Abstract
Identification and prioritization of erosion-prone watersheds have remarkable significance for planning of conservation schemes at the sub-watershed level, as it is too costly to enforce watershed development structures on the whole watershed at a time. Hence, the prime objective of the study is identifying and ranking of erosion-risk regions of the Weyib watershed, situated at the Genale-Dawa basin in Ethiopia. The watershed covers an area of 3973 km2 with a basin length of 369 km. Morphometric analysis and RUSLE models have been used with the aid of arc GIS and remote sensing techniques to identify and map erosion-risk areas. The morphometric assessment involved both linear and shape parameters through the compound parameter ranking approach while RUSLE parameters like rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope steepness and length, land cover, and management activities have generated from their respective datasets and overlaid to quantify potential soil erosion. The result of the morphometric analysis revealed that SW-3 (sub-watershed), SW-4, SW-7, and SW-8 necessitated urgent interventions. On the other hand, the results of RUSLE estimated the mean annual rate of soil loss as 27.77t/ha/year, that is beyond the tolerable limit of 10t/ha/year. Based on this value, SW-7 and SW-8 are categorized as high erosion-prone areas. Hence 224.8 km2 area of the watershed is labeled under high erosion risk area. Sensitivity analysis result indicated that RUSLE is more sensitive to cover and topographic factors in the watershed. The overall result of the two models specified that the lower part of the watershed demanded prime attention. Thus, the government has to reinforce the watershed development endeavors initiated by focusing on high erosion susceptible sub-watersheds in the Weyib watershed.

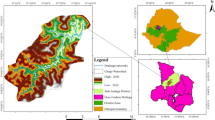
(Source: Own Compilation based on Ethio-GIS Dataset, 2021)

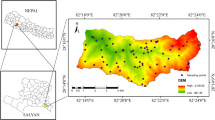
(Source: Own Compilation from SRTM DEM, 2021)

(Source: Own Compilation from SRTM DEM, 2021)

(Source: Own Compilation, 2021)

(Source: Own Construction from SRTM DEM, 2021)

(Source: Own Compilation, 2021)

(Source: Own compilation based on RF data, 2021)

(Source: Own compilation based on Soil Data, 2021)

(Source: Own compilation based on DEM Data, 2021)

(Source: Own compilation based on Landsat Data, 2021)

(Source: Own compilation based on Landsat Data, 2021)

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe, M. (2015). Soil erosion risk assessment using RUSLE, MCE and GIS in Gerbi river watershed. MSc Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia.
Aher, P. D., Adinarayana, J., & Gorantiwar, S. D. (2014). Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: A remote sensing and GIS approach. Journal of Hydrology, 511, 850–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.028
Ahmed, F., & Rao, K. S. (2016). Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on morphometric analysis using remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing and GIS, 4(2), 51–65.
Aisha, M., Tamene, M., & Wakjira, T. (2018). Morphometric analysis and prioritization of watersheds for soil erosion management in upper gibe catchment. Journal of Degraded and Mining Lands Management, 6(1), 1419–1426.
Alemu, M., Mahmud, Y., Menale, K., & Pender, J. (2005). Cost of land degradation in Ethiopia: A critical review of past studies. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia EFPRI/EEPFE, 1(1), 1–82.
Asfaw, D., & Workineh, G. (2019). Quantitative analysis of morphometry on Ribb and Gumara watersheds: Implications for soil and water conservation. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7(2), 150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2019.02.003
Berry, L., Oslo, J., & Campbell, D. (2003). Assessing the extent, cost and impact of land degradation at the national level: Findings and lessons learned from seven pilot case studies. Technical Report Commissioned by Global Mechanism with Support from the World Bank.
Bisht, S., Chaudhry, S., Sharma, S., & Soni, S. (2018). Assessment of flash flood vulnerability zonation through geospatial technique in high altitude Himalayan watershed, Himachal Pradesh India. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 12(September), 35–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.09.001
Blanco, H., & Lal, R. (2008). Principles of soil conservation and management. Springer.
Bosco, C., de Rigo, D., Dewitte, O., Poesen, J., & Panagos, P. (2015). Modelling soil erosion at European scale: Towards harmonization and reproducibility. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 15, 225–245. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-15-225-2015
Chang, T. J., Zhou, H., & Guan, Y. (2016). Applications of erosion hotspots for watershed investigation in the Appalachian hills of the United States. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 142(3). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000974
Chopra, R., Dhiman, R. D., & Sharma, P. K. (2005). Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in Gurdaspur district, Punjab using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33, 531–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990738
Colman, C. B., Oliveira, P. T. S., Almagro, A., Soares-Filho, B. S., & Rodrigues, D. B. (2019). Effects of climate and land-cover changes on soil erosion in Brazilian Pantanal. Sustainability, 11(24), 7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247053
CSA. (2007). Housing and population census of Ethiopia. Central Statistical Agency, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. http://www.statsethiopia.gov.et/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Population-and-Housing-Census-2007-National_Statistical.pdf
Debelo, G., Tadele, K., & Koriche, S. A. (2017). Morphometric analysis to identify erosion prone areas on the upper blue nile using gis (Case Study of Didessa and Jema Sub-Basin, Ethiopia). International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(8), 1773–1784. www.irjet.net
Dubey, S. K., Sharma, D., & Mundetia, N. (2015). Morphometric analysis of banas river basin using the geographical information system, Rajasthan India. Hydrology, 3(5), 47–54. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.hyd.20150305.11
Durigon, V. L., Carvalho, D. F., Antunes, M. A. H., Oliveira, P. T. S., & Fernandes, M. M. (2014). NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(2), 441–453. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2013.871081
Estrada-carmona, N., Harper, E. B., Declerck, F., Fremier, K., Harper, E. B., & Declerck, F. (2017). Quantifying model uncertainty to improve watershed-level ecosystem service quantification: A global sensitivity analysis of the RUSLE. International Journal of Biodiversity Science, Ecosystem Services & Management, 13(1), 40–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/21513732.2016.1237383
Evans, R. (2002). An alternative way to assess water erosion of cultivated land – field-based measurements: And analysis of some results. Applied Geography, 22(2), 187–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-6228(02)00004-8
FAO. (1984). Degradation processes in the Ethiopian highlands, their Impacts and Hazards. Report, FAO, Rome.
Farhan, Y., Anbar, A., Al-Shaik, N., & Mousa, N. (2017). Prioritization of semi-arid agricultural watershed using morphometric and principal component analysis, remote sensing, GIS technique, the Zerqa Watershed, Northern Jordan. Journal of Agricultural Science, 8(1), 113–148. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2017.81009
Fernandez, C., & Vega, J. A. (2016). Evaluation of RUSLE and PESERA models for predicting soil erosion losses in the first year after wildfire in NW Spain. Geoderma, 273, 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.03.016
Ferreira, V. A., Weesies, G. A., Yoder, D. C., Foster, G. R., & Renard, K. G. (1995). The site and condition specific nature of sensitivity analysis. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 50(5), 493–497.
Gizachew, K., & Berhan, G. (2018). Hydro-geomorphological characterization of Dhidhessa River Basin, Ethiopia. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 6(2), 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.02.003
Gravelius, H. (1914). Flusskunde Goschen Verlagshandlung Berlin. In Morphometric of drainage basins. Elsevier.
Gudeta, K. (2010). GIS-based conservation priority area identification in mojo river watershed on the basis of erosion risk. MSc thesis, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia.
Gudu Tufa, F. (2018). Morphometric analysis of Kito and Awetu Sub Basins Jimma, Ethiopia. American Journal of Water Science and Engineering, 4(3), 80–90. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajwse.20180403.14
Hana, M. A. (2014). Assessment of soil Erosion risk with RUSLE and GIS in Geffersa watershed, West Shewa Zone Oromiya region. MSc Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia.
Horton, R. E. (1945). Erosional development of stream and their drainage basin. Hydrogeological approach to quantitative morphology. Bulletin of Geological Society of America, 56(3), 275–370.
Hudson, N. W. (1981). Soil conservation. Batsford: London.
Hurni, H. (1985). Erosion–productivity–conservation systems in Ethiopia. IV International Conference on Soil Conservation November 3–9, 1985 Maracay, Venezuela, January 1985, 654–674.
Hurni, H. (1983). Soil erosion and soil formation in agricultural ecosystems in Ethiopia and Northern Thailand. Mountain Research and Development, 3(2), 131–142.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Ahmed, R. (2009). Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(2), 261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-009-0016-8
Karamage, F., Zhang, C., Liu, T., Maganda, A., & Isabwe, A. (2017). Soil erosion risk assessment in Uganda. Forests, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-009-0016-8
Kleijnen, J. P. (2005). An overview of the design and analysis of simulation experiments for sensitivity analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 164(2), 287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.02.005
Kumar, A., Jayappa, K. S., & Deepika, B. (2011). Prioritization of sub-basins based on geomorphology and morphometric analysis using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. Geocarto International, 26(7), 569–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2011.606925
Lal, R., Sobecki, T. M., Iivari, T., & Kimble, J. M. (2004). Soil degradation in the United States: Extent, severity, and trends. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203496381
Lemlem, T. (2016). Assessing the impact of watershed development programs on soil erosion and biomass production using remote sensing and GIS: The case of Yezat Watershed, West Gojam Zone of Amhara Region, Ethiopia.
Lu, D., Li, G., Valladares, G. S., & Batistella M. (2004). Mapping soil erosion risk in RondoˆNia, Brazilian Amazonia: Using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degradation and Development, 15(1), 499–512. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.634
Manjunath, H., & Suresh, T. (2014). Morphometric and land use/land cover based sub-watershed prioritization of torehalla using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Applied and Natural Sciences, 3(1), 41–48.
Marondedze, A. K., & Schutt, B. (2020). Assessment of soil erosion using the RUSLE model for the Epworth district of the Harare Metropolitan Province Zimbabwe. Sustainability, 12(20), 8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
Mhiret, D. A., Dagnew, D. C., Assefa, T. T., Tilahun, S. A., Zaitchik, B. F., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2019). Erosion hotspot identification in the sub-humid Ethiopian highlands. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology, 19(1), 146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2018.08.004
Moisa, M. B. (2021). Impact of land-use and land-cover change on soil erosion using the RUSLE model and the geographic information system: A case of Temeji watershed, Western Ethiopia. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 12(7), 3404–3420. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2021.131
Nooka Ratnam, K., Srivastava, Y. K., Venkateswara Rao, V., Amminedu, E., & Murthy, K. S. R. (2005). Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro-watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis and remote sensing and GIS perspective. Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33(1), 25–38.
Oliveira, A. da S. M., Silva, M., Curi, N., Neto, G., A., & de Freitas, D. (2013). Development of topographic factor modelling for application in soil erosion models (pp. 112–138).
Pal, B., Samanta, S., & Pal, D. K. (2012). Morphometric and hydrological analysis and mapping for Watut watershed using remote sensing and GIS techniques. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, 2(1), 357–368.
Pandey, S., Kumar, P., Zlatic, M., Nautiyal, R., & Panwar, V. P. (2021). Recent advances in assessment of soil erosion vulnerability in a watershed. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 9(3), 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.03.001
Patel, D. P., Dholakia, M., Naresh, N., & Srivastava, P. K. (2012). Water harvesting structure positioning by using geo-visualization concept and prioritization of mini-watersheds through morphometric analysis in the lower Tapi Basin. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 40(2), 299–312.
Prasuhn, V., Liniger, H., Gisler, S., Herweg, K., Candinas, A., & Clément, J.-P. (2013). A high-resolution soil erosion risk map of Switzerland as strategic policy support system. Land Use Policy, 32, 281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.11.006
Renard, K., Foster, R., Weesies, G., McCool, D., & Yoder, D. (1997). Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) (No. 703).
Strahler, A. N. (1964). Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basin and channel networks. In V.T. Chow (pp. 439–476). McGraw Hill Book: New York.
Tessema, Y. M., Jasińska, J., Yadeta, L. T., Świtoniak, M., Puchałka, R., & Gebregeorgis, E. G. (2020). Soil loss estimation for conservation planning in the welmel watershed of the Genale Dawa Basin, Ethiopia. Agronomy, 10(6), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060777
Tirkey, A., Pandey, A. C., & Nathawat, M. S. (2013). Use of satellite data, GIS and RUSLE for estimation of average annual soil loss in Daltonganj watershed of Jharkhand (India). Journal of Remote Sensing Technology, 9(34). https://doi.org/10.18005/JRST0101004
Tucker, C. J. (1979). Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 8(2), 127–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/00344257(79)90013-0
Waikar, M., & A. P. Nilawar. (2014). Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin using geographical information system: A case study. International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research, 2(1), 179–184. http://ijmcr.com
Warren, S. D., Mitasova, H., Hohmann, M. G., Landsberger, S., Iskander, F. Y., Ruzycki, T. S., & Senseman, G. M. (2005). Validation of a 3-D enhancement of the universal soil loss equation for prediction of soil erosion and sediment deposition. CATENA, 64, 281–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2005.08.010
Williams, J. R. (1975). Sediment routing for agricultural watersheds. Water Resources, 11, 965–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1975.tb01817.x
Wischmeier, W. H., & Smith, D. D. (1978). Predicting rainfall erosion losses—a guide to conservation planning. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No. 537.
Woldemariam, G., Iguala, A., Tekalign, S., & Reddy, R. (2018). Spatial modeling of soil erosion risk and its implication for conservation planning: The case of the Gobele watershed, East Hararghe Zone, Ethiopia. Land, 7(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7010025
Woreka, B. B. (2004). Evaluation of soil erosion in the Harerge region of Ethiopia using soil loss models, rainfall simulation and field trials. Phd Thesis, University of Pretoria, South Africa.
Yesuph, A. Y., & Dagnew, A. B. (2019). Soil erosion mapping and severity analysis based on RUSLE model and local perception in the Beshillo Catchment of the Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-019-0145-1
Zaidi, F. K. (2011). Drainage basin morphometry for identifying zones for artificial recharge: A case study from the Gagas river basin India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 77(2), 160–166.
Zeleke, G. (2000). Landscape dynamics and soil erosion process modeling in the Northwestern Ethiopia highlands. Mountain Research Development, 21(2), 184–191.
Zeleke, G., & Hurni, H. (2001). Implications of land use and land cover dynamics for mountain resources degradation in the Northwestern Ethiopian highlands. Journal of Mountain Research and Development, 21, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1659/0276-4741(2001)021[0184:IOLUAL]2.0.CO
Zeleke, G., Amdihun, A., Ephraim Gebremariam, A., & Rebelo, L. (2014). Modeling soil erosion dynamics in the Blue Nile (Abbay) basin: A land scape approach. Research Journal of Environmental Science, 8(5), 243–258. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2014.243.258
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Getachew Demissie Desta contributed to conceptualization, data acquisition, formal analysis, investigation, methodology and visualization. Mersha Alemu Wodajo contributed to supervision, review and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Desta, G.D., Wodajo, M.A. Identifying Soil Erosion Risks for Planning of Watershed Management: The Case of Weyib Watershed, Southeast Ethiopia. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 52, 505–523 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-024-01831-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-024-01831-3