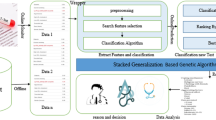
Abstract
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is one among the main factors for the increase in mortality rate worldwide. The analysis and prediction of this disease is yet a highly formidable task in medical data analysis. Recent advancements in technology such as Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and the need for automated models have paved the way for developing a more reliable and efficient model for predicting heart disease. Several researches have been carried out in predicting heart diseases but the focus on choosing the important attributes that play a significant role in predicting CVD is inadequate. Hence the choice of right features for the classification and the diagnosis of the heart disease is important. The core aim of this work is to identify and select the important features and machine learning methodologies that can enhance the prediction capability of the classification models for accurately predicting CVD. The results show that the proposed enhanced evolutionary feature selection with the hybrid ensemble model outperforms the existing approaches in terms of precision, recall and accuracy. The experimental outcomes show that the proposed approach attains the maximum classification accuracy of 93.65% for statlog dataset, 82.81% for SPECTF dataset and 84.95% for coronary heart disease dataset. The proposed classification model performance is demonstrated using ROC curve against state-of-the-art methods in machine learning.
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniadis A, Lambert-Lacroix S, Leblanc F (2003) Effective dimension reduction methods for tumor classification using gene expression data. Bioinformatics 19(5):563–570. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg062
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach Learn 46(1):389–422. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012487302797
Yu JS, Ongarello S, Fiedler R, Chen XW, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Trajanoski Z (2005) Ovarian cancer identification based on dimensionality reduction for high-throughput mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 21(10):2200–2209. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti370
Oh IS, Lee JS, Moon BR (2004) Hybrid genetic algorithms for feature selection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(11):1424–1437. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2004.105
Remeseiro B, Bolon-Canedo V (2019) A review of feature selection methods in medical applications. Comput Biol Med 112:103375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103375
Tallón-Ballesteros AJ, Correia L, Xue B (2018) Featuring the attributes in supervised machine learning. In: International conference on hybrid artificial intelligence systems. Springer, Cham, pp 350–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92639-1_29
Garcia VHM, Rodriguez JR, Usaquén MAO (2018) A comparative study between feature selection algorithms. In: International conference on data mining and big data. Springer, Cham, pp 65–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93803-5_7
Jain D, Singh V (2018) Feature selection and classification systems for chronic disease prediction: a review. Egyptian Inform J 19(3):179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2018.03.002
Jordan MI, Mitchell TM (2015) Machine learning: trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 349(6245):255–260
Gavhane A, Kokkula G, Pandya I, Devadkar K (2018) Prediction of heart disease using machine learning. In: 2018 second international conference on electronics, communication and aerospace technology (ICECA) (pp 1275–1278). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474922
Repaka AN, Ravikanti SD, Franklin RG (2019) Design and implementing heart disease prediction using Naives Bayesian. In: 2019 3rd International conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI) (pp 292–297). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOEI.2019.8862604
Babu S, Vivek EM, Famina KP, Fida K, Aswathi P, Shanid M, Hena M (2017) Heart disease diagnosis using data mining technique. In: 2017 international conference of electronics, communication and aerospace technology (ICECA) Vol. 1. pp 750–753. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECA.2017.8203643
Parthiban G, Srivatsa SK (2012) Applying machine learning methods in diagnosing heart disease for diabetic patients. Int J Appl Inf Syst 3(7):25–30. https://doi.org/10.5120/ijais12-450593
Tan KC, Teoh EJ, Yu Q, Goh KC (2009) A hybrid evolutionary algorithm for attribute selection in data mining. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):8616–8630
Ordonez C (2006) Association rule discovery with the train and test approach for heart disease prediction. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 10(2):334–343
Rairikar, A, Kulkarni V, Sabale V, Kale H, Lamgunde A (2017) Heart disease prediction using data mining techniques. In: 2017 International conference on intelligent computing and control (I2C2) (pp 1–8). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2C2.2017.8321771
Nahiduzzaman M, Nayeem MJ, Ahmed MT, Zaman MSU (2019) Prediction of heart disease using multi-layer perceptron neural network and support vector machine. In: 2019 4th International conference on electrical information and communication technology (EICT) (pp 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/EICT48899.2019.9068755
Nahar J, Imam T, Tickle KS, Chen YPP (2013) Computational intelligence for heart disease diagnosis: a medical knowledge driven approach. Expert Syst Appl 40(1):96–104
Dutta A, Batabyal T, Basu M, Acton ST (2020) An efficient convolutional neural network for coronary heart disease prediction. Expert Syst Appl 159:113408
Tougui I, Jilbab A, El Mhamdi J (2020) Heart disease classification using data mining tools and machine learning techniques. Heal Technol 10:1137–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12553-020-00438-1
Uyar K, İlhan A (2017) Diagnosis of heart disease using genetic algorithm based trained recurrent fuzzy neural networks. Procedia Comput Sci 120:588–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.11.283
Pathak AK, Valan JA (2020) A predictive model for heart disease diagnosis using fuzzy logic and decision tree. In: Smart computing paradigms: new progresses and challenges. Springer, Singapore, pp 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9680-9_10
Baitharu TR, Pani SK (2016) Analysis of data mining techniques for healthcare decision support system using liver disorder dataset. Procedia Comput Sci 85:862–870
Bouaziz F, Boutana D, Oulhadj H (2018) Diagnostic of ECG arrhythmia using wavelet analysis and K-nearest neighbor algorithm. In: 2018 International conference on applied smart systems (ICASS) (pp 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASS.2018.8652020
Sharma P, Saxena K (2017) Application of fuzzy logic and genetic algorithm in heart disease risk level prediction. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8(2):1109–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-017-0578-8
Tripathi D, Edla DR, Cheruku R, Kuppili V (2019) A novel hybrid credit scoring model based on ensemble feature selection and multilayer ensemble classification. Comput Intell 35(2):371–394
Tripathi D, Edla DR, Cheruku R (2018) Hybrid credit scoring model using neighborhood rough set and multi-layer ensemble classification. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34(3):1543–1549
Balogun AO, Basri S, Abdulkadir SJ, Hashim AS (2019) Performance analysis of feature selection methods in software defect prediction: a search method approach. Appl Sci 9(13):2764
Akintola AG, Balogun A, Lafenwa-Balogun FB, Mojeed HA (2018) Comparative analysis of selected heterogeneous classifiers for software defects prediction using filter-based feature selection methods. FUOYE J Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.46792/fuoyejet.v3i1.178
Balogun AO, Basri S, Mahamad S, Abdulkadir SJ, Almomani MA, Adeyemo VE et al (2020) Impact of feature selection methods on the predictive performance of software defect prediction models: an extensive empirical study. Symmetry 12(7):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071147
Kolukisa B, Yavuz L, Soran A, Bakir-Gungor B, Tuncer D, Onen A, Gungor VC (2020) Coronary artery disease diagnosis using optimized adaptive ensemble machine learning algorithm. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.17706/ijbbb.2020.10.1.58-65
Latha CBC, Jeeva SC (2019) Improving the accuracy of prediction of heart disease risk based on ensemble classification techniques. Inf Med Unlocked 16:100203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2019.100203
Harvey HB, Sotardi ST (2018) The Pareto principle. J Am College Radiol 15(6):931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2018.02.026
Nenavath H, Jatoth RK (2018) Hybridizing sine cosine algorithm with differential evolution for global optimization and object tracking. Appl Soft Comput 62:1019–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.039
Djellali H, Guessoum S, Ghoualmi-Zine N, Layachi S (2017) Fast correlation based filter combined with genetic algorithm and particle swarm on feature selection. In: 2017 5th International conference on electrical engineering-boumerdes (ICEE-B) (pp 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEE-B.2017.8192090
Radovic M, Ghalwash M, Filipovic N, Obradovic Z (2017) Minimum redundancy maximum relevance feature selection approach for temporal gene expression data. BMC Bioinform 18(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-016-1423-9
Wu Z, Dong YN, Wei HL, Tian W (2020) Consistency measure based simultaneous feature selection and instance purification for multimedia traffic classification. Comput Netw 173:107190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107190
Zhang G, Hou J, Wang J, Yan C, Luo J (2020) Feature selection for microarray data classification using hybrid information gain and a modified binary Krill Herd Algorithm. Interdiscip Sci 12:288–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-020-00372-w
Shi S, Li G, Chen H, Liu J, Hu Y, Xing L, Hu W (2017) Refrigerant charge fault diagnosis in the VRF system using Bayesian artificial neural network combined with ReliefF filter. Appl Therm Eng 112:698–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.10.043
Zaffar M, Hashmani MA, Savita KS (2018) Comparing the performance of FCBF, Chi-Square and relief-F filter feature selection algorithms in educational data mining. In: International conference of reliable information and communication technology. Springer, Cham, pp 151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99007-1_15
Sharma S, Jain A (2020) An empirical evaluation of correlation based feature selection for tweet sentiment classification. In: Advances in cybernetics, cognition, and machine learning for communication technologies. Springer, Singapore, pp 199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3125-5_22
Kohavi R, John GH (1997) Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artif Intell 97(1–2):273–324
Kostrzewa D, Brzeski R (2017) The data dimensionality reduction in the classification process through greedy backward feature elimination. In: International Conference on Man–Machine Interactions. Springer, Cham, pp 397–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67792-7_39
Lu H, Chen J, Yan K, Jin Q, Xue Y, Gao Z (2017) A hybrid feature selection algorithm for gene expression data classification. Neurocomputing 256:56–62
Darst BF, Malecki KC, Engelman CD (2018) Using recursive feature elimination in random forest to account for correlated variables in high dimensional data. BMC Genet 19(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-018-0633-8
Rodriguez-Galiano VF, Luque-Espinar JA, Chica-Olmo M, Mendes MP (2018) Feature selection approaches for predictive modelling of groundwater nitrate pollution: an evaluation of filters, embedded and wrapper methods. Sci Total Environ 624:661–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.152
Hu R, Zhu X, Zhu Y, Gan J (2020) Robust SVM with adaptive graph learning. World Wide Web 23(3):1945–1968
Chen CW, Tsai YH, Chang FR, Lin WC (2020) Ensemble feature selection in medical datasets: combining filter, wrapper, and embedded feature selection results. Expert Syst 37(5):e12553
Antony Rosewelt L, Arokia Renjit J (2020) A content recommendation system for effective e-learning using embedded feature selection and fuzzy DT based CNN. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-191721 (Preprint)
Choi SH, Jung HY, Kim H (2019) Ridge fuzzy regression model. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(7):2077–2090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00692-0
Spencer B, Alfandi O, Al-Obeidat F (2018) A refinement of lasso regression applied to temperature forecasting. Procedia Comput Sci 130:728–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.04.127
Guha R, Ghosh M, Kapri S, Shaw S, Mutsuddi S, Bhateja V, Sarkar R (2019) Deluge based Genetic Algorithm for feature selection. Evol Intel. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-019-00218-5
Stripling E, vanden Broucke S, Antonio K, Baesens B, Snoeck M (2018) Profit maximizing logistic model for customer churn prediction using genetic algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 40:116–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2017.10.010
Amirkhani A, Mosavi MR, Mohammadi K, Papageorgiou EI (2018) A novel hybrid method based on fuzzy cognitive maps and fuzzy clustering algorithms for grading celiac disease. Neural Comput Appl 30(5):1573–1588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2765-y
Ghasemiyeh R, Moghdani R, Sana SS (2017) A hybrid artificial neural network with metaheuristic algorithms for predicting stock price. Cybern Syst 48(4):365–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969722.2017.1285162
Baioletti M, Milani A, Santucci V (2017) A new precedence-based ant colony optimization for permutation problems. In: Asia-Pacific conference on simulated evolution and learning. Springer, Cham, pp 960–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68759-9_79
Moslehi F, Haeri A (2020) A novel hybrid wrapper–filter approach based on genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization for feature subset selection. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(3):1105–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01364-5
Benouini R, Batioua I, Ezghari S, Zenkouar K, Zahi A (2019) Fast feature selection algorithm for neighborhood rough set model based on Bucket and Trie structures. Granular Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-019-00162-w
Malik AJ, Khan FA (2018) A hybrid technique using binary particle swarm optimization and decision tree pruning for network intrusion detection. Clust Comput 21(1):667–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0971-8
Chakraborty T, Banik SK, Bhadra AK, Nandi D (2021) Dynamically learned PSO based neighborhood influenced fuzzy c-means for pre-treatment and post-treatment organ segmentation from CT images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 202:105971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.105971
Wang L, Ni H, Yang R, Pappu V, Fenn MB, Pardalos PM (2014) Feature selection based on meta-heuristics for biomedicine. Optim Methods Software 29(4):703–719. https://doi.org/10.1080/10556788.2013.834900
Da Silva SF, Ribeiro MX, Neto JDEB, Traina-Jr C, Traina AJ (2011) Improving the ranking quality of medical image retrieval using a genetic feature selection method. Decis Support Syst 51(4):810–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2011.01.015
Sharaff A, Gupta H (2019) Extra-tree classifier with metaheuristics approach for email classification. In: Advances in computer communication and computational sciences. Springer, Singapore, pp 189–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6861-5_17
Sayed S, Nassef M, Badr A, Farag I (2019) A nested genetic algorithm for feature selection in high-dimensional cancer microarray datasets. Expert Syst Appl 121:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.12.022
Leardi R, Boggia R, Terrile M (1992) Genetic algorithms as a strategy for feature selection. J Chemom 6(5):267–281
Das AK, Pati SK, Ghosh A (2020) Relevant feature selection and ensemble classifier design using bi-objective genetic algorithm. Knowl Inf Syst 62(2):423–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-019-01341-6
Tyagi S, Mittal S (2020) Sampling approaches for imbalanced data classification problem in machine learning. In: Proceedings of ICRIC 2019. Springer, Cham, pp 209–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29407-6_17
Dietterich TG (2000) An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: Bagging, boosting, and randomization. Mach Learn 40(2):139–157
Polikar R (2006) Ensemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 6(3):21–45
Ribeiro VHA, Reynoso-Meza G (2020) Ensemble learning by means of a multi-objective optimization design approach for dealing with imbalanced data sets. Expert Syst Appl 147:113232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113232
Galar M, Fernandez A, Barrenechea E, Bustince H, Herrera F (2011) A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet Part C (Applications and Reviews) 42(4):463–484
Bryll R, Gutierrez-Osuna R, Quek F (2003) Attribute bagging: improving accuracy of classifier ensembles by using random feature subsets. Pattern Recogn 36(6):1291–1302
Bartlett P, Freund Y, Lee WS, Schapire RE (1998) Boosting the margin: a new explanation for the effectiveness of voting methods. Ann Stat 26(5):1651–1686
Freund Y, Schapire RE (1997) A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J Comput Syst Sci 55(1):119–139. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcss.1997.1504
Shahraki A, Abbasi M, Haugen Ø (2020) Boosting algorithms for network intrusion detection: a comparative evaluation of Real AdaBoost, Gentle AdaBoost and Modest AdaBoost. Eng Appl Artif Intell 94:103770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103770
Rätsch G, Onoda T, Müller KR (2001) Soft margins for AdaBoost. Mach Learn 42(3):287–320
Palit I, Reddy CK (2011) Scalable and parallel boosting with mapreduce. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(10):1904–1916
Ho TK (1998) The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(8):832–844
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Zhong Y, Yang H, Zhang Y, Li P (2020) Online random forests regression with memories. Knowl-Based Syst 201:106058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106058
Han T, Jiang D, Zhao Q, Wang L, Yin K (2018) Comparison of random forest, artificial neural networks and support vector machine for intelligent diagnosis of rotating machinery. Trans Inst Meas Control 40(8):2681–2693
Bahad P, Saxena P (2020) Study of adaboost and gradient boosting algorithms for predictive analytics. In: International conference on intelligent computing and smart communication 2019. Springer, Singapore, pp 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0633-8_22
Natekin A, Knoll A (2013) Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front Neurorobot 7:21
Chen J, Zhao F, Sun Y, Yin Y (2020) Improved XGBoost model based on genetic algorithm. Int J Comput Appl Technol 62(3):240–245. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCAT.2020.106571
Sun X, Liu M, Sima Z (2020) A novel cryptocurrency price trend forecasting model based on LightGBM. Financ Res Lett 32:101084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2018.12.032
Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L (2006) Extremely randomized trees. Mach Learn 63(1):3–42
Pinto A, Pereira S, Rasteiro D, Silva CA (2018) Hierarchical brain tumour segmentation using extremely randomized trees. Pattern Recogn 82:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.05.006
Sharif M, Amin J, Raza M, Anjum MA, Afzal H, Shad SA (2020) Brain tumor detection based on extreme learning. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04679-8
Soltaninejad M, Yang G, Lambrou T, Allinson N, Jones TL, Barrick TR et al (2017) Automated brain tumour detection and segmentation using superpixel-based extremely randomized trees in FLAIR MRI. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12(2):183–203
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24(2):123–140
Jiang T, Li J, Zheng Y, Sun C (2011) Improved bagging algorithm for pattern recognition in UHF signals of partial discharges. Energies 4(7):1087–1101
Panda D, Dash SR (2020) Predictive system: comparison of classification techniques for effective prediction of heart disease. In: Smart intelligent computing and applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 203–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9282-5_19
Kurgan LA, Cios KJ, Tadeusiewicz R, Ogiela M, Goodenday LS (2001) Knowledge discovery approach to automated cardiac SPECT diagnosis. Artif Intell Med 23(2):149–169
Dhankhar A, Jain S (2021) Prediction of disease using machine learning algorithms. Smart Sustain Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119752134.ch8
Verma AK, Pal S, Kumar S (2020) Prediction of skin disease using ensemble data mining techniques and feature selection method—a comparative study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 190(2):341–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03093-z
Cateni S, Colla V, Vannucci M (2014) A hybrid feature selection method for classification purposes. In: 2014 European Modelling Symposium (pp 39–44). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMS.2014.44
Khaire UM, Dhanalakshmi R (2019) Stability of feature selection algorithm: a review. J King Saud Univ-Comput Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.06.012
Edla DR, Tripathi D, Cheruku R, Kuppili V (2018) An efficient multi-layer ensemble framework with BPSOGSA-based feature selection for credit scoring data analysis. Arab J Sci Eng 43(12):6909–6928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2905-4
Aher CN, Jena AK (2020) Rider-chicken optimization dependent recurrent neural network for cancer detection and classification using gene expression data. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2020.1830436
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Yang XS (2014) Binary bat algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 25(3):663–681
Lee SH (2015) Feature selection based on the center of gravity of BSWFMs using NEWFM. Eng Appl Artif Intell 45:482–487
Smith MC, Barber PA, Stinear CM (2017) The TWIST algorithm predicts time to walking independently after stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 31(10–11):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968317736820
Tomar D, Agarwal S (2014) Feature selection based least square twin support vector machine for diagnosis of heart disease. Int J Bio-Sci Bio-Technol 6(2):69–82
Liu X, Wang X, Su Q, Zhang M, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Wang Q (2017) A hybrid classification system for heart disease diagnosis based on the RFRS method. Comput Math Methods Med 2017:1–11
Polat K, Güneş S (2009) A new feature selection method on classification of medical datasets: Kernel F-score feature selection. Expert Syst Appl 36(7):10367–10373
Kahramanli H, Allahverdi N (2008) Design of a hybrid system for the diabetes and heart diseases. Expert Syst Appl 35(1–2):82–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jothi Prakash, V., Karthikeyan, N.K. Enhanced Evolutionary Feature Selection and Ensemble Method for Cardiovascular Disease Prediction. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 13, 389–412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00430-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00430-x