Abstract
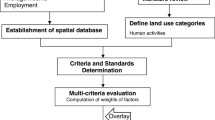
Identification of most appropriate land use for a given area is an important and inevitable task for urban planners. Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information System (GIS)-based Multi Criteria Evaluation approaches for land suitability analysis has empowered urban planners with effective decision support tools. However, earlier studies have always treated urban development as a single land use allocation problem, but, in reality, urban land use distribution is a multi-use allocation problem. Each urban land use i.e., residential, industrial, recreational etc. has distinct suitability requirements. GIS-based Multi-Objective Land Allocation (MOLA) approach has been applied in a land pocket of around 1686 ha in Navi Mumbai, India to address the multi-urban land use allocation problem in this study. Various input layers generated from Computer Aided Design software and RS data were integrated using ordered weighted averaging approach to derive suitability for overall urban development and each specific urban land use. Further, suitability layer for each urban land use was integrated using MOLA approach. Comparison of single objective land allocation for urban development with MOLA-based land allocation for various urban land uses are found to be highly suitable and quite near to the allocation proposed by urban planners working in the area. MOLA-based land allocation provided an objective approach for decision making and it is found to be an effective tool for minimizing conflicts between possible land uses.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci, H., Özalp, A. Y., & Bülent, T. (2013). Agricultural land use suitability analysis using GIS and AHP technique. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 97, 71–82.
AlFanatseh, A. (2021). Land suitability analysis of urban development in the Aqaba area, Jordan, using a GIS-based analytic hierarchy process. GeoJournal, pp. 1–17.
Belton, V., & Stewart, T. (2002). Multiple criteria decision analysis: An integrated approach. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Berhane, T. M., Lane, C. R., Wu, Q., Anenkhonov, O. A., Chepinoga, V. V., Autrey, B. C., & Liu, H. (2018). Comparing pixel- and object-based approaches in effectively classifying wetland-dominated landscapes. Remote Sensing, 10, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010046
CIDCO (2016). Draft Development Plan for Navi Mumbai Airport Influence Notified Area, Navi Mumbai Development Plan Report, https://cidco.maharashtra.gov.in/pdf/other/Combined_Report.pdf (accessed 10 October, 2020).
Collins, M. G., Steiner, F. R., & Rushman, M. J. (2001). Land-use suitability analysis in the United States: historical development and promising technological achievements. Environmental Management, 28(5), 611–621.
Eldrandaly, K. A., & AL-Amari, M. A. (2014). An expert GIS-based ANP-OWA decision making framework for tourism development site selection. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications, 6(7), 1–11.
Fung, T., & Wong, F.K.-K. (2007). Ecotourism planning using multiple criteria evaluation with GIS. Geocarto International, 22(2), 87–105.
Greene, R., Devillers, R., Luther, J. E., & Eddy, B. G. (2011). GIS-based multiple-criteria decision analysis. Geography Compass, 5(6), 412–432.
Hsu, C.-C., & Sandford, B. A. (2007). The Delphi technique: Making sense of consensus. Practical Assessment Research and Evaluation, 12(1), 10.
Jeganathan, C., Roy, P. S., & Jha, M. N. (2011). Multi-objective spatial decision model for land use planning in a tourism district of India. Journal of Environmental Informatics, 17(1), 15–24.
Jensen, J. R. (1986). Introductory digital image processing: A remote sensing perspective. Prentice Hall.
Kechebour Boualem, E. L. (2015). Relation between stability of slope and the urban density: Case study. Procedia Engineering, 114, 824–831.
Kumar, S., & Kumar, R. (2014). Site suitability analysis for urban development of a Hill Town using GIS based multi-criteria evaluation technique: A case study of Nahan Town, Himachal Pradesh, India. International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS, 3(1), 516–524.
Leila, F., Laercio, N., Emiliano, C., Lino, C., Carolina, P. & Aylton, P. (2011). Image fusion for remote sensing applications, image fusion and its applications, Dr. Yufeng Zheng (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-182-4, InTech, http://www.intechopen.com/books/image-fusion-andits-applications/image-fusion-for-remote-sensing-applications (accessed 10 October, 2020).
Lingjun, L., Zong, H., & Hu, Y. (2008). Study on land use suitability assessment of urban–rural planning based on remote sensing: A case study of Liangping in Chongqing. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 37(8), 123–130.
Liu, R., Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., & Borthwick, A. G. (2014). Land-use suitability analysis for urban development in Beijing. Journal of Environmental Management, 145, 170–179.
Luan, C., Liu, R., & Peng, S. (2021). Land-use suitability assessment for urban development using a GIS-based soft computing approach: A case study of Ili Valley, China. Ecological Indicators, 123, 107333.
Modi, M., Kumar, R., Shankar, G. R., & Martha, T. R. (2014). Land cover change detection using object-based classification technique: A case study along the Kosi River, Bihar. The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 40(8), 839–843.
Parry, J. A., Ganaie, S. A., & Bhat, M. S. (2018). GIS based land suitability analysis using AHP model for urban services planning in Srinagar and Jammu urban centers of J&K. India. Journal of Urban Management, 7(2), 46–56.
Pramanik, M. K. (2016). Site suitability analysis for agricultural land use of Darjeeling district using AHP and GIS techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0116-8
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytical hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. Decision making series. McGraw-Hill International Book Company.
Safitri, S., Wikantika, K., Riqqi, A., Deliar, A., & Sumarto, I. (2021). Spatial allocation based on physiological needs and land suitability using the combination of ecological footprint and SVM (Case Study: Java Island, Indonesia). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(4), 259.
Sharma, S. K., Lees, B. G. (2004). A comparison of simulated annealing and GIS based MOLA for solving the problem of multi-objective land use assessment and allocation, MCDM 2004, Whistler, B. C. Canada August 6–11. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/brian_lees/publication/228580629_a_comparison_of_simulated_annealing_and_gis_based_molafor_solving_the_problem_of_multi-objective_land_use_assessment/links/004635266f114de8d0000000.pdf (accessed 10 October, 2020).
Steiner, F., McSherry, L., & Cohen, J. (2000). Land suitability analysis for the Upper Gila river watershed. Landscape and Urban Planning, 50, 199–214.
United Nations. (2018). World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision, Key Facts. https://population.un.org/wup/Publications/Files/WUP2018-KeyFacts.pdf
Urban and Regional Development Plans Formulation and Implementation Guidelines. India (2014). Ministry of Urban development, Government of India, New Delhi., Last Accessed on September 20, 2021 from http://mohua.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/URDPFI%20Guidelines%20Vol%20I(2).pdf.
Xiaoxia, S., Jixian, Z., & Zhengjun, L., (2005). A comparison of object-oriented and pixel-based classification approaches using Quick Bird imagery. International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Conference Proceedings XXXV 1/2 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255588848_A_COMPARISON_OF_OBJECT-ORIENTED_AND_PIXEL-BASED_CLASSIFICATION_APPROACHS_USING_QUICKBIRD_IMAGERY (accessed 10 October, 2020).
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Indian Institute of Remote Sensing, Dehradun (a unit of Indian Space Research Organization) for logistics support. They are also grateful to CIDCO, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India and National Remote Sensing Centre, Hyderabad, India for providing remote sensing and CAD data. Authors wish to thank editor and reviewers for their valuable time and critical suggestions for improvement in manuscript.
Funding
No research grant was availed to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors whose names appear on the submission has made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; or the creation of code used in the work. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics Approval
The work is carried out at Indian Institute of Remote Sensing/ISRO, Dehradun as part of ongoing research. The work reported is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere. All the research articles has been cited appropriately in the manuscript as per the defined style and format.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Bodhankar, S., Gupta, K., Kumar, P. et al. GIS-Based Multi-Objective Urban Land Allocation Approach for Optimal Allocation of Urban Land Uses. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 50, 763–774 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01492-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01492-0