. Y. Gong, J. Alloy. Compd. 484, 360 (2009).
E. A. Marquis and D. N. Seidman, Acta. Mater. 53, 4259 (2005).
S. Lathabai and P. G. Lloyd, Acta. Mater. 50, 4275 (2002).
R. Sawtell and C. Jensen, MTA. 21, 421 (1990).
R. Abbaschian, L. Abbaschian, and R. E. Reed-Hill, Physical Metallurgy Principles, 4th ed., pp. 439–442, Cengage Learning, Stamford, USA (2008).
B. S. Murty, S. A. Kori, and M. Chakraborty, Int. Mater. Rev. 47, 3 (2002).
M. Johnsson, L. Backerud, and G. Sigworth, Metall and Mat Trans A 24, 481 (1993).
H. T. Li, Y. Wang, and Z. Fan, Acta. Mater. 60, 1528 (2012).
S. Costa, H. Puga, J. Barbosa, and A. M. P. Pinto, Mater. Design. 42, 347 (2012).
U. Patakham, J. Kajornchaiyakul, and C. Limmaneevichitr, J. Alloy. Compd. 542, 177 (2012).
W. G. Zhang, Y. C. Ye, L. J. He, P. J. Li, X. Feng, and L. S. Novikov, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 578, 35 (2013).
A. Pisch, J. Gröbner, and R. Schmid-Fetzer, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 289, 123 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuan, N.Q., Puga, H., Barbosa, J. et al. Grain refinement of Al-Mg-Sc alloy by ultrasonic treatment. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 72–78 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-1008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-1008-6