Abstract
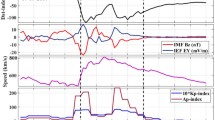
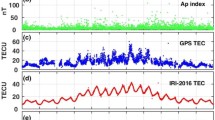
The effect of total solar eclipse on ionospheric total electron contents (TECs) over the ionospheric region of Indonesia was studied using GNSS-/GPS-based retrieved data. Continuous TEC analysis in conjunction with total solar eclipse of 09 March 2016 has been made from 08 to 10 March 2016 over Cibinong station of Indonesia sector (6° 28′ S, 106° 51′ E). Over Cibinong GNSS/GPS station of Indonesia, around ~ 94% of maximum obscurity of solar eclipse was observed. The eclipse event reached its maximum development at 00:58 UTC on 09 March 2016 with a magnitude (the fraction of the angular diameter of a celestial body being eclipsed) 1.045 and a duration of around 210 s (3 m 10 s). Results of the ionospheric vertical total electron contents during the total solar eclipse of 09 March 2016 over the Indonesian region were compared with the normal days. GNSS-/GPS-measured TEC over Cibinong of Indonesia was observed to be less than the pre- and post-eclipse days before the occurrence of total solar eclipse, but these were found to be more than the pre-eclipse day and less than the post-eclipse day after the occurrence of total solar eclipse of 09 March 2016. For both pre- and post-eclipse days, trend lines of proton temperature were found to have negative slopes, whereas a positively increasing trend line was observed on the eclipse day of 09 March 2016. The proton fluxes with energy (> 10 MeV) were found to show almost similar behavior on pre-, post-, and eclipse days of the study period. However, a small but positive constant slope was found on pre-eclipse day.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebiyi, S. J., Odeyemi, O. O., Adimula, I. A., Oladipo, O. A., Ikubanni, S. O., Adebesin, B. O., & Joshua, B. W. (2014). GPS derived TEC and foF2 variability at an equatorial station and the performance of IRI-model. Journal of Advances in Space Research, 54(4), 565–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.03.026
Amicis, R. D., Marco, R. D., Bruno, R., & Perrone, D. (2019). Investigating the nature of the link between magnetic field orientation and proton temperature in the solar wind. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 632, A92. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201936728
Arunpold, S., Tripathi, N., Chowdhary, R., Chowdhary, V. R., Raju, D. K. (2014). Comparison of GPS-TEC measurements with IRI-2007 and IRI-2012 modeled TEC at an equatorial latitude station, Bangkok, Thailand. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 117, 88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2014.06.001
Bhuyan, P. K., & Hazarika, R. (2013). GPS TEC near the crest of the EIA at 95E during the ascending half of solar cycle 24 and comparison with IRI simulations. Advances in Space Research, 52(7), 1247–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.06.029
Bilitza, D., Altadill, D., Zhang, Y., Mertens, C., Truhlik, V., Richards, P., McKinnell, L. A., & Reinisch, B. (2014). The International Reference Ionosphere 2012–a model of international collaboration. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 4(A07), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2014004
Calamas, D. M., Nutter, C., & Guajardo, D. N. (2019). Effect of 21 August 2017 solar eclipse on surface-level irradiance and ambient temperature. International Journal of Energy and Environment, 10, 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-018-0290-8
Chandra, H., Sharma, S., & Lele, P. D. (2007). Ionospheric measurements during the total solar eclipse of 11 August 1999. Earth, Planets and Space, 59, 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352023
Chen, C. H., Lin, C. H. C., & Matsuo, T. (2019). Ionospheric responses to the 21 August 2017 solar eclipse by using data assimilation approach. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-019-0263-4
Chernyshov, A. A., Chugunin, D. V., Mogilevsky, M. M., & Petrukovich, A. A. (2020). Studies of the ionosphere using radiophysical methods on ultra-small spacecrafts. Acta Astronautica, 167, 455–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.11.031
Chung, Y. S., Kim, H. S., & Choo, S. H. (2010). The solar eclipse and associated atmospheric variations observed in South Korea on 22 July 2009. Air Quality, Atmosphere and Health, 3, 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-009-0060-0
Dashora, N., & Pandey, R. (2005). Observation in equatorial anomaly region of total electron content enhancements and depletion. Annales Geophysicae, 23, 2449–2456. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-23-2449-2005
Feltens, J., Angling, M., Jackson-Booth, N., Jakowski, N., Hoque, M., Hernández-Pajares, M., Aragón, A., María, A., & Orús-Pérez, R. (2011). Comparative testing of four ionospheric models driven with GPS measurements. Radio Science, 46(6), RS0D12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010RS004584
Founda, D., Melas, D., Lykoudis, S., Lisaridis, I., Gerasopoulos, E., Kouvarakis, G., Petrakis, M., & Zerefos, C. (2007). The effect of the total solar eclipse of 29 March 2006 on meteorological variables in Greece. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7, 5543–5553. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-5543-2007
Jenan, R., Dammalage, T. L., & Panda, S. K. (2021). Ionospheric total electron content response to September-2017 geomagnetic storm and December-2019 annular solar eclipse over Sri Lankan region. Acta Astronautica, 180, 575–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.01.006
Jin, R. S., & Feng, G. (2012). M_DCB: Matlab code for estimating GNSS satellite and receiver differential code biases. GPS Solutions, 16(4), 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-012-0279-3
Kakoty, R., Bora, S., & Bhuyan, P. K. (2019). Spatial asymmetry in topside ion density and vertical E × B plasma drift velocity within 75°E–95°E. Advances in Space Research, 63(3), 1176–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.10.013
Karia, S. P., Patel, N. C., & Pathak, K. N. (2015). Comparison of GPS based TEC measurements with the IRI-2012 Model for the period of low to moderate solar activity (2009–2012) at the crest of equatorial anomaly in Indian region. Advances in Space Research, 55(8), 1965–1975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.10.026
Kumar, A. (2014). Variations in atmospheric aerosol concentration of various sizes during the total solar eclipse of 22 July 2009 over a semi urban tropical site of Northern India. Indian Journal of Physics, 88(5), 449–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0434-x
Kumar, A. (2016). Spatio-temporal synoptic variability of aerosol optical depth and cloud properties over the Central North region of India through MODIS collection V satellite sensors. Indian Journal of Physics, 90(6), 613–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0783-8
Kurdyaeya, Y., Borechevkina, O., Katpov, I., & Kshevetskii, S. (2021). Thermospheric disturbances caused by the propagation of acoustic-gravity waves from the lower atmosphere during a solar eclipse. Advances in Space Research, 68(3), 1390–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.03.024
Lee, H. B., Jee, G., Kim, Y. H., & Shim, J. S. (2013). Characteristics of global plasmaspheric TEC in comparison with the ionosphere simultaneously observed by Jason-1 satellite. Journal of Geophysical Research, 118(2), 935–946. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgra.50130
Leong, S. K., Musa, T. A., Omar, K., Subari, M. D., Pathy, N. B., & Asilam, M. F. (2015). Assessment of ionosphere models at Banting: Performance of IRI- 2007, IRI-2012 and Ne-Quick 2 models during the ascending phase of Solar Cycle 24. Advances in Space Research, 55(8), 1928–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.01.026
Li, Z., Yuan, Y., Wang, N., Hernandez-Pajares, M., & Huo, X. (2015). SHPTS: Towards a new method for generating precise global ionospheric TEC map based on spherical harmonic and generalized trigonometric series functions. Journal of Geodesy, 89(4), 331–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0778-9
Lin, C. Y., Liu, J. Y., & Lin, C. H. (2012). Using the IRI, the MAGIC model, and the co-located ground-based GPS receivers to study ionospheric solar eclipse and storm signatures on July 22, 2009. Earth, Planets and Space, 64, 513–520. https://doi.org/10.5047/eps.2011.08.016
Lin, C. H., Liu, J. Y., Tsai, H. F., & Cheng, C. Z. (2007). Variations in the equatorial ionization anomaly peaks in the west pacific region during the April 6 and July 15, 2000 geomagnetic storms. Earth, Planets and Space, 59(5), 401–405. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352701
Liu, K., Li, G., & Ning, B. (2019). Possible evidence for small-scale wave seeding of equatorial plasma bubbles. Advances in Space Research, 63(11), 3612–3620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.02.025
Luo, W., Liu, Z., Li, M. (2014). A preliminary evaluation of the performance of multiple ionospheric models in low- and mid-latitude regions of China in 2010–2011. GPS Solutions, 18(2), 297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-013-0330-z
Maltseva, O. A., Mozhaeva, N. S., Poltavsky, O. S., & Zhbankov, G. A. (2012). Use of TEC global maps and the IRI model to study ionospheric response to geomagnetic disturbances. Advances in Space Research, 49(6), 1076–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2012.01.005
Mannucci, A. J., Wilson, B. D., Yuan, D. N., Ho, C. H., & Lindqwister, U. J., & Runge, T. F. (1998). A global mapping technique for GPS-derived ionospheric total electron content measurements. Radio Science, 33, 565–582. https://doi.org/10.1029/97RS02707
Mishra, R. K., Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N. P., Baral, R., Das, P. K., Klausner, V., & Sharma, M. (2020). Variation on solar wind parameters and total electron content over middle- to low-latitude regions during intense geomagnetic storms. Radio Science, 55(11), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/essoar.10503097.1
Okoh, D., McKinnell, L., Cilliers, P., & Okeke, P. (2013). Using GPS-TEC data to calibrate VTEC computed with the IRI model over Nigeria. Advances in Space Research, 52(10), 1791–1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2012.11.013
Pakkattil, A., Muhsin, M., John, S., Saseendran, A., Thomas, A. P., Deepa, V., & Verma, R. (2019). Trace pollutant fluctuations observed in Calicut city, India, during the annular solar eclipse on 26 December 2019. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 11(11), 2049–2055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.07.026
Panda, S. K., Gedam, S. S., & Rajaram, G. (2015). Study of Ionospheric TEC from GPS observations and comparisons with IRI and SPIM model predictions in the low latitude anomaly Indian sub continental region. Advances in Space Research, 55(8), 1948–1964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.09.004
Pasachoff, J. M. (2009). Scientific observations at total solar eclipse. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 9, 613–634. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4527/9/6/001
Rabiu, A. B., Adewale, A. O., Abdulrahim, R. B., & Oyeyemi, E. O. (2014). TEC derived from some GPS stations in Nigeria and comparison with the IRI and Ne Quick models. Advances in Space Research, 53(9), 1290–1303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.02.009
Rao, S. S., Chakraborty, M., & Singh, A. K. (2021). A study on TEC reduction during the tail phase of the 21st June 2020 annular solar eclipse. Advances in Space Research, 67(6), 1948–1957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.12.035
Reddy, T. L., Balakrishnaiah, G., Reddy, R. O., Siva Kumar, R. N. K., Rao, C. T., Gopal, R. K., & Bhavyasree, A. (2020). Perturbations of atmospheric surface layer characteristics during the annular solar eclipse on 26 December 2019 over a semi-arid region Anantapur in southern India. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 211, 105467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2020.105467
Sasmal, S., Chowdhury, S., Kundu, S., Politis, D. Z., Potirakis, S. M., Balasis, G., Hayakawa, M., & Chakrabarti, S. k. (2021). Pre-seismic irregularities during the 2020 samos (Greece) earthquake (M = 6.9) as investigated from multi-parameter approach by ground and space-based techniques. Atmosphere, 12(8), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12081059
Sau, s., Narayanan, V. L., Gurubaran, S., & Emperumal, K. (2018). Study of wave signatures observed in thermospheric airglow imaging over the dip equatorial region. Advances in Space Research, 62(7), 1762–1774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.06.039
Scidá, L. A., Ezquer, R. G., Cabrera, M. A., Mosert, M., Brunini, C., & Buresova, D. (2012). On the IRI 2007 performance as a TEC predictor for the South American sector. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 81–82, 50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2012.04.001
Senturk, E., Arqim, M., & Saqib, A. M. (2021). Ionospheric total electron content response to annular solar eclipse on June 21, 2020. Advances in Space Research, 67(6), 1937–1947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.12.024
Sethia, G., Chandra, H., & Deshpande, M. R. (1980). On the effect of the partial solar eclipse of 29 April 1976 on electron content. Proceedings of Indian Academy of Sciences- Earth and Planetary Science, 89, 153–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02913747
Sharma, A. K., Gurav, O. B., Chavan, G. A., Gaikwad, H. P., Ghodpage, R. N., & Patil, P. T. (2017). Variation in occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles (EPBs) using All Sky Imager from low latitude station Kolhapur (16.8 °N, 74.2 °E, 10.6 ° dip Lat). Advances in Space Research, 60(11), 2452–2463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.09.014
Silwal, A., Gautam, S. P., Poudel, P., Karki, M., Adhikari, B., Chapagain, N. P., Mishra, R. K., Ghimire, B. D., & Migoya-Orue, Y. (2021). Global positioning system observations of ionospheric total electron content variations during the 15th January 2010 and 21st June 2020 solar eclipse. Radio Science, 56(5), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020RS007215
Singh, A. K., Niwas, S., Kumar, a., Nigam, M. J., & Rai, J. (1999). Variations in atmospheric aerosols and electrical conductivity at Roorkee during the total solar eclipse of October 1995. Indian Journal of Radio and Space Physics, 28, 1–10. http://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/17319
Srinivasu, V. K., Dashora, N., Prasad, D. S., Niranjan, K., & Krishna, S. G. (2018). On the occurrence and strength of multi-frequency multi-GNSS Ionospheric Scintillations in Indian sector during declining phase of solar cycle 24. Advances in Space Research, 61(7), 1761–1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.08.036
Szalowski, K. (2002). The effect of the solar eclipse on the air temperature near the ground. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 64, 1589–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00134-7
Xiang, Y., Yuan, Y., Li, Z., & Wang, N. (2015). Analysis, and validation of different global ionospheric maps (GIMs) over China. Advances in Space Research, 55(1), 199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.09.008
Yeboah, A. E., Paulino, I., Medeiros, A. F., Buriti, R. A., & Wrasse, C. M. (2019). Seasonal variation of plasma bubbles during solar cycle 23–24 over the Brazilian equatorial region. Advances in Space Research, 64(7), 1365–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.06.041
Zakharenkova, I. E., Cherniak, Iu V., Krankowski, A., & Shagimuratov, I. I. (2015). Vertical TEC representation by IRI 2012 and IRI Plas models for European mid latitudes. Advances in Space Research, 55(8), 2070–2076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2014.07.027
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to data distribution centers of GNSS network for total electron contents data over Indonesia. Further, special thanks are also due to NASA scientists for providing online access of space weather parameters through their web.
Funding
There is no funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lakshmi contributed to data analysis, data curation and interpretation, writing-revised draft preparation; VKS contributed to reviewing, editing, and supervision; AK contributed to conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Dagar, L., Soni, V.K. & Kumar, A. Variations in GNSS-/GPS-Measured Ionospheric TEC and Solar Wind Plasma Parameters During the Total Solar Eclipse of 09 March 2016. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 52, 557–568 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-024-01835-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-024-01835-z